Point Where Perpendicular Bisectors Of A Triangle Intersect
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
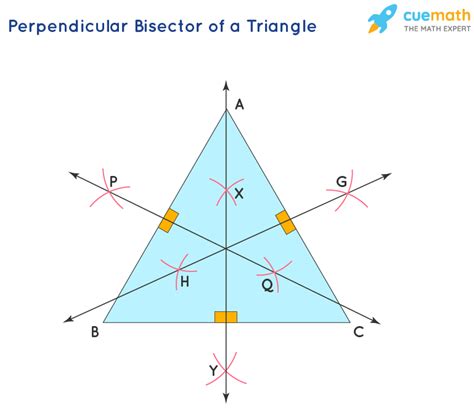
Table of Contents
The Amazing Point Where Perpendicular Bisectors Meet: The Circumcenter
The seemingly simple triangle holds a wealth of fascinating geometric properties. One particularly intriguing point within a triangle is the intersection of its perpendicular bisectors – a point with a unique name and significant mathematical implications: the circumcenter. This article delves deep into the circumcenter, exploring its definition, properties, construction, and applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of its importance in geometry.
Understanding Perpendicular Bisectors
Before diving into the circumcenter, let's establish a clear understanding of perpendicular bisectors. A perpendicular bisector of a line segment is a line that:
- Is perpendicular: It forms a right angle (90 degrees) with the line segment.
- Bisects the segment: It divides the line segment into two equal halves.
Every line segment has only one perpendicular bisector. Imagine drawing a line segment on a piece of paper. You can construct its perpendicular bisector using a compass and straightedge, a classic geometric construction technique we'll revisit later.
Defining the Circumcenter
Now, let's consider a triangle. Each side of the triangle is a line segment. Therefore, each side has its own perpendicular bisector. The remarkable fact is that these three perpendicular bisectors are concurrent, meaning they all intersect at a single point. This point of intersection is known as the circumcenter of the triangle.
In simpler terms: The circumcenter is the point where the perpendicular bisectors of the three sides of a triangle meet.
Properties of the Circumcenter
The circumcenter possesses several important properties that make it a key element in triangle geometry:
-
Equidistant from Vertices: The most crucial property is that the circumcenter is equidistant from all three vertices of the triangle. This distance is the radius of the circumcircle.
-
Circumcircle: The circumcenter is the center of the unique circle that passes through all three vertices of the triangle. This circle is called the circumcircle. Every triangle has one and only one circumcircle.
-
Location: The location of the circumcenter depends on the type of triangle:
- Acute Triangle: In an acute triangle (all angles less than 90 degrees), the circumcenter lies inside the triangle.
- Right Triangle: In a right triangle (one angle equals 90 degrees), the circumcenter lies on the midpoint of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle).
- Obtuse Triangle: In an obtuse triangle (one angle greater than 90 degrees), the circumcenter lies outside the triangle.
Constructing the Circumcenter
Constructing the circumcenter is a straightforward process using only a compass and straightedge:
-
Bisect One Side: Choose one side of the triangle and construct its perpendicular bisector. This involves using the compass to draw arcs of equal radius from each endpoint of the side, then drawing a line through the points where the arcs intersect.
-
Bisect Another Side: Repeat the process for a second side of the triangle, constructing its perpendicular bisector.
-
Point of Intersection: The point where the two perpendicular bisectors intersect is the circumcenter. While constructing the third perpendicular bisector verifies the concurrence, it's not strictly necessary to locate the circumcenter.
Applications of the Circumcenter and Circumcircle
The circumcenter and circumcircle find applications in various areas of mathematics and beyond:
-
Trigonometry: The circumradius (the distance from the circumcenter to each vertex) is used in several trigonometric formulas and identities, particularly those involving the sine rule.
-
Coordinate Geometry: The coordinates of the circumcenter can be calculated using the coordinates of the triangle's vertices through formulas derived from the perpendicular bisector equations.
-
Computer Graphics: The circumcircle is utilized in algorithms for creating smooth curves and arcs, particularly in computer-aided design (CAD) software and other graphical applications.
-
Navigation: In some navigation systems or surveying, the circumcenter of three known points can be used to determine a location.
Advanced Concepts and Related Theorems
The circumcenter's properties are interwoven with other important concepts in geometry:
-
Euler Line: In any triangle, the circumcenter, orthocenter (intersection of altitudes), and centroid (intersection of medians) are collinear. This line is known as the Euler line.
-
Nine-Point Circle: The nine-point circle is a circle that passes through nine significant points associated with a triangle, including the midpoints of the sides, the feet of the altitudes, and the midpoints of the segments connecting the vertices to the orthocenter. The circumcenter plays a role in the relationship between the nine-point circle and the circumcircle.
Practical Examples and Exercises
Let's consider a few practical examples to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: A triangle has vertices at A(1,1), B(5,1), and C(3,5). Find the coordinates of its circumcenter.
This problem involves calculating the equations of two perpendicular bisectors and finding their intersection point. The detailed solution requires solving a system of linear equations.
Example 2: Given a triangle with sides of length 6, 8, and 10, is this triangle acute, right, or obtuse? Where would its circumcenter lie?
Given that 6² + 8² = 10², this is a right-angled triangle (Pythagorean theorem). Consequently, the circumcenter lies on the midpoint of the hypotenuse (the side of length 10).
These examples illustrate how the circumcenter's properties can be applied to solve problems in coordinate geometry and triangle classification.
Conclusion: The Circumcenter's Significance in Geometry
The circumcenter, a seemingly simple point of intersection, represents a powerful concept in geometry. Its properties, its relationship to the circumcircle, and its involvement in various theorems underscore its significance. Understanding the circumcenter enriches our comprehension of triangles, offering insights into their geometric structure and facilitating the solution of numerous geometric problems. From its basic construction to its applications in advanced geometry and computer graphics, the circumcenter remains a fundamental and fascinating point within the world of triangles. Its study enhances our appreciation of the elegance and power of geometric principles. Further exploration into related theorems and concepts will only deepen this appreciation and broaden the application of this crucial geometric point.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Animal That Lays Eggs And Is Not A Bird
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Part Of The Cell Stores Water
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Sides Are In A Parallelogram
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Change A Ratio Into A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
-
Common Denominator Of 3 And 4
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Point Where Perpendicular Bisectors Of A Triangle Intersect . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
