Rotational Symmetry Letters Of The Alphabet
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
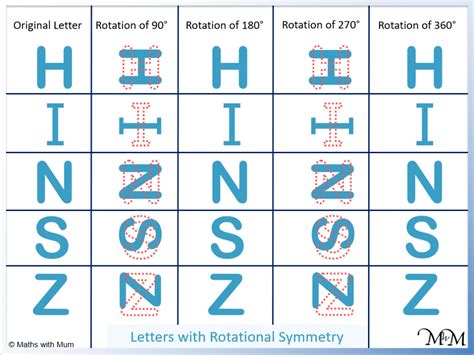
Table of Contents
Rotational Symmetry Letters of the Alphabet: A Deep Dive
Rotational symmetry, a captivating concept in geometry, refers to the ability of a shape to be rotated around a central point and still appear identical. This property isn't limited to simple shapes; it extends to letters of the alphabet, presenting an intriguing area of exploration within both mathematics and design. This article delves into the fascinating world of rotational symmetry within the English alphabet, exploring which letters possess this property and the implications it has across various fields.
Understanding Rotational Symmetry
Before diving into the alphabet, let's solidify our understanding of rotational symmetry. A shape possesses rotational symmetry if it can be rotated by a certain angle (less than 360 degrees) and still look exactly the same. This angle is called the angle of rotation, and the number of times the shape looks identical during a 360-degree rotation is the order of rotational symmetry.
For instance, a square has rotational symmetry of order 4 because it looks identical after rotations of 90, 180, and 270 degrees. A circle possesses infinite rotational symmetry, as it looks the same after any rotation. Letters with rotational symmetry, however, are less common.
Identifying Letters with Rotational Symmetry
Let's examine the English alphabet to identify letters that exhibit rotational symmetry. A crucial point to consider is the typeface or font used. The presence or absence of rotational symmetry can vary significantly depending on the font. This article primarily focuses on standard sans-serif and serif fonts, acknowledging that highly stylized fonts may alter the symmetry properties.
Letters with 180° Rotational Symmetry (Order 2):
This is the most common type of rotational symmetry found in letters. A letter possesses 180° rotational symmetry if it appears unchanged after a 180-degree rotation. These letters often have a vertical axis of symmetry. In standard fonts, the following letters typically exhibit this symmetry:
- H: A clear example; rotating it 180 degrees results in an identical appearance.
- I: The simplicity of the vertical line makes 180-degree rotation effortless.
- N: Though less obvious than 'H' or 'I', 'N' retains its form after rotation.
- O: A perfect circle (in many fonts) would have infinite rotational symmetry; a round letter 'O' in most fonts will have 180-degree symmetry.
- S: The mirror-image nature of 'S' contributes to its 180-degree rotational symmetry.
- X: Another clear example of 180-degree rotational symmetry.
- Z: Similar to 'X', 'Z' shows clear 180-degree rotational symmetry.
Letters without Rotational Symmetry:
The majority of letters in the alphabet lack any rotational symmetry. These letters look significantly different after any rotation less than 360 degrees. This includes letters like:
- A: Rotating 'A' changes its orientation completely.
- B: The loops and lines of 'B' are not preserved under rotation.
- C: The curved shape of 'C' radically changes with rotation.
- D: Similar to 'C', 'D' loses its shape upon rotation.
- E: The horizontal lines and vertical line are drastically altered by rotation.
- F: The horizontal and vertical components fundamentally change.
- G: The loops are not retained after rotation.
- J: The shape is drastically altered by rotation.
- K: The slanted lines are irreversibly changed.
- L: The vertical line and horizontal line will change orientation.
- M: The distinctive peaks are not preserved under rotation.
- P: The loop is not retained.
- Q: The tail and loop drastically change orientation.
- R: The loops and lines are irrevocably altered.
- T: The horizontal and vertical lines change orientation.
- U: The curves are not preserved.
- V: The lines change orientation.
- W: The peaks and curves are dramatically affected.
- Y: The orientation of the lines is fundamentally altered.
Influence of Font and Style:
The presence or absence of rotational symmetry can be affected by the typeface. While the letters mentioned above generally follow these rules in common fonts, highly stylized fonts can introduce exceptions. Consider a highly decorative font – the rotational symmetry might be lost or altered due to added flourishes or unique design elements.
Implications of Rotational Symmetry in Design and Art
The concept of rotational symmetry isn't just a mathematical curiosity; it plays a significant role in design and art. Understanding this property allows designers to create visually appealing and balanced compositions.
-
Logos and Branding: Many logos utilize rotational symmetry to create a sense of stability and harmony. The symmetrical nature of these logos often makes them instantly recognizable and memorable.
-
Architecture: Rotational symmetry is frequently used in architectural design, contributing to both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. Many buildings and structures incorporate this principle, showcasing its practical and artistic value.
-
Textiles and Patterns: Patterns in textiles often utilize rotational symmetry to create repeating designs. These patterns can be found in clothing, fabrics, and other decorative items. Rotational symmetry enhances the visual interest and cohesiveness of these designs.
Rotational Symmetry and Letter Recognition
While the presence of rotational symmetry doesn’t necessarily make a letter easier to recognize, it does contribute to its overall visual balance and memorability. The symmetrical nature of some letters might aid in quicker processing for individuals with certain cognitive strengths. Further research is needed to definitively establish this correlation.
Rotational Symmetry in Other Alphabets
The discussion so far has primarily focused on the English alphabet. However, the presence of rotational symmetry within letters varies significantly across different alphabets. For instance, alphabets using cursive scripts or those with vastly different letterforms might exhibit different patterns of rotational symmetry. Investigating rotational symmetry across different writing systems presents a fascinating research area in itself.
Beyond the Alphabet: Expanding the Exploration
The concept of rotational symmetry extends far beyond the letters of the alphabet. It's a fundamental concept in geometry, applicable to a vast array of shapes and objects. From snowflakes to flowers, and from molecules to man-made designs, rotational symmetry plays a crucial role in the beauty and order of the world around us. Understanding this property enhances our appreciation for the underlying patterns and structures found in nature and design.
Conclusion: Symmetry in Letters and Beyond
The investigation into rotational symmetry within the alphabet reveals a fascinating interplay between mathematics and visual design. Although not all letters possess this property, the symmetrical letters contribute to the overall visual balance and aesthetic appeal of the written language. Moreover, the concept of rotational symmetry extends beyond the alphabet, showcasing its importance across diverse fields, from design and art to the natural world itself. Understanding this concept deepens our appreciation for symmetry’s role in creating visual harmony and underlying order in numerous contexts. This exploration provides a glimpse into the rich mathematical principles woven into even the simplest elements of our everyday lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Larger A Pound Or Kilogram
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Are Characteristics Of Natural Selection Select Three Options
Mar 16, 2025
-
Why Is Melting Ice A Physical Change
Mar 16, 2025
-
Whats The Roman Numeral For 500
Mar 16, 2025
-
5 Letter Words With A Y In The Middle
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rotational Symmetry Letters Of The Alphabet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
