Prime Numbers Between 90 And 100
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
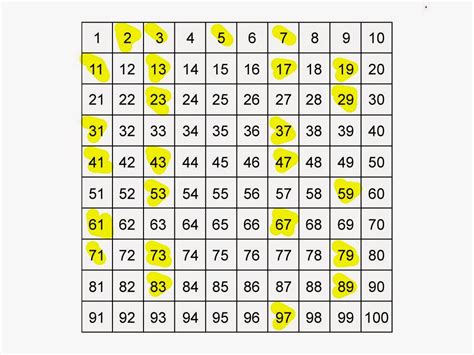
Table of Contents
Prime Numbers Between 90 and 100: A Deep Dive into the Fascinating World of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers, the fundamental building blocks of arithmetic, hold a unique fascination for mathematicians and number enthusiasts alike. Defined as whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves, they are the cornerstone of number theory and cryptography. This article delves into the intriguing subset of prime numbers found within the range of 90 to 100, exploring their properties, significance, and the broader context of prime number distribution.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before focusing on the specific range of 90 to 100, it's crucial to establish a solid understanding of prime numbers. Their defining characteristic—divisibility only by 1 and themselves—sets them apart from composite numbers, which have multiple factors. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite; it stands alone in its unique numerical identity.
Identifying Prime Numbers: Methods and Techniques
Several methods exist for identifying prime numbers. The simplest, albeit time-consuming for larger numbers, involves trial division. This method systematically tests if a number is divisible by any integer from 2 up to its square root. If no such divisor is found, the number is prime. More sophisticated algorithms, such as the Sieve of Eratosthenes, offer a more efficient approach for finding primes within a given range. The Sieve of Eratosthenes is particularly useful for identifying primes within a specified range, as we will explore later in the context of primes between 90 and 100.
The Infinitude of Primes: A Fundamental Theorem
One of the most celebrated theorems in number theory is Euclid's proof of the infinitude of primes. This theorem demonstrates that there is no largest prime number—they extend infinitely, a testament to the rich and boundless nature of number theory. This seemingly simple statement has profound implications for our understanding of the distribution and properties of these fundamental numbers. The search for ever-larger primes continues to be a driving force in computational mathematics, pushing the boundaries of computing power and algorithm design.
Prime Numbers Between 90 and 100: A Detailed Examination
Now, let's narrow our focus to the specific range of numbers between 90 and 100. This relatively small interval provides a manageable yet insightful case study for understanding prime number distribution. Let's systematically examine each number in this range to identify the primes:
- 91: Divisible by 7 (7 x 13 = 91), therefore not prime.
- 92: Divisible by 2, therefore not prime.
- 93: Divisible by 3, therefore not prime.
- 94: Divisible by 2, therefore not prime.
- 95: Divisible by 5, therefore not prime.
- 96: Divisible by 2, therefore not prime.
- 97: Only divisible by 1 and 97, therefore prime.
- 98: Divisible by 2, therefore not prime.
- 99: Divisible by 3, therefore not prime.
- 100: Divisible by 2, therefore not prime.
From this analysis, we find that 97 is the only prime number between 90 and 100. This highlights the fact that the distribution of prime numbers is not uniform; there can be significant gaps between consecutive primes.
The Significance of 97
The prime number 97, while seemingly insignificant in isolation, holds a place within the larger context of prime number distribution and mathematical exploration. Its very existence reinforces the fundamental theorem of the infinitude of primes. Its relative isolation within the range of 90 to 100 demonstrates the sometimes erratic nature of prime number spacing.
97 in Cryptography and Security
Prime numbers, especially large primes, play a vital role in modern cryptography. Algorithms like RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) rely on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors. The security of many online transactions and data encryption schemes depends on the computational intractability of this factorization problem. While 97 itself is too small for robust cryptographic applications, its existence serves as a representative example of the fundamental numbers that underpin these critical security systems.
Prime Number Distribution: Patterns and Irregularities
The distribution of prime numbers is a complex and fascinating area of mathematical research. While there is no simple formula to predict the exact location of primes, mathematicians have identified patterns and made significant progress in understanding their distribution.
The Prime Number Theorem
The Prime Number Theorem provides an asymptotic approximation of the number of primes less than or equal to a given number. This theorem offers valuable insight into the average distribution of primes, although it doesn't predict the precise location of individual primes. Understanding the Prime Number Theorem is crucial for gaining a deeper appreciation of the overall distribution of prime numbers across the number line.
Gaps Between Primes: Twin Primes and Other Patterns
The spacing between consecutive primes is highly irregular. Sometimes primes are clustered closely together, such as twin primes (pairs of primes differing by 2, like 3 and 5, or 11 and 13). Other times, there are significant gaps between primes, as exemplified by the range between 90 and 100. The study of these gaps, including the distribution of twin primes, remains an area of active research, with many unsolved problems and open questions.
The Riemann Hypothesis: A Millennium Prize Problem
The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most famous unsolved problems in mathematics, is deeply connected to the distribution of prime numbers. This hypothesis proposes a precise description of the distribution of prime numbers, and its resolution would have profound implications for our understanding of number theory and related fields. It remains one of the most challenging and sought-after results in mathematics, offering a significant prize for its successful solution.
Conclusion: The Enduring Mystery of Prime Numbers
The search for prime numbers, and the study of their distribution, continues to captivate mathematicians and computer scientists alike. While 97, the lone prime between 90 and 100, may seem like a small detail in the grand scheme of things, its existence serves as a powerful reminder of the fundamental role prime numbers play in mathematics and its applications. From the seemingly simple definition of a prime number to the complex and challenging problems surrounding their distribution, the enduring mystery and profound significance of prime numbers ensure that their study will continue to fascinate and inspire for generations to come. The solitary prime number within the range of 90 to 100 serves not as an endpoint, but as a stepping stone in the continuing exploration of these intriguing and foundational numbers. The quest to understand the distribution and properties of primes is a journey of discovery, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and computational capabilities. The simple act of identifying the single prime between 90 and 100 underscores the rich tapestry of number theory and the enduring allure of prime numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 15 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 25, 2025
-
Facilitated Diffusion And Active Transport Differ In That
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes Does A Zygote Have
Mar 25, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 4 And 7
Mar 25, 2025
-
Adjectives That Start With The Letter X
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Prime Numbers Between 90 And 100 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
