The Ratio Between Map Distance And Ground Distance Is Called
Juapaving
Apr 07, 2025 · 6 min read
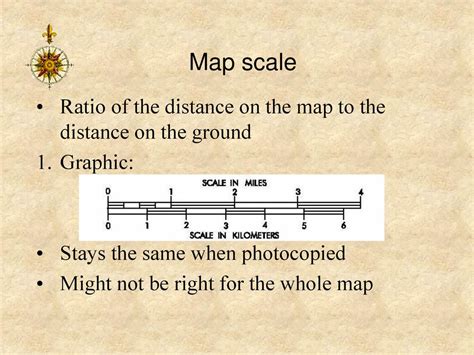
Table of Contents
The Ratio Between Map Distance and Ground Distance is Called: Scale and Its Applications
The ratio between map distance and ground distance is called scale. Understanding scale is fundamental to interpreting maps and using them effectively for various applications, from navigation and urban planning to geographic information systems (GIS) and environmental studies. This article delves deep into the concept of map scale, exploring its different types, applications, and the importance of accurate scaling in map creation and interpretation.
Understanding Map Scale: A Foundation of Cartography
Map scale represents the proportional relationship between a distance measured on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It's a crucial element in cartography, the science and art of mapmaking. Essentially, scale tells us how much smaller the map representation is compared to the actual area it depicts. This ratio is usually expressed in three primary ways:
1. Representative Fraction (RF):
This is the most common and precise way to express map scale. It's written as a ratio, for example, 1:50,000 or 1/50,000. This means that one unit of measurement on the map (e.g., 1 centimeter, 1 inch) represents 50,000 of the same units on the ground. The RF remains consistent regardless of the units used.
Advantages: Universal understanding, precise and unambiguous.
Disadvantages: Can be less intuitive for those unfamiliar with ratios.
2. Verbal Scale:
This method expresses the scale using words, for example, "One centimeter equals one kilometer," or "One inch represents 10 miles." It's more user-friendly for those unfamiliar with representative fractions.
Advantages: Easy to understand, directly relates map units to ground units.
Disadvantages: Less precise than RF, needs to be specified for particular units (e.g., cm, inches). Converting between units requires calculation.
3. Graphic Scale:
This is a visual representation of the scale, typically a bar line divided into segments representing ground distances. It's advantageous because it remains accurate even if the map is enlarged or reduced.
Advantages: Unaffected by map reproduction changes, visually intuitive, useful for quick estimations.
Disadvantages: Less precise for very small or large measurements, requires a ruler for precise measurements if the scale bar is not sufficiently detailed.
Types of Map Scales and Their Suitability
The choice of map scale depends on the purpose of the map and the area it covers. Different scales cater to different levels of detail and application.
Large-Scale Maps:
These maps cover smaller areas with greater detail. Examples include city maps, cadastral maps (showing property boundaries), and topographic maps of small regions. They generally have a scale of 1:10,000 or larger. The larger the denominator in the RF, the larger the scale.
Examples: 1:1,000, 1:2,000, 1:5,000, 1:10,000, 1:25,000.
Applications: Detailed urban planning, surveying, precise location identification.
Medium-Scale Maps:
These maps show a balance between detail and coverage area. They are commonly used for regional planning and depicting features of a district or county. Typical scales range from 1:25,000 to 1:250,000.
Examples: 1:50,000, 1:100,000, 1:250,000.
Applications: Regional planning, transportation networks, geological mapping.
Small-Scale Maps:
These maps cover extensive areas with less detail. Examples include world maps, country maps, and continental maps. The scale is typically smaller than 1:250,000.
Examples: 1:500,000, 1:1,000,000, 1:10,000,000, and even smaller.
Applications: Global perspectives, broad overview of geographical regions, thematic mapping (e.g., climate, population).
Calculating Distances Using Map Scale
Calculating ground distances from map distances is straightforward. Let's assume we have a map with a scale of 1:50,000, and we measure a distance of 3 centimeters on the map.
-
Convert to the same units: If the scale is in centimeters and the measurement is in centimeters, this step is already done. If your map scale is in inches and your measurement is in centimeters, you need to convert one to the other.
-
Apply the scale: The map distance (3 cm) is multiplied by the scale's denominator (50,000).
-
Calculate: 3 cm * 50,000 = 150,000 cm.
-
Convert to a more manageable unit: This is often kilometers or miles. 150,000 cm is equal to 1.5 kilometers (100 cm = 1 m, 1000 m = 1 km).
Therefore, the ground distance represented by 3 cm on the map is 1.5 kilometers.
Applications of Map Scale in Different Fields
Map scale plays a critical role in various disciplines. Here are a few examples:
Navigation:
Accurate scale is crucial for accurate navigation, whether it's using printed maps or digital mapping systems like GPS. Knowing the scale helps to determine the distance between locations and plan routes efficiently.
Urban Planning:
Urban planners rely on maps of various scales to understand the layout of cities, assess the needs of different areas, and design infrastructure. Large-scale maps are useful for detailed planning of individual buildings and streets, while smaller scales provide an overview of the entire city or region.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
GIS uses map data to analyze and visualize spatial relationships. Scale is essential for managing data resolution and ensuring accuracy in spatial analysis. GIS software allows users to change scales dynamically, providing flexibility for analysis at different levels of detail.
Environmental Studies:
Environmental scientists use maps of various scales to study land use, monitor environmental changes, and manage natural resources. Scale influences the level of detail available for analysis, such as the identification of individual trees in a forest (large scale) versus the overall extent of deforestation (small scale).
Archaeology:
Archaeologists use maps to record the location of artifacts and features at archaeological sites. Large-scale maps are crucial for precise mapping of excavations, while smaller scales show the site's relationship to the surrounding landscape.
Challenges and Considerations in Map Scale
While map scale is essential for accurate representation, several challenges need to be addressed:
Scale Variation:
Maps may have varying scales across different parts of the map, especially for large areas or maps with complex topography. This can occur due to distortions in map projections.
Map Distortion:
The curvature of the Earth makes it difficult to represent its surface accurately on a flat map. Map projections inevitably introduce distortions in area, shape, distance, or direction, impacting the accuracy of the scale.
Data Resolution:
The level of detail that can be shown on a map is constrained by the scale and data resolution. Smaller-scale maps inherently have less detail than large-scale maps.
Map Generalization:
To avoid cluttering maps, cartographers use generalization techniques, such as simplifying shapes and omitting minor features. This process can affect the accuracy of distance measurements on the map.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Map Scale
Understanding the ratio between map distance and ground distance, represented by map scale, is fundamental for anyone working with maps. The choice of scale significantly influences the level of detail, the area covered, and the application of the map. Whether using representative fractions, verbal scales, or graphic scales, accuracy in scale is paramount for precise measurements, effective communication, and informed decision-making across a wide range of disciplines. The awareness of potential challenges related to map projections, data resolution, and generalization is also crucial for accurate map interpretation and responsible utilization of map data.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 59 In Roman Numerals
Apr 07, 2025
-
3 Letter Words Beginning With X
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Can Be Divided By 36
Apr 07, 2025
-
Difference Between Sent From And By
Apr 07, 2025
-
Do Gasses Have A Definite Volume
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Ratio Between Map Distance And Ground Distance Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.