Simplify The Square Root Of 50
Juapaving
Mar 05, 2025 · 4 min read
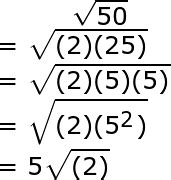
Table of Contents
Simplifying the Square Root of 50: A Comprehensive Guide
Simplifying square roots is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications ranging from basic algebra to advanced calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of simplifying the square root of 50, providing a step-by-step explanation, exploring the underlying principles, and offering practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll go beyond a simple answer and explore the why behind the simplification process, making this concept clear and accessible for everyone.
Understanding Square Roots
Before we tackle the square root of 50, let's refresh our understanding of square roots. A square root of a number x is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals x. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3, because 3 multiplied by itself (3 x 3 = 9) equals 9. Similarly, the square root of 16 (√16) is 4 (4 x 4 = 16).
However, many numbers don't have perfect square roots – meaning they aren't the product of an integer multiplied by itself. This is where simplification comes in. We aim to express the square root in its simplest form, extracting any perfect square factors.
Prime Factorization: The Key to Simplification
The most efficient method for simplifying square roots involves prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of breaking down a number into its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.).
Let's apply this to 50:
-
Find the prime factors of 50: 50 can be broken down as 2 x 25. Since 25 is 5 x 5, the prime factorization of 50 is 2 x 5 x 5, or 2 x 5².
-
Identify perfect squares: Notice that we have a pair of 5s (5 x 5 = 5²). This is a perfect square.
-
Simplify the square root: Now, we can rewrite the square root of 50 as follows:
√50 = √(2 x 5²) = √2 x √5² = √2 x 5 = 5√2
Therefore, the simplified form of √50 is 5√2.
Step-by-Step Simplification of √50
To further clarify the process, let's break down the simplification into distinct, manageable steps:
-
Write the number under the square root sign: √50
-
Find the prime factorization: 50 = 2 x 5 x 5 = 2 x 5²
-
Rewrite the square root using the prime factorization: √(2 x 5²)
-
Separate the square root into individual terms: √2 x √5²
-
Simplify the perfect square: √5² = 5
-
Combine the terms: 5√2
This clearly shows that the simplified form of √50 is 5√2. This is the most accurate and efficient representation of the square root.
Why Simplify Square Roots?
Simplifying square roots is more than just a mathematical exercise; it's a crucial step for several reasons:
-
Accuracy: Simplified square roots provide a more precise representation of the value compared to a long decimal approximation. Using 5√2 avoids rounding errors that occur when using decimal approximations.
-
Efficiency: Simplified forms are more concise and easier to work with in further calculations. Imagine trying to multiply or add decimals approximations of square roots versus working with their simplified forms.
-
Understanding Mathematical Concepts: The process of simplifying square roots reinforces the understanding of prime factorization, perfect squares, and the properties of radicals. This deeper understanding is critical for tackling more complex mathematical problems.
Further Examples of Simplifying Square Roots
Let's reinforce our understanding with some additional examples:
Example 1: Simplifying √72
-
Prime factorization: 72 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2³ x 3²
-
Rewriting: √(2³ x 3²) = √(2² x 2 x 3²)
-
Separating: √2² x √2 x √3²
-
Simplifying: 2 x √2 x 3 = 6√2
Therefore, √72 simplifies to 6√2.
Example 2: Simplifying √128
-
Prime factorization: 128 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2⁷
-
Rewriting: √(2⁷) = √(2⁶ x 2)
-
Separating: √2⁶ x √2
-
Simplifying: 2³√2 = 8√2
Therefore, √128 simplifies to 8√2.
Applications of Simplified Square Roots
Simplified square roots are not just theoretical concepts; they have practical applications in various fields:
-
Geometry: Calculating the lengths of diagonals in squares and rectangles often involves simplifying square roots.
-
Physics: Many physics formulas, particularly those involving vectors and distances, rely on the simplification of square roots.
-
Engineering: Structural calculations and design often incorporate the simplification of square roots for accuracy and efficiency.
-
Computer Graphics: Rendering and modeling in 3D graphics frequently utilizes simplified square roots for precision in calculations.
Conclusion: Mastering Square Root Simplification
Simplifying square roots, particularly as exemplified by simplifying the square root of 50, is a crucial skill in mathematics and has far-reaching practical implications. By understanding the process of prime factorization and applying it methodically, you can efficiently simplify square roots, leading to more accurate and efficient calculations across a variety of disciplines. The ability to confidently simplify square roots demonstrates a fundamental grasp of mathematical principles and lays a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges. Remember to always break down the number into its prime factors; this is the key to unlocking the simplest form of any square root. Practice consistently with different numbers to master this valuable skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Find The Instantaneous Rate Of Change
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Divisor Of 24 And 32
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Factor Of 44
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Sum Of The Interior Angles Of Hexagon
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Do The Arrows On A Food Chain Represent
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Simplify The Square Root Of 50 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
