The Si Unit Of Force Is The
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
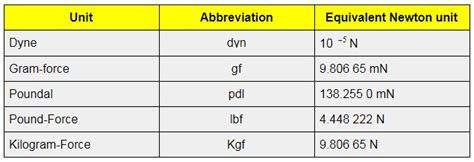
Table of Contents
The SI Unit of Force Is the Newton: A Deep Dive into Force Measurement
The fundamental concept of force underpins much of physics and engineering. Understanding force, its measurement, and its impact on the world around us is crucial. This article delves into the SI unit of force, the newton, exploring its definition, applications, and significance in various fields. We will also examine related concepts like mass, acceleration, and the importance of consistent units in scientific measurements.
Understanding Force: A Fundamental Concept
Force, in simple terms, is any interaction that, when unopposed, will change the motion of an object. This change in motion can involve a change in speed, direction, or both. A force can be a push or a pull, and its effects are always relative to a reference frame. Whether it's the gentle force of a breeze or the immense force of a rocket launch, the underlying principle remains consistent. The quantitative measure of this interaction is what we refer to as force, measured using the newton (N) in the International System of Units (SI).
Types of Forces
Forces manifest in various forms, each with its own characteristics and mechanisms:
- Gravitational Force: The force of attraction between two objects with mass. This is the force that keeps us grounded to the Earth.
- Electromagnetic Force: The force exerted by electric and magnetic fields on charged particles. This force underlies many everyday phenomena, from electricity to magnetism.
- Strong Nuclear Force: The force that binds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of an atom. This force is incredibly strong over short distances.
- Weak Nuclear Force: Responsible for radioactive decay, this force is weaker than the strong nuclear force but plays a vital role in nuclear processes.
- Contact Force: Forces that arise from direct physical contact between objects, such as friction, tension, and normal force.
The Newton: Defining the SI Unit of Force
The newton, symbolized by N, is the SI unit of force. It's defined based on Newton's second law of motion: F = ma, where:
- F represents force (measured in newtons)
- m represents mass (measured in kilograms)
- a represents acceleration (measured in meters per second squared, m/s²)
Therefore, one newton is defined as the amount of force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared. This concise definition ties the unit directly to fundamental physical quantities, ensuring consistency and reproducibility across scientific measurements.
Understanding the Components: Mass and Acceleration
To grasp the meaning of a newton, understanding mass and acceleration is critical:
- Mass: A measure of an object's resistance to changes in its state of motion. It's essentially the amount of matter in an object.
- Acceleration: The rate of change of an object's velocity. This can involve a change in speed, direction, or both.
The relationship between force, mass, and acceleration is fundamental to classical mechanics. A larger mass requires a larger force to achieve the same acceleration, while a larger acceleration requires a larger force for a given mass.
Applications of the Newton: Measuring Force in Various Scenarios
The newton's applicability extends across numerous scientific disciplines and everyday applications:
Physics and Engineering
In physics and engineering, the newton is essential for analyzing and predicting the behavior of physical systems. It's used in:
- Statics: The study of bodies at rest or in equilibrium. Determining the forces acting on bridges, buildings, and other structures involves precise newton calculations.
- Dynamics: The study of bodies in motion. Analyzing the motion of projectiles, vehicles, and other moving objects relies on understanding force and its measurement in newtons.
- Fluid Mechanics: The study of fluids (liquids and gases) involves calculating forces like pressure and drag, which are expressed in newtons.
- Material Science: Understanding the strength and deformation of materials involves measuring tensile strength, compressive strength, and shear strength—all expressed in newtons.
Everyday Applications
Beyond formal scientific applications, the newton plays a role in various everyday scenarios:
- Weight Measurement: Weight, often confused with mass, is actually the force of gravity acting on an object. Your weight, in newtons, represents the force with which the Earth pulls you downward.
- Sports and Exercise: Analyzing athletic performance often involves measuring forces involved in activities like jumping, throwing, or hitting. The force exerted by a baseball bat, for instance, can be measured in newtons.
- Automotive Engineering: The design and testing of vehicles involve measuring forces exerted during braking, acceleration, and cornering. These forces, crucial for safety and performance, are all expressed in newtons.
- Aerospace Engineering: Designing aircraft and spacecraft requires meticulous calculations of aerodynamic forces (lift, drag) and thrust, all expressed in newtons.
Importance of Consistent Units: The SI System
The use of the newton, as part of the SI system, ensures consistency and clarity in scientific communication and calculations. The SI system (Système International d'Unités) is a globally accepted system of units, standardizing measurements across different fields and nations. Using a consistent system prevents confusion and allows for accurate comparisons and reproducibility of scientific results. Using different units for the same physical quantity can lead to errors, hindering scientific progress and technological innovation.
The Significance of Standardization
The standardization provided by the SI system is paramount for several reasons:
- Global Communication: Scientists and engineers worldwide can easily understand and collaborate when using a common system of units.
- Error Reduction: Using a standardized system minimizes the risk of errors arising from unit conversions or misunderstandings.
- Reproducibility: Scientists can repeat experiments and obtain consistent results when using standardized units.
- Technological Advancement: Consistent measurement is crucial for designing and building reliable technology.
Beyond the Newton: Related Concepts and Units
While the newton is the primary unit for force, related concepts and units are frequently used in scientific and engineering contexts:
- Dyne: An older CGS unit of force, equal to 10<sup>-5</sup> newtons. It's rarely used in modern science and engineering.
- Pound-force (lbf): A unit of force in the imperial system, approximately equal to 4.448 newtons.
- Kilonewton (kN): A multiple of the newton, equal to 1000 newtons. Frequently used for larger forces, such as those encountered in structural engineering.
- Meganeuton (MN): Another multiple, equal to 1,000,000 newtons. Used for extremely large forces.
Conclusion: The Newton's Enduring Importance
The newton, as the SI unit of force, plays a fundamental role in our understanding and application of physical phenomena. Its clear definition, based on Newton's second law, ensures consistency and accuracy in scientific measurements. From the subtle forces shaping the natural world to the immense forces driving technological advancements, the newton provides a standardized and universally understood measure of force, facilitating progress across diverse scientific disciplines and engineering fields. Its continued use is vital for maintaining clarity, accuracy, and global cooperation within the scientific community. Mastering the concept of the newton and its relationship to mass and acceleration is crucial for anyone seeking a deep understanding of physics and its applications in the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 15 And 18
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In 40 Inches
Apr 01, 2025
-
Organisms That Make Their Own Food Is Called
Apr 01, 2025
-
How To Multiply By A Reciprocal
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Does Passive Transport Differ From Active Transport
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Si Unit Of Force Is The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
