Sum Of The Infinite Geometric Series Calculator
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
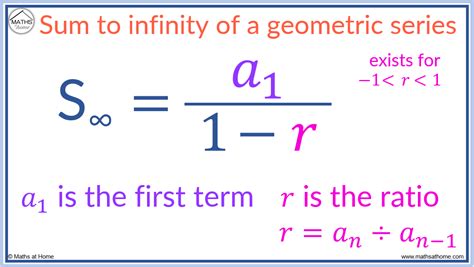
Table of Contents
Sum of the Infinite Geometric Series Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
The sum of an infinite geometric series is a fascinating concept with applications across various fields, from finance and physics to computer science and engineering. Understanding how to calculate this sum and the conditions under which it's possible is crucial for anyone working with these types of mathematical sequences. This article will delve deep into the concept, explaining the formula, its limitations, and how to use a sum of the infinite geometric series calculator effectively. We’ll also explore practical examples and address common misconceptions.
Understanding Geometric Series
Before we tackle the infinite series, let's review the basics of geometric sequences and series. A geometric sequence is a sequence where each term is found by multiplying the previous term by a constant value called the common ratio, denoted by 'r'. For instance, 2, 6, 18, 54... is a geometric sequence with a common ratio of 3 (each term is multiplied by 3 to get the next).
A geometric series is the sum of the terms in a geometric sequence. The sum of the first 'n' terms of a geometric series is given by the formula:
S<sub>n</sub> = a(1 - r<sup>n</sup>) / (1 - r)
where:
- a is the first term of the sequence
- r is the common ratio
- n is the number of terms
The Infinite Geometric Series: When Does it Converge?
An infinite geometric series is, as the name suggests, the sum of an infinite number of terms in a geometric sequence. This might seem impossible to calculate, but under certain conditions, the sum converges to a finite value. The crucial condition is that the absolute value of the common ratio, |r|, must be less than 1 (|r| < 1). If |r| ≥ 1, the series diverges, meaning the sum grows infinitely large (or oscillates without approaching a limit).
Intuitively, if you're repeatedly multiplying by a number smaller than 1, each subsequent term gets smaller and smaller, contributing less and less to the overall sum. This allows the sum to approach a finite limit.
The Formula for the Sum of an Infinite Geometric Series
When |r| < 1, the sum of an infinite geometric series (S<sub>∞</sub>) is given by a remarkably simple formula:
S<sub>∞</sub> = a / (1 - r)
This formula elegantly captures the idea that as the number of terms approaches infinity, the contribution of the later terms becomes negligible. The sum essentially "settles" on a finite value.
Using a Sum of the Infinite Geometric Series Calculator
While the formula is straightforward, using a calculator can save time and reduce the risk of errors, especially when dealing with complex or repetitive calculations. A well-designed calculator should:
- Clearly label input fields: It should have designated places for entering the first term ('a') and the common ratio ('r').
- Provide error handling: The calculator should alert you if |r| ≥ 1, indicating that the series diverges and the sum is undefined.
- Display results accurately: The calculator should present the sum with sufficient precision.
- Offer a step-by-step solution (optional): Some advanced calculators might show the calculations involved, helping users understand the process better.
Practical Examples and Applications
Let's look at a few examples to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: A Simple Case
Consider the series: 1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + ...
Here, a = 1 and r = 1/2. Since |r| < 1, the series converges. Using the formula:
S<sub>∞</sub> = 1 / (1 - 1/2) = 1 / (1/2) = 2
The sum of this infinite series is 2.
Example 2: A More Complex Series
Let's consider a slightly more complex example: 3 - 1 + 1/3 - 1/9 + ...
Here, a = 3 and r = -1/3. Again, |r| < 1, so the series converges. Using the formula:
S<sub>∞</sub> = 3 / (1 - (-1/3)) = 3 / (4/3) = 9/4 = 2.25
The sum of this infinite series is 2.25. Note that the series involves negative terms, but the formula still applies.
Example 3: A Divergent Series
Consider the series: 2 + 4 + 8 + 16 + ...
Here, a = 2 and r = 2. Since |r| > 1, this series diverges. There is no finite sum for this series; it grows infinitely large. A sum of the infinite geometric series calculator would ideally indicate this divergence.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of infinite geometric series finds applications in many areas:
- Finance: Calculating the present value of a perpetuity (a series of payments that continues indefinitely).
- Physics: Modeling the motion of bouncing balls or the decay of radioactive isotopes.
- Computer Science: Analyzing algorithms and data structures.
- Engineering: Designing systems with repetitive processes.
- Economics: Modeling economic growth or decline with a constant rate of change.
Common Misconceptions
- All infinite series converge: This is false. Only infinite geometric series with |r| < 1 converge. Other types of infinite series may converge or diverge based on different criteria.
- The formula works for all values of r: The formula S<sub>∞</sub> = a / (1 - r) is only valid when |r| < 1. For other values of r, the series diverges.
- The calculator always gives the correct answer: While a well-designed calculator is accurate, user error in inputting 'a' and 'r' can lead to incorrect results. Always double-check your input.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Scenarios
While the basic formula provides a solid foundation, there are more complex scenarios:
- Series with complex numbers as the common ratio: The formula still applies, but calculations will involve complex number arithmetic.
- Series with a starting term other than the first: The formula can be adapted by finding the first term and then calculating accordingly.
- Approximating sums: Even if a series converges slowly (r close to but less than 1), the formula gives the exact sum; however, a calculator might show approximations due to computational limitations.
Conclusion
The ability to calculate the sum of an infinite geometric series is a powerful mathematical tool with widespread practical applications. Understanding the formula, its limitations, and how to use a calculator effectively is crucial for anyone working with geometric sequences. Remember to always check the condition |r| < 1 before applying the formula and always double-check your inputs in any calculator to ensure accuracy. This guide provides a solid foundation for further exploration of this fascinating mathematical concept. By understanding the underlying principles and using available tools efficiently, you can confidently tackle problems involving infinite geometric series.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Compare And Contrast A Light Microscope And An Electron Microscope
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 6 25 Meters In Feet And Inches
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Are In 50 Millimeters
May 09, 2025
-
Describe The Epithelium Found In The Uterine Tube
May 09, 2025
-
What Animal Lay Eggs And Is Not A Bird
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of The Infinite Geometric Series Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.