Sum Of Exterior Angles Of A Heptagon
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
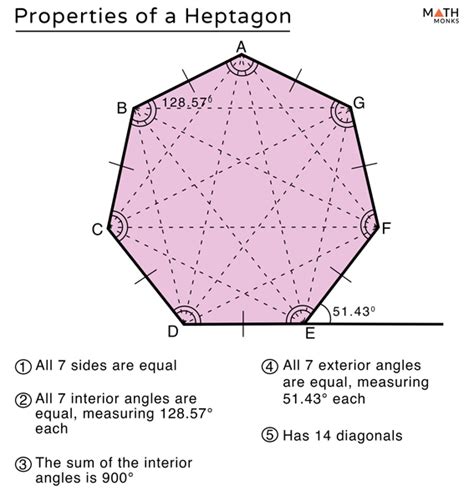
Table of Contents
The Sum of Exterior Angles of a Heptagon: A Deep Dive into Geometry
The world of geometry, with its shapes, angles, and theorems, can be both fascinating and challenging. One fundamental concept often explored in geometry is the sum of the exterior angles of polygons. This article delves deep into the specifics of this concept, focusing on a heptagon – a seven-sided polygon. We'll explore the theorem, its proof, practical applications, and even touch upon related concepts to give you a comprehensive understanding.
Understanding Polygons and Exterior Angles
Before we dive into the intricacies of a heptagon, let's establish a firm grasp of the basic terminology. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by joining line segments. These line segments are called the sides of the polygon. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess: triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), hexagons (6 sides), heptagons (7 sides), octagons (8 sides), and so on.
An exterior angle of a polygon is the angle formed by extending one of its sides. At each vertex of the polygon, there are two exterior angles, but we usually consider only one, and it's supplementary to the corresponding interior angle. In other words, the interior angle and its adjacent exterior angle add up to 180 degrees.
The Sum of Exterior Angles Theorem
A crucial theorem in geometry states that the sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, one at each vertex, is always 360 degrees. This holds true regardless of the number of sides the polygon has – be it a triangle, a quadrilateral, a heptagon, or a polygon with a hundred sides. This consistency is a fundamental property of polygons.
Proof of the Sum of Exterior Angles Theorem
Several methods can be used to prove this theorem. One intuitive approach involves visualizing walking around the polygon. Imagine walking along each side of the polygon, turning at each vertex. The total amount you turn is a complete circle, which is 360 degrees. Each turn is equal to the exterior angle at that vertex. Therefore, the sum of the exterior angles must be 360 degrees.
A more rigorous proof uses the concept of interior angles. The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with 'n' sides is given by the formula (n-2) * 180 degrees. Since each interior angle and its adjacent exterior angle add up to 180 degrees, the sum of all interior and exterior angles together is n * 180 degrees. Subtracting the sum of interior angles from the total sum, we get:
n * 180 degrees - (n-2) * 180 degrees = 360 degrees.
This elegantly demonstrates that the sum of exterior angles remains consistently 360 degrees regardless of the polygon's number of sides.
Applying the Theorem to a Heptagon
Now, let's specifically address the heptagon. A heptagon, with its seven sides and seven vertices, perfectly conforms to the sum of exterior angles theorem. The sum of its exterior angles, one at each vertex, is invariably 360 degrees. This holds true regardless of the heptagon's shape – whether it's regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular (sides and angles of varying lengths and measures).
Regular Heptagons: A Special Case
A regular heptagon is a heptagon where all sides are equal in length, and all interior angles are equal in measure. In a regular heptagon, each interior angle measures approximately 128.57 degrees (calculated using the formula (n-2) * 180 / n, where n = 7). Consequently, each exterior angle in a regular heptagon measures approximately 51.43 degrees (180 degrees - 128.57 degrees). Even though the individual exterior angles are different from those in other heptagons, their sum still remains precisely 360 degrees (7 * 51.43 degrees ≈ 360 degrees). The slight discrepancy arises from rounding off the interior angle calculation.
Practical Applications of the Sum of Exterior Angles Theorem
The sum of exterior angles theorem, though seemingly abstract, has several practical applications:
- Navigation: The concept of turning angles is directly related to navigation. Pilots and sailors use this principle to chart courses and calculate turns during long journeys.
- Construction and Engineering: Architects and engineers use geometrical principles, including the sum of exterior angles, in designing structures such as buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects. The stability and integrity of these structures depend on precise angular calculations.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: In creating two-dimensional and three-dimensional models, the principles of polygon geometry, including exterior angles, are crucial. The rendering and animation of objects rely on accurate calculations to create realistic images.
- Cartography and Mapping: The creation of maps involves geometrical principles in representing geographical features. The relationships between angles and shapes are crucial for accuracy in map design.
Exploring Related Concepts: Interior Angles and Irregular Heptagons
While we've primarily focused on exterior angles, understanding the relationship between interior and exterior angles is crucial. In any polygon, the sum of an interior angle and its adjacent exterior angle is always 180 degrees. This supplementary relationship provides a powerful tool for solving problems involving both interior and exterior angles.
In irregular heptagons, the individual exterior angles will vary, but their sum will always remain 360 degrees. The uneven sides and angles result in different exterior angle measurements at each vertex, but the theorem's fundamental principle remains unchallenged. Calculating the specific measure of each exterior angle in an irregular heptagon requires knowing the measure of each interior angle or other relevant information about the heptagon's dimensions.
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of a Geometric Theorem
The sum of exterior angles theorem is a cornerstone of geometry. Its consistent application across all polygons, including the heptagon, underscores its fundamental importance. Understanding this theorem provides a strong foundation for tackling more advanced geometrical concepts and solving various practical problems across various fields. From navigation to computer graphics, the power of this seemingly simple theorem is far-reaching and consistently relevant in our world. Its elegant proof and consistent application cement its place as a valuable tool for anyone interested in the intricacies of geometry. The next time you encounter a heptagon, remember the unfailing truth: its exterior angles, when summed together, will always amount to 360 degrees.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Words That End With A S
May 09, 2025
-
25 Is 50 Of What Number
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 9 Percent In Decimal Form
May 09, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Containing S And I
May 09, 2025
-
Difference Between Experimental Probability And Theoretical Probability
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Exterior Angles Of A Heptagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.