Negative Ions Have _______________________________ Protons Than Electrons.
Juapaving
May 24, 2025 · 5 min read
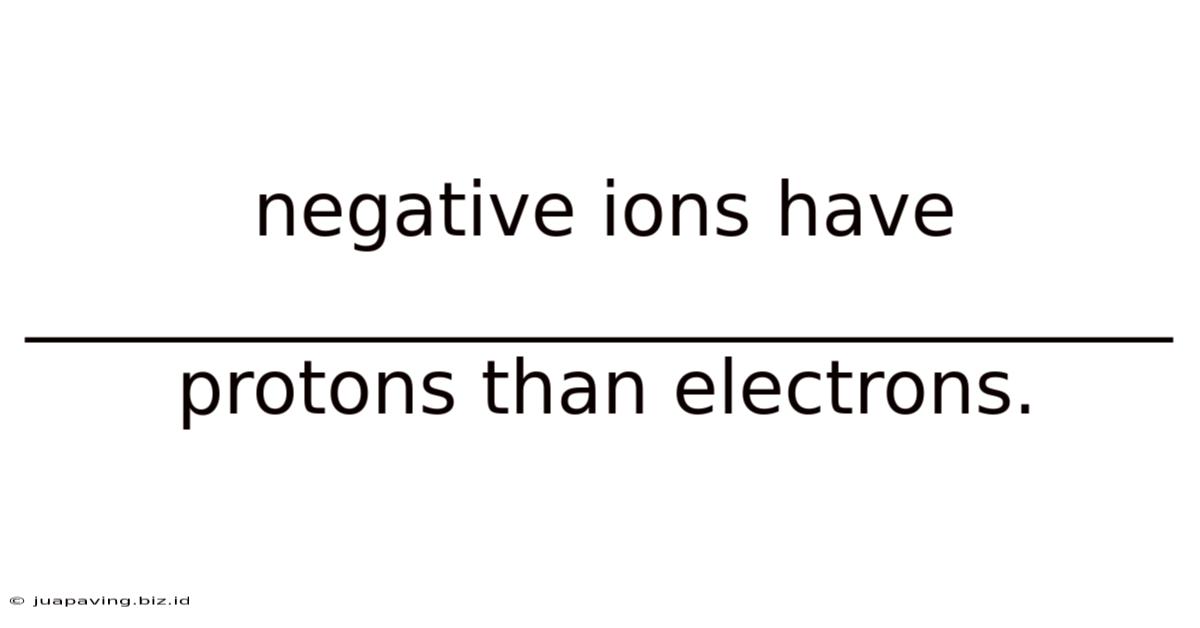
Table of Contents
Negative Ions Have More Electrons Than Protons
Negative ions, often touted for their potential health benefits, are atoms or molecules that carry a negative charge. This negative charge arises from an imbalance between the number of protons and electrons within the atom or molecule. Crucially, negative ions have more electrons than protons. This fundamental characteristic is what distinguishes them from positive ions (cations) and neutral atoms. Understanding this difference is key to grasping their properties and potential impacts.
The Fundamentals of Atomic Structure
Before delving into the specifics of negative ions, let's refresh our understanding of basic atomic structure. Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, composed of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element (e.g., an atom with one proton is hydrogen, with two is helium, and so on).
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also located in the atom's nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels. Their number typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
In a neutral atom, the positive charge of the protons is exactly balanced by the negative charge of the electrons, resulting in a net charge of zero. However, atoms can gain or lose electrons, disrupting this balance and creating ions.
Ionization: The Creation of Ions
Ionization is the process by which an atom or molecule acquires a net electrical charge by gaining or losing electrons. When an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called a negative ion or anion. Conversely, when an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a positive ion or cation.
Mechanisms of Ionization
Several processes can lead to the formation of negative ions:
-
Electron Attachment: This is the most common mechanism. A neutral atom attracts a free electron, becoming negatively charged. The strength of this attraction depends on the atom's electron affinity – its ability to attract and bind an extra electron. Atoms with high electron affinities are more likely to form negative ions.
-
Chemical Reactions: Many chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or molecules. If an atom gains electrons during a reaction, it forms a negative ion. Examples include the formation of ionic compounds like sodium chloride (NaCl), where chlorine gains an electron from sodium.
-
Radiation: Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as X-rays or gamma rays, can knock electrons out of atoms, leading to the formation of both positive and negative ions. The freed electrons can then attach to other neutral atoms, forming negative ions.
Properties of Negative Ions
The extra electrons in a negative ion significantly affect its properties compared to its neutral counterpart:
-
Increased Size: The addition of electrons increases the electron cloud's size, making the negative ion larger than the neutral atom.
-
Chemical Reactivity: Negative ions are often more reactive than their neutral counterparts due to the presence of the extra electrons. This increased reactivity can influence their participation in chemical reactions and their interactions with other molecules.
-
Electrical Conductivity: Solutions containing negative ions can conduct electricity because the negatively charged ions can move freely and carry an electrical current.
-
Interaction with Electric and Magnetic Fields: Because negative ions carry a charge, they interact with electric and magnetic fields. This interaction is exploited in various scientific instruments and techniques.
Negative Ions and Their Significance
The presence and concentration of negative ions play a crucial role in various natural phenomena and technological applications:
-
Atmospheric Ions: The Earth's atmosphere naturally contains both positive and negative ions. Negative ions are often generated near waterfalls, oceans, and forests due to the breaking of water molecules and interactions with air molecules. These atmospheric ions can affect weather patterns and air quality.
-
Industrial Applications: Negative ions are used in various industrial processes, including air purification, electrostatic precipitators for removing particulate matter from industrial exhaust gases, and in some manufacturing techniques.
-
Health and Wellness: Negative ions have been associated with several potential health benefits, although the scientific evidence remains somewhat controversial. Some studies suggest that exposure to negative ions can improve mood, reduce stress, and enhance respiratory function. However, more rigorous research is needed to definitively confirm these claims and establish optimal exposure levels.
Misconceptions about Negative Ions
While negative ions are a fascinating area of study, several misconceptions surround them. It’s vital to distinguish scientific fact from speculation:
-
"Negative ion generators" and their effectiveness: Many commercially available "negative ion generators" claim to significantly improve air quality and health. However, the actual ion concentrations produced by these devices are often significantly lower than those found naturally in environments like forests or near waterfalls. The effectiveness of these devices in improving health is not definitively proven.
-
Overly simplified explanations: It’s important to understand that the effects of negative ions are complex and involve interactions with various biological systems. Simply stating that "negative ions are good for you" is an oversimplification.
Conclusion
Negative ions, with their characteristic excess of electrons compared to protons, are fundamental components of matter with diverse properties and roles. Their formation through ionization processes, their involvement in atmospheric phenomena, and their potential applications in various fields highlight their importance in both natural and human-made environments. While ongoing research explores their potential health implications, it's crucial to approach claims about their therapeutic effects with a healthy dose of skepticism, relying instead on well-designed scientific studies for reliable information. The exploration of negative ions remains an exciting area of scientific investigation, continuously revealing new insights into their behavior and impact on the world around us. As our understanding advances, we can expect more refined applications of these fundamental particles in various fields, bringing about new advancements and technologies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Four Major Types Of Enterprise Applications Are
May 24, 2025
-
Summary Chapter 26 To Kill A Mockingbird
May 24, 2025
-
When A Sailor Is Undecided About Remaining In The Navy
May 24, 2025
-
Chapter 12 Summary Of The Scarlet Letter
May 24, 2025
-
Summary Of Act 3 Scene 2 Julius Caesar
May 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Negative Ions Have _______________________________ Protons Than Electrons. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.