Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Dodecagon
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
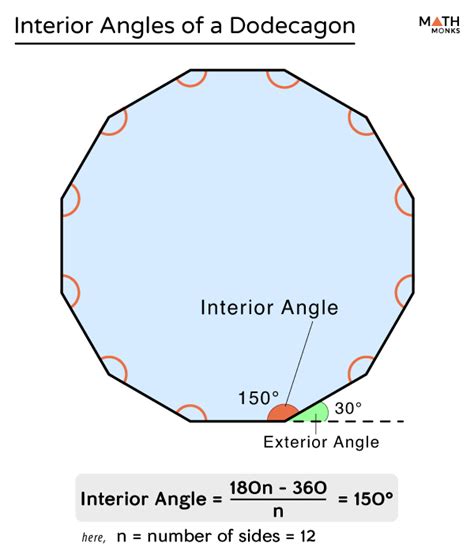
Table of Contents
The Sum of Interior Angles of a Dodecagon: A Comprehensive Guide
The dodecagon, a captivating polygon with twelve sides and twelve angles, holds a special place in geometry. Understanding its properties, particularly the sum of its interior angles, unlocks a deeper appreciation for geometric principles and their applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the calculation and significance of the sum of interior angles of a dodecagon, exploring various approaches and real-world examples.
Understanding Polygons and Their Angles
Before diving into the specifics of a dodecagon, let's establish a foundational understanding of polygons and their angles. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a series of straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon, and the points where the sides meet are called vertices. The angles formed at each vertex are called interior angles.
Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess:
- Triangle (3 sides): The simplest polygon.
- Quadrilateral (4 sides): Examples include squares, rectangles, and trapezoids.
- Pentagon (5 sides): A five-sided polygon.
- Hexagon (6 sides): Often found in nature, like honeycombs.
- Heptagon (7 sides): Also known as a septagon.
- Octagon (8 sides): A familiar shape found in stop signs.
- Nonagon (9 sides): A nine-sided polygon.
- Decagon (10 sides): A ten-sided polygon.
- Undecagon (11 sides): An eleven-sided polygon.
- Dodecagon (12 sides): Our focus for this article.
And so on, with the number of sides increasing infinitely.
Calculating the Sum of Interior Angles: The Formula
The sum of the interior angles of any polygon can be calculated using a single, elegant formula. This formula is derived from the fact that any polygon can be divided into triangles by drawing diagonals from a single vertex. The number of triangles formed is always two less than the number of sides of the polygon (n). Since the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180°, the total sum of interior angles of a polygon with 'n' sides is:
Sum of Interior Angles = (n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' represents the number of sides of the polygon.
Applying the Formula to a Dodecagon
A dodecagon has 12 sides (n = 12). Substituting this value into the formula, we can calculate the sum of its interior angles:
Sum of Interior Angles = (12 - 2) * 180° = 10 * 180° = 1800°
Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of a regular dodecagon (a dodecagon where all sides and angles are equal) is 1800°. This holds true for any dodecagon, regardless of whether it's regular or irregular. The shape may be distorted, but the total sum of the interior angles will always remain 1800°.
Understanding Regular vs. Irregular Dodecagons
While the formula applies to both regular and irregular dodecagons, it's crucial to understand the difference:
-
Regular Dodecagon: All sides are of equal length, and all interior angles are equal (150° each, as 1800°/12 = 150°). These are highly symmetrical shapes.
-
Irregular Dodecagon: The sides and angles are of varying lengths and measures. The only constant is the sum of the interior angles, which remains 1800°.
Real-World Applications of Dodecagons and Angle Summation
Dodecagons, while perhaps not as prominently featured as triangles or squares in everyday life, appear in various contexts:
-
Tessellations: Dodecagons, particularly regular ones, can be used in creating intricate tessellations or tilings, often found in architectural designs and artwork. Understanding the angle sum is crucial for ensuring these patterns fit together seamlessly.
-
Architecture and Design: The unique shape and properties of dodecagons can inspire innovative architectural designs, from building layouts to decorative elements. The interior angle sum informs the structural integrity and aesthetic balance of such designs.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: In computer-generated imagery and game design, dodecagons are utilized in modeling complex three-dimensional shapes and environments. Precise angle calculations are essential for realistic rendering and smooth animation.
-
Crystallography: Certain crystals exhibit dodecahedral structures, and understanding their angles is fundamental in crystallography and materials science.
-
Nature: Though less common than other shapes, some natural formations might exhibit approximate dodecagonal characteristics, requiring an understanding of angle sums for analysis.
Alternative Methods for Calculating the Sum of Interior Angles
While the (n - 2) * 180° formula is the most efficient, other methods can be employed, particularly for visualizing the concept:
-
Triangulation: Dividing the dodecagon into triangles by drawing diagonals from a single vertex offers a visual demonstration of why the formula works. Each triangle contributes 180°, and the total number of triangles is (n - 2).
-
Exterior Angles: The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360°. Since each interior angle and its corresponding exterior angle are supplementary (add up to 180°), you can deduce the sum of interior angles by working with the exterior angles. However, this method is less direct than the primary formula.
Advanced Concepts and Related Topics
The understanding of the sum of interior angles in a dodecagon opens doors to more advanced geometric concepts:
-
Interior Angle of a Regular Dodecagon: As mentioned earlier, a regular dodecagon has all its interior angles equal. To find the measure of each individual angle, simply divide the total sum of interior angles (1800°) by the number of sides (12): 1800°/12 = 150°.
-
Relationship to Other Polygons: The formula for the sum of interior angles is applicable to all polygons, regardless of the number of sides. This emphasizes the underlying unity in geometric principles.
-
Non-Euclidean Geometry: While the (n - 2) * 180° formula works in Euclidean geometry (the geometry of flat surfaces), the concept of angle sums changes in non-Euclidean geometries, such as spherical or hyperbolic geometry.
-
Applications in Higher Mathematics: Understanding polygons and their angles forms a base for more advanced mathematical concepts, including topology and abstract algebra.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Dodecagon Angles
The sum of interior angles of a dodecagon, while seemingly a specific geometric property, exemplifies fundamental principles applicable to a wide range of polygons and mathematical disciplines. From its straightforward calculation using a simple formula to its real-world applications in architecture, design, and computer graphics, understanding this concept provides a deeper appreciation for the elegance and practicality of geometry. This knowledge forms a solid base for further exploration into advanced geometric principles and their applications in various fields. The seemingly simple dodecagon, therefore, holds a significant place in the world of mathematics and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Subset Or Part Of A Population
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 3 6 And 9
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Pair Of Triangles Can Be Proven Congruent By Sss
Mar 23, 2025
-
Why Cant Sound Travel Through A Vacuum
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is A Net Charge Of An Atom
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Dodecagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
