The Main Circuit Board In A Computer Is Called A
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
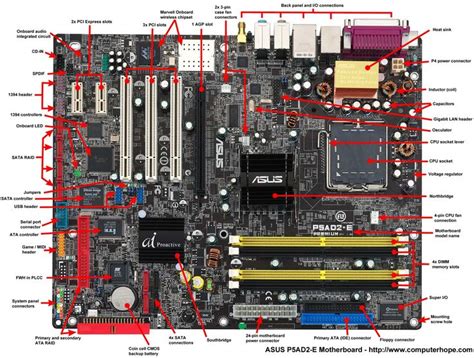
Table of Contents
The Main Circuit Board in a Computer is Called a Motherboard: A Deep Dive
The heart of any computer, the central nervous system orchestrating the symphony of data processing, is the motherboard. Also known as the mainboard, system board, or logic board, this complex circuit board is the foundation upon which all other components are built. Understanding its role, functionality, and components is crucial for anyone looking to build, repair, or simply understand their computer better. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of the motherboard, exploring its intricacies and importance in the realm of computing.
What is a Motherboard?
At its core, the motherboard is a large printed circuit board (PCB) that houses and connects all the essential components of a computer system. Think of it as the central hub, a sophisticated communication network connecting the CPU, RAM, storage devices, expansion cards, and peripherals. It facilitates communication between these components, enabling the seamless execution of tasks and the transfer of data. This intricate network of pathways, or traces, allows electrical signals to flow, effectively acting as the bloodstream of the computer.
Key Functions of a Motherboard:
- Connects Components: The most fundamental function is to provide a physical connection point for all the computer's components. This includes the CPU, RAM, storage controllers, expansion slots, and various ports for peripherals.
- Facilitates Communication: Beyond physical connection, the motherboard enables communication between these components. This is achieved through various buses and interfaces, enabling data transfer and synchronization.
- Provides Power: The motherboard distributes power supplied by the power supply unit (PSU) to all connected components. It regulates the voltage and ensures each component receives the required power.
- Houses the BIOS/UEFI: The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is stored on a chip on the motherboard. This firmware initiates the boot process, enabling the operating system to load and run.
- Supports Expansion: The motherboard provides expansion slots that allow users to add extra functionality through expansion cards, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network interface cards (NICs).
Understanding Motherboard Components: A Closer Look
The motherboard is a complex assembly of interconnected components, each playing a crucial role in the computer's overall functionality. Let's examine some of the key components:
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU) Socket:
This is the crucial connector for the CPU (the brain of the computer). The socket type is specific to the CPU's architecture, requiring careful consideration when choosing components. Modern motherboards often utilize sockets such as LGA (Land Grid Array) or PGA (Pin Grid Array). The CPU socket's design dictates the type of CPU compatible with the motherboard.
2. Random Access Memory (RAM) Slots:
RAM slots hold the computer's short-term memory, crucial for running programs and storing data actively used by the system. The number of slots and the type of RAM supported (e.g., DDR4, DDR5) vary depending on the motherboard. More RAM slots generally mean greater potential for memory upgrades.
3. Chipset:
The chipset is a group of integrated circuits that control the communication between the CPU and other components on the motherboard. It bridges the gap between the CPU, RAM, and peripheral devices. The chipset significantly impacts the motherboard's overall performance and features. Northbridge and Southbridge chipsets are older designs; modern motherboards often integrate these functions onto a single chip.
4. Expansion Slots:
Expansion slots allow the user to add extra functionality through expansion cards. Common types include PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots for graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards; and older PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) and AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) slots.
5. BIOS/UEFI Chip:
This chip contains the firmware that initializes the system at startup. The BIOS/UEFI is responsible for checking the hardware, loading the operating system, and managing low-level I/O operations. UEFI is a more modern replacement for BIOS, offering improved features and capabilities.
6. Storage Controllers:
The motherboard incorporates controllers for various storage devices, such as SATA (Serial ATA) and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) interfaces. These controllers manage communication with hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and other storage devices. The number and type of these interfaces determine the variety and capacity of storage devices compatible with the motherboard.
7. I/O Panel:
The I/O panel is a crucial component located on the rear of the motherboard, providing access points for various peripherals. It typically includes ports such as USB, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, and display ports (HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA). The variety and number of these ports greatly affect usability and connectivity.
Motherboard Form Factors: Size Matters
Motherboards come in various sizes and form factors, each designed for different cases and computer builds. The form factor dictates the physical dimensions and layout of the motherboard, influencing the size and type of components it can accommodate. Some common form factors include:
- ATX (Advanced Technology Extended): The most common form factor, suitable for most desktop computers. It offers a good balance between size and expandability.
- Micro-ATX (µATX): A smaller version of ATX, suitable for smaller cases and systems with fewer expansion needs.
- Mini-ITX: A significantly smaller form factor, often used in compact and space-saving systems. It has limited expansion capabilities.
- EATX (Extended ATX): A larger form factor than ATX, designed for high-end systems with extensive expansion needs and multiple graphics cards.
Choosing the right form factor depends on the intended size and functionality of the computer build.
Choosing the Right Motherboard: Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate motherboard is a critical decision when building or upgrading a computer. Several factors must be considered to ensure compatibility and optimal performance:
- CPU Socket Compatibility: The most important factor is CPU socket compatibility. The motherboard must have a socket that matches the CPU you intend to use.
- Chipset: The chipset determines the motherboard's features and capabilities. Choose a chipset that supports the desired features and performance levels.
- RAM Type and Speed: Ensure the motherboard supports the type and speed of RAM you plan to use.
- Expansion Slots: Consider the number and types of expansion slots needed to accommodate future upgrades.
- Storage Interfaces: Check for the availability of the necessary storage interfaces (SATA, NVMe) for your intended storage devices.
- I/O Ports: Assess the number and types of I/O ports required to connect peripherals.
- Form Factor: Select a form factor compatible with your computer case.
- BIOS/UEFI Features: Consider features like UEFI support, secure boot, and overclocking capabilities.
Motherboard Troubleshooting: Common Issues and Solutions
Even the most reliable motherboards can encounter problems. Understanding common issues and potential solutions is crucial for troubleshooting. Some frequent problems include:
- No Power: Check power supply connections to the motherboard and the power switch.
- No Boot: Check RAM modules, try reseating them, and try booting with only one module. Check the BIOS battery.
- System Instability: Check RAM for errors, ensure proper CPU cooling, and check for overheating components.
- Peripheral Issues: Check cable connections, try different ports, and update drivers.
The Motherboard: The Unsung Hero of Computing
The motherboard is often overlooked, yet it's the backbone of any computer system. Its complex design and intricate functionality are essential for the seamless operation of all components. Understanding its role, components, and potential issues is crucial for anyone involved in building, maintaining, or simply appreciating the inner workings of a computer. From the CPU socket to the I/O panel, every component on this central circuit board plays a vital role in the overall performance and functionality of the computer. Mastering the intricacies of the motherboard is key to unlocking the full potential of your computer system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Result Of Glycolysis
May 09, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 40
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Inches In 12 Meters
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes Does A Fly Have
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Smallest Parts Of An Atom
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Main Circuit Board In A Computer Is Called A . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.