The Secretory Phase Of The Uterine Cycle Coincides With
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
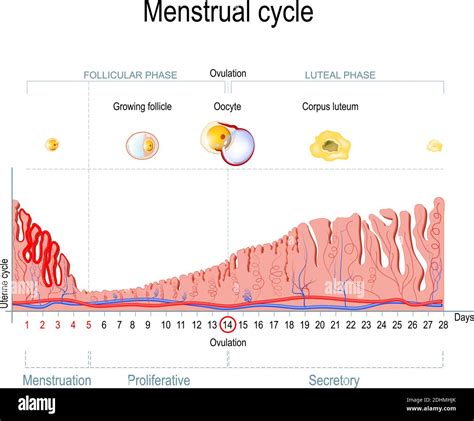
Table of Contents
The Secretory Phase of the Uterine Cycle Coincides With: A Comprehensive Guide
The female reproductive cycle is a marvel of biological precision, a finely tuned orchestra of hormonal fluctuations and physiological changes culminating in the possibility of conception. A key component of this cycle is the uterine cycle, which prepares the uterus for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. This article delves deep into the secretory phase of the uterine cycle, exploring what it coincides with, its crucial role in fertility, and the potential implications of disruptions within this phase.
Understanding the Uterine Cycle: A Recap
Before diving into the intricacies of the secretory phase, let's briefly revisit the overall uterine cycle. This cycle, typically spanning 28 days (though it can vary considerably), is divided into three primary phases:
-
Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5): Characterized by the shedding of the uterine lining (endometrium) if fertilization hasn't occurred. This results in menstrual bleeding.
-
Proliferative Phase (Days 6-14): The endometrium rebuilds and thickens in response to rising estrogen levels. This phase prepares the uterine lining for potential implantation.
-
Secretory Phase (Days 15-28): This is the focus of this article. It's the phase where the endometrium becomes highly receptive to a fertilized egg.
The Secretory Phase: A Detailed Look
The secretory phase, also known as the luteal phase, begins after ovulation. Its primary characteristic is the secretion of glycogen and other nutrients by the endometrial glands, transforming the uterine lining into a nourishing environment for a potential embryo. This transformation is orchestrated primarily by progesterone, a hormone produced by the corpus luteum, the remnant of the ovarian follicle after ovulation.
Hormonal Orchestration: The Role of Progesterone
Progesterone, the star player of the secretory phase, is responsible for:
-
Endometrial Glandular Growth and Secretion: Progesterone stimulates the endometrial glands to produce and secrete glycogen, lipids, and other nutrients crucial for embryonic development. These secretions create a rich, receptive environment for implantation.
-
Endometrial Vascularization: Progesterone enhances blood flow to the endometrium, providing the necessary oxygen and nutrients for a potential embryo. This increased vascularization is responsible for the characteristic thickening of the endometrium.
-
Cervical Mucus Changes: Progesterone causes the cervical mucus to become thicker and less hospitable to sperm, aiding in the prevention of polyspermy (fertilization by multiple sperm) should fertilization occur.
What the Secretory Phase Coincides With:
The secretory phase coincides with several crucial events and processes within the female reproductive system:
-
Corpus Luteum Function: The secretory phase is directly linked to the lifespan and functionality of the corpus luteum. This temporary endocrine gland produces progesterone, the driving force behind the endometrial changes during this phase. The corpus luteum's lifespan is typically around 14 days. If fertilization doesn't occur, it regresses, progesterone levels plummet, and menstruation begins.
-
Implantation Window: The secretory phase encompasses the implantation window, the period when the endometrium is optimally prepared to receive and support a fertilized egg. This window typically lasts for a few days, and its precise timing varies slightly from cycle to cycle. Successful implantation requires the synchronized arrival of a blastocyst (early embryo) and a receptive endometrium.
-
Elevated Basal Body Temperature: Many women experience a slight elevation in their basal body temperature (BBT) during the secretory phase. This increase is a direct consequence of the progesterone surge. Monitoring BBT can be a useful tool for tracking ovulation and confirming the onset of the secretory phase.
-
Premenstrual Symptoms: Towards the end of the secretory phase, if fertilization doesn't occur, decreasing progesterone levels trigger a cascade of hormonal changes that can lead to premenstrual symptoms (PMS). These can include mood swings, bloating, breast tenderness, and fatigue.
The Secretory Phase and Fertility: A Crucial Connection
The secretory phase is absolutely vital for fertility. A properly functioning secretory phase ensures:
-
Adequate Endometrial Receptivity: Without sufficient progesterone and the resulting endometrial changes, the uterine lining won't be receptive to implantation. This can lead to infertility.
-
Optimal Nutrient Supply: The nutrients secreted by the endometrial glands provide the necessary sustenance for the early embryo during its critical initial growth stages.
-
Stable Uterine Environment: A properly functioning secretory phase maintains a stable uterine environment crucial for successful implantation and early embryonic development.
Disruptions in the Secretory Phase: Potential Causes and Consequences
Several factors can disrupt the secretory phase, potentially leading to infertility or other reproductive problems:
-
Luteal Phase Defect (LPD): This refers to a shortened or otherwise dysfunctional secretory phase, often characterized by insufficient progesterone production. LPD can significantly impair endometrial receptivity, hindering implantation.
-
Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the hormonal balance necessary for a normal secretory phase, impacting progesterone production and endometrial development.
-
Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and endometriosis can interfere with the hormonal regulation of the secretory phase.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of certain nutrients, like zinc and vitamin B6, can impair progesterone production and endometrial function.
-
Certain Medications: Some medications can interfere with hormonal balance, potentially affecting the secretory phase.
Diagnosing and Treating Secretory Phase Issues:
Diagnosing problems with the secretory phase often involves:
-
Tracking Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Monitoring BBT can provide clues about ovulation timing and the length of the secretory phase.
-
Endometrial Biopsy: This procedure involves taking a small sample of the endometrium to evaluate its structure and glandular development.
-
Hormone Testing: Blood tests can measure progesterone levels and other hormones to assess the functionality of the corpus luteum.
-
Ultrasound: Ultrasound can visualize the uterus and endometrium to assess their thickness and structure.
Treatment for secretory phase issues depends on the underlying cause and may include:
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Stress reduction techniques and a healthy diet can improve hormonal balance.
-
Supplementation: Supplements containing progesterone or other nutrients may be recommended to address deficiencies.
-
Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to regulate hormone levels and support the secretory phase.
Conclusion: The Secretory Phase – A Cornerstone of Fertility
The secretory phase is a critical juncture in the female reproductive cycle. Its intricate hormonal orchestration and physiological changes are essential for successful fertilization and implantation. Understanding the processes involved, the potential for disruptions, and available diagnostic and treatment options is crucial for addressing infertility and ensuring reproductive health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking medical attention when necessary are all vital steps in supporting a healthy and effective secretory phase. This comprehensive overview should equip you with valuable knowledge about this pivotal stage in the female reproductive cycle, highlighting its profound influence on fertility and overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Tall Is 65 Inches To Feet
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Types Of Muscles Is Voluntary Muscle
May 09, 2025
-
What Is Force Measured In Units
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Degrees Are In A Half Circle
May 09, 2025
-
What Force Keeps The Planets In Orbit Around The Sun
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Secretory Phase Of The Uterine Cycle Coincides With . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.