Straight Line Is How Many Degrees
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
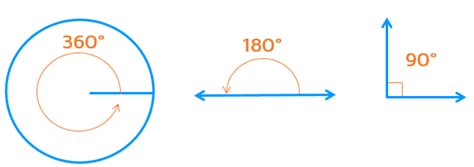
Table of Contents
Straight Line: How Many Degrees? Exploring Angles and Geometry
A straight line, a fundamental concept in geometry, is often visually understood but requires a precise definition when discussing angles and measurements. The question "how many degrees is a straight line?" leads us into a fascinating exploration of angles, their classifications, and their importance in various fields. This article will delve into the intricacies of straight lines, angles, and their applications.
Understanding Angles
Before we define the degree measure of a straight line, let's establish a firm understanding of angles. An angle is formed by two rays that share a common endpoint, called the vertex. These rays are called the sides of the angle. Angles are typically measured in degrees, represented by the symbol °.
Types of Angles
Angles are classified based on their measure:
- Acute Angle: An angle whose measure is greater than 0° and less than 90°.
- Right Angle: An angle whose measure is exactly 90°. It is often represented by a small square at the vertex.
- Obtuse Angle: An angle whose measure is greater than 90° and less than 180°.
- Straight Angle: An angle whose measure is exactly 180°. This is where our focus lies.
- Reflex Angle: An angle whose measure is greater than 180° and less than 360°.
- Full Angle (or Perigon): An angle whose measure is exactly 360°.
The Straight Angle: 180°
A straight line forms a straight angle, measuring 180°. This is a crucial concept. Imagine a line extending infinitely in both directions. If you place a point on this line and draw two rays extending from this point, along the line, in opposite directions, you have formed a straight angle. This angle represents half of a full rotation (360°).
Visualizing the 180° Straight Angle
Think of a perfectly straight road stretching out before you. The road itself represents a straight line, and the angle formed by extending the road infinitely in either direction forms a 180° straight angle. This visual helps to solidify the understanding of the concept.
Straight Angles and Supplementary Angles
Straight angles are intrinsically linked to supplementary angles. Two angles are supplementary if their sum is 180°. A straight angle can be divided into two supplementary angles. For example, an angle measuring 75° and an angle measuring 105° are supplementary because 75° + 105° = 180°. They together form a straight angle.
Applications of Straight Angles and Lines
The concept of a straight line and the 180° straight angle is fundamental in various fields:
Geometry and Trigonometry
- Linear Pairs: When two angles form a linear pair, they are adjacent and supplementary. Understanding straight angles is essential for solving problems involving linear pairs.
- Triangles: The sum of angles in any triangle is always 180°. This fundamental theorem in geometry directly relates to the concept of straight angles. The straight line formed by extending a side of a triangle can be used to analyze the exterior angle.
- Solving Geometric Problems: Many geometric problems, such as finding missing angles in polygons or proving geometric theorems, rely on the properties of straight lines and angles.
- Trigonometry: Straight lines and angles are foundational in trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent. Understanding angles helps determine the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles.
Engineering and Architecture
- Structural Design: In engineering and architecture, understanding straight lines and angles is crucial for designing stable and functional structures. Bridges, buildings, and other structures rely on precise angle measurements and straight lines for their integrity.
- Surveying: Surveyors use straight lines and angles to accurately measure land and create maps. The principles of geometry, including the 180° straight angle, are essential tools in this field.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software uses straight lines and angles as fundamental elements in designing and modeling various objects, from simple shapes to complex machines.
Computer Science and Graphics
- Computer Graphics: In computer graphics, straight lines are fundamental building blocks for creating images and animations. Algorithms for drawing lines and shapes rely on the geometric properties of straight lines and angles.
- Vector Graphics: Vector graphics use mathematical equations to represent images, and straight lines are often the basis for these equations.
Everyday Life
Beyond technical applications, straight lines and angles are present in everyday life:
- Directions: We use straight lines and angles to understand directions and distances. The concept of a straight path is fundamental to navigation.
- Construction: From building furniture to constructing houses, straight lines and angles are crucial for creating stable and functional structures.
- Art and Design: Straight lines and angles are often used in art and design to create balance, symmetry, and visual interest.
Advanced Concepts and Related Topics
The concept of a straight angle and its 180° measurement opens doors to more advanced topics:
Angles in Higher Dimensions
While we've focused on two-dimensional geometry, the concepts of angles and lines extend to higher dimensions. Understanding straight lines in three dimensions or more involves linear algebra and vector calculus.
Non-Euclidean Geometry
In Euclidean geometry, the sum of angles in a triangle is always 180°. However, in non-Euclidean geometries (like spherical geometry), this isn't the case. Exploring these different geometric systems expands our understanding of angles and lines beyond the conventional.
Projective Geometry
Projective geometry deals with properties that remain invariant under projective transformations. This involves a deeper study of lines and their intersections, leading to a richer understanding of straight lines and their properties.
Conclusion: The Significance of the 180° Straight Angle
The seemingly simple statement that a straight line is 180° degrees encapsulates a fundamental concept in geometry with far-reaching implications across various disciplines. From the foundational principles of geometric proofs to the complex calculations in engineering and computer graphics, the 180° straight angle serves as a cornerstone of mathematical understanding and practical applications. Its significance extends beyond the classroom, permeating our everyday experiences and influencing the design and construction of the world around us. A comprehensive understanding of straight angles and their properties is essential for anyone seeking a deeper appreciation of mathematics and its profound impact on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Si Unit Of Momentum
Mar 05, 2025
-
What 2 Planets Have No Moons
Mar 05, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Components Of A Nucleotide
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is A 7 8 Grade Percentage
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Vitamin Is Neither Fat Nor Water Soluble
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Straight Line Is How Many Degrees . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
