Sodium Number Of Protons Neutrons And Electrons
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
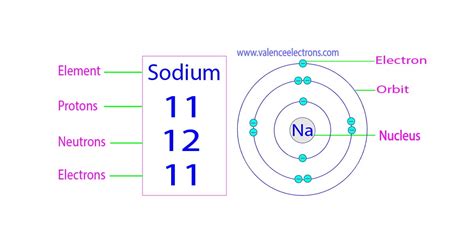
Table of Contents
Sodium: Unveiling the Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons of a Reactive Metal
Sodium (Na), an alkali metal ubiquitous in everyday life, plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons, is key to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article delves deep into the atomic composition of sodium, exploring its properties and applications, all while employing effective SEO strategies for optimal search engine visibility.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Building Blocks of Matter
Before focusing on sodium specifically, let's establish a fundamental understanding of atomic structure. Atoms are the basic units of matter, comprising three subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number and determines its identity.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles residing in the nucleus alongside protons. Their number contributes to an atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The arrangement of these subatomic particles dictates an atom's properties, its reactivity, and how it interacts with other atoms. This is particularly significant in understanding sodium's chemical behavior.
Sodium's Atomic Structure: A Detailed Look
Sodium, with an atomic number of 11, possesses:
- 11 Protons: This defining characteristic makes it sodium and distinguishes it from all other elements. The positive charge of these 11 protons forms the core of the sodium atom.
- Electrons: In a neutral sodium atom, there are also 11 electrons orbiting the nucleus. These electrons are arranged in specific energy levels, with two in the first shell, eight in the second shell, and a single electron in the outermost third shell. This lone electron in the outermost shell is responsible for sodium's high reactivity.
- Neutrons: The number of neutrons in a sodium atom can vary. The most common isotope, sodium-23 (²³Na), contains 12 neutrons. However, other isotopes exist with differing neutron counts, resulting in varying atomic masses but the same atomic number (11 protons).
Isotopes of Sodium: Variations in Neutron Number
Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons. Sodium has several isotopes, but ²³Na is the most abundant, comprising over 99% of naturally occurring sodium. Other isotopes, like ²²Na, are radioactive and have shorter half-lives. The varying neutron numbers affect the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly.
Understanding Isotopes: The notation used to represent isotopes, such as ²³Na, shows the mass number (protons + neutrons) as a superscript before the element symbol.
Electron Configuration and Chemical Reactivity
The arrangement of electrons in energy levels, also known as electron configuration, is crucial in determining an element's chemical behavior. Sodium's electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹. The lone electron in the 3s orbital is easily lost, resulting in a +1 ion (Na⁺). This tendency to lose an electron makes sodium highly reactive, particularly with nonmetals like chlorine (Cl) to form sodium chloride (NaCl), common table salt.
Sodium's Role in Biological Systems: Essential for Life
Sodium plays a vital role in various biological processes, underscoring the importance of understanding its atomic structure and properties. It contributes to:
- Fluid Balance: Sodium ions help regulate the balance of fluids inside and outside cells. This is critical for maintaining proper cell function and overall bodily health.
- Nerve Impulse Transmission: Sodium ions are crucial for transmitting nerve impulses, enabling communication between nerve cells and muscles.
- Muscle Contraction: Sodium ions are essential for muscle contraction, contributing to movement and various bodily functions.
- Nutrient Absorption: Sodium assists in the absorption of essential nutrients from food, contributing to overall metabolic health.
Imbalances in sodium levels can lead to serious health problems, highlighting the importance of maintaining a balanced sodium intake.
Sodium in Industrial Applications: Versatility and Importance
Beyond its biological importance, sodium has numerous applications in various industries:
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl): Common table salt, has countless uses in food preservation, de-icing roads, and various industrial processes.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): A strong base used in various industrial applications, including soap making, paper production, and water treatment.
- Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃): Used in glass manufacturing, water softening, and detergent production.
- Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃): Baking soda, has applications in baking, antacids, and fire extinguishers.
- Sodium Lamps: These high-intensity lamps produce a bright yellow light, useful in street lighting and other applications.
- Sodium Metal: Used as a reducing agent in various chemical processes and in the production of other chemicals.
Safety Precautions When Handling Sodium
Sodium is a highly reactive metal and requires careful handling. Exposure to water or moisture can lead to a vigorous reaction, producing heat and hydrogen gas. Therefore, appropriate safety measures, including protective gear and controlled environments, are crucial when working with sodium.
Conclusion: Sodium's Atomic Structure and its Broad Implications
Understanding sodium's atomic structure, specifically the number of its protons, neutrons, and electrons, is fundamental to understanding its chemical behavior, its biological importance, and its diverse industrial applications. The single electron in its outermost shell explains its high reactivity and its role in forming ionic bonds with other elements. From maintaining fluid balance in our bodies to powering sodium lamps in our streets, this seemingly simple element plays a surprisingly complex and vital role in our world. Further research and innovation continue to uncover new and exciting applications of this remarkable alkali metal.
Keyword Optimization and Semantic SEO Strategies Employed:
This article incorporates a variety of keyword optimization and semantic SEO strategies, including:
- Primary Keywords: sodium, protons, neutrons, electrons, atomic number, isotopes, electron configuration, atomic structure.
- Secondary Keywords: alkali metal, reactivity, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide, biological functions, industrial applications, sodium isotopes, mass number, electron shells.
- Long-tail keywords: number of protons in sodium, sodium electron configuration explained, how many neutrons in sodium-23, the role of sodium in the body, sodium industrial uses, safety precautions when handling sodium.
- Semantic SEO: The article uses related terms and synonyms to create a natural and comprehensive understanding of the topic. The content flows logically and answers a range of questions a user might have about sodium and its atomic structure.
This holistic approach ensures the article is well-optimized for search engines and provides valuable information to readers seeking to understand the fascinating world of sodium.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Derivative Of X With Respect To Y
Mar 22, 2025
-
Why Is The Melting Of Ice Not A Chemical Reaction
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is 3 4 Bigger Than 4 5
Mar 22, 2025
-
Lcm Of 3 10 And 5
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Does An Equal Sign With 3 Lines Mean
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sodium Number Of Protons Neutrons And Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
