Okasaki Fragments Would Be Found At The ____________________ Strand.
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
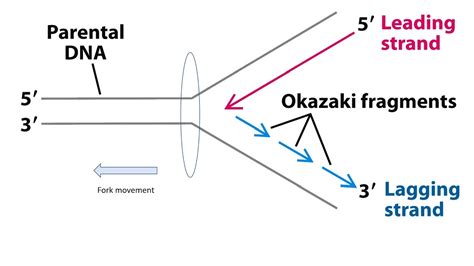
Table of Contents
Okasaki Fragments Would Be Found at the Lagging Strand
Okasaki fragments, also known as Okazaki fragments, are short, newly synthesized DNA fragments that are formed during the replication of the lagging strand of DNA. Understanding their location and the process of their creation is crucial to grasping the complexities of DNA replication. This article delves deep into the intricacies of Okazaki fragments, explaining their formation, significance, and the reasons why they are exclusively found on the lagging strand.
Understanding DNA Replication
Before diving into the specifics of Okasaki fragments, it's essential to understand the broader context of DNA replication. DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. This process is crucial for cell division, growth, and the transmission of genetic information.
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, meaning each new DNA molecule retains one strand from the original molecule and synthesizes a new complementary strand. This process takes place in several key steps:
1. Initiation:
The replication process begins at specific sites called origins of replication. These are specific nucleotide sequences where the DNA double helix unwinds, separating the two strands. Enzymes like helicases are responsible for this unwinding.
2. Unwinding and Stabilization:
Once the DNA strands separate, they form a replication fork, a Y-shaped structure where the new DNA strands are synthesized. Single-strand binding proteins (SSBs) bind to the separated strands, preventing them from reannealing and protecting them from degradation.
3. Primer Synthesis:
DNA polymerase, the enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands, cannot initiate synthesis de novo. It requires a pre-existing 3'-OH group to add nucleotides to. This is provided by an RNA primer, a short RNA sequence synthesized by an enzyme called primase.
4. Elongation:
DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides to the 3'-OH end of the RNA primer, extending the new DNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction. This is where the difference between leading and lagging strand synthesis becomes apparent.
Leading vs. Lagging Strand Synthesis: The Role of Okasaki Fragments
The DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction. This poses a challenge because the two strands of the DNA double helix are antiparallel—one runs 5' to 3', and the other runs 3' to 5'.
Leading Strand Synthesis: On the strand oriented 3' to 5' (relative to the replication fork), DNA polymerase can synthesize a continuous, new strand in the 5' to 3' direction, following the replication fork seamlessly. This continuously synthesized strand is called the leading strand.
Lagging Strand Synthesis: On the other strand, oriented 5' to 3' (relative to the replication fork), DNA polymerase cannot synthesize a continuous strand. Instead, it synthesizes short, discontinuous fragments called Okasaki fragments. These fragments are synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork. Each Okasaki fragment requires its own RNA primer.
The Formation of Okasaki Fragments: A Step-by-Step Process
-
Primer Synthesis: Primase synthesizes an RNA primer on the lagging strand.
-
Fragment Synthesis: DNA polymerase III extends the RNA primer, synthesizing a short DNA fragment (Okasaki fragment) in the 5' to 3' direction.
-
Primer Removal: After a few Okasaki fragments are synthesized, DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primers.
-
Gap Filling: DNA polymerase I fills the gaps left by the removed primers with DNA nucleotides.
-
Ligation: DNA ligase joins the adjacent Okasaki fragments, creating a continuous lagging strand.
Why Okasaki Fragments are Exclusively Found on the Lagging Strand
The fundamental reason for the exclusive presence of Okasaki fragments on the lagging strand lies in the inherent directionality of DNA polymerase. Since DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in the 5' to 3' direction, it can only continuously synthesize the leading strand which is oriented 3' to 5' relative to the replication fork. On the lagging strand (5' to 3' relative to the replication fork), continuous synthesis is impossible. The discontinuous synthesis resulting in the production of Okasaki fragments is a necessary adaptation to overcome this directional constraint.
The Significance of Okasaki Fragments
Okasaki fragments are not simply a byproduct of the replication process; they are integral to its successful completion. Their discontinuous synthesis allows for the replication of both strands simultaneously, even though DNA polymerase can only synthesize in one direction. The efficient processing and joining of these fragments ensures the faithful replication of the entire genome. Errors in the formation, processing, or ligation of Okasaki fragments can lead to mutations and genomic instability.
Okasaki Fragments and DNA Replication Fidelity
The process of Okasaki fragment synthesis and processing involves multiple enzymes and proteins, each contributing to the overall fidelity of DNA replication. The removal of RNA primers and the filling of the resulting gaps by DNA polymerase I are crucial steps in ensuring the accuracy of the newly synthesized DNA. DNA ligase plays a vital role in joining the fragments seamlessly, preventing gaps and ensuring the integrity of the lagging strand. Any errors in these steps can result in mutations that can have severe consequences.
Clinical Significance and Research Implications
Research on Okasaki fragments continues to provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of DNA replication and its fidelity. Understanding the complexities of Okasaki fragment processing is crucial for developing effective treatments for genetic disorders and cancer. Disruptions in Okasaki fragment processing can contribute to genomic instability, which is a hallmark of many cancers. Therefore, studying the mechanisms regulating Okasaki fragment formation, processing, and ligation could potentially lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting cancer cells.
Evolutionary Considerations of Okasaki Fragments
The existence of Okasaki fragments is a testament to the elegance and efficiency of biological systems. This discontinuous method of lagging strand synthesis, though seemingly complex, allows for the simultaneous replication of both DNA strands, maximizing the speed and efficiency of the process. The evolution of this mechanism is a testament to natural selection favoring mechanisms that optimize the replication of genetic material, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information across generations. The conserved nature of the enzymes and proteins involved in Okasaki fragment processing across diverse species indicates their fundamental importance in DNA replication.
Conclusion: Okasaki Fragments - A Cornerstone of DNA Replication
In conclusion, Okasaki fragments are indispensable components of DNA replication, specifically found on the lagging strand. Their formation is a direct consequence of the inherent directionality of DNA polymerase, which necessitates a discontinuous synthesis mechanism on the lagging strand. The meticulous processing and joining of these fragments are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of the newly synthesized DNA molecule. Continued research on Okasaki fragments promises to further illuminate the intricacies of DNA replication and provide valuable insights into various biological processes and diseases. Understanding these fragments solidifies our comprehension of the fundamental mechanisms that underpin life itself. Their presence on the lagging strand is not just a consequence of biochemistry; it's a testament to the efficiency and elegance of the machinery of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 48 Inches
Mar 04, 2025
-
How To Find The Perimeter Of A Parallelogram
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Rectangle Have
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is Correct
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 121
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Okasaki Fragments Would Be Found At The ____________________ Strand. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
