Name Two Quadrilaterals That Have Four Right Angles
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
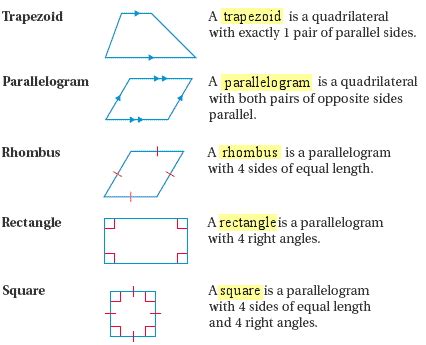
Table of Contents
Name Two Quadrilaterals That Have Four Right Angles: A Deep Dive into Squares and Rectangles
Squares and rectangles are two fundamental shapes in geometry, both distinguished by their possession of four right angles. While seemingly simple, understanding the nuances of their definitions, properties, and applications reveals a surprising depth of mathematical richness. This comprehensive article delves into the characteristics of squares and rectangles, comparing and contrasting them, and exploring their significance in various fields.
Defining Squares and Rectangles: A Closer Look
Before we explore the similarities and differences, let's clearly define each quadrilateral.
What is a Square?
A square is a two-dimensional geometric shape that is both a quadrilateral (a four-sided polygon) and a regular polygon. This means it possesses the following key characteristics:
- Four equal sides: All four sides of a square are of equal length.
- Four right angles: Each of the four interior angles measures exactly 90 degrees.
- Parallel sides: Opposite sides of a square are parallel to each other.
- Equal diagonals: The diagonals of a square are equal in length and bisect each other at a 90-degree angle.
- Symmetry: A square exhibits both rotational and reflectional symmetry.
These properties make the square a highly symmetrical and stable shape, frequently utilized in construction and design.
What is a Rectangle?
A rectangle is also a four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) but, unlike a square, it doesn't necessarily have equal sides. Its defining characteristics are:
- Four right angles: Like a square, all four interior angles measure 90 degrees.
- Opposite sides are equal and parallel: Opposite sides of a rectangle have equal lengths and are parallel to each other.
- Diagonals bisect each other: The diagonals of a rectangle intersect at their midpoints, dividing each other into two equal segments.
The rectangle is less symmetrical than a square, as it lacks the equal side length constraint. This allows for a greater variety of shapes within the rectangle family.
Comparing Squares and Rectangles: Similarities and Differences
Both squares and rectangles belong to a broader family of quadrilaterals known as parallelograms. Parallelograms are characterized by having opposite sides that are both parallel and equal in length. However, squares and rectangles possess additional properties that distinguish them from other parallelograms and from each other.
Here's a table summarizing the key similarities and differences:
| Feature | Square | Rectangle |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Sides | 4 | 4 |
| Angles | Four 90-degree angles | Four 90-degree angles |
| Side Lengths | All four sides are equal | Opposite sides are equal, adjacent sides may differ |
| Diagonals | Equal in length, bisect at 90 degrees | Equal in length, bisect each other |
| Parallel Sides | Opposite sides are parallel | Opposite sides are parallel |
| Symmetry | High rotational and reflectional symmetry | Reflectional symmetry across diagonals |
As you can see, the crucial difference lies in the length of the sides. A square is a special case of a rectangle where all four sides are equal. Every square is a rectangle, but not every rectangle is a square.
Applications of Squares and Rectangles in Real Life
The prevalence of squares and rectangles in our daily lives is undeniable. Their geometric properties make them ideally suited for various applications across numerous fields:
Architecture and Construction:
- Building foundations and structures: The stability and rigidity of squares and rectangles make them essential for constructing strong and stable buildings. Rooms are typically rectangular, providing efficient use of space.
- Window and door frames: The right angles and straight lines of rectangles are perfectly suited for creating windows and doors.
- Floor tiles and bricks: The consistent dimensions of square and rectangular tiles and bricks simplify construction and provide a visually appealing pattern.
Design and Art:
- Graphic design: Squares and rectangles are fundamental elements in graphic design, used for layouts, images, and text boxes.
- Painting and sculpture: These shapes provide a foundational structure for compositions in both two- and three-dimensional art.
- Packaging: Rectangular boxes are efficient for packaging and shipping.
Engineering and Technology:
- Electronics and circuit boards: The precise angles and dimensions of squares and rectangles are crucial for the design of electronic components and circuit boards.
- Robotics: Rectangular and square components are commonly found in robotic structures and mechanisms.
- Computer graphics: Squares and rectangles form the basis of many computer-generated images and animations.
Everyday Objects:
- Books and papers: Rectangular shapes are commonly found in everyday objects such as books, papers, and screens.
- Tables and desks: The stability and practicality of rectangular surfaces are ideal for furniture design.
- Photographs and digital images: Many photographs and digital images are displayed in rectangular formats.
The examples above only scratch the surface of the myriad ways squares and rectangles are utilized. Their simple yet robust geometric properties ensure their continued significance in our world.
Exploring Deeper Mathematical Concepts Related to Squares and Rectangles
Beyond their basic definitions and applications, squares and rectangles provide a gateway to exploring more advanced mathematical concepts:
Area and Perimeter:
Calculating the area and perimeter of squares and rectangles is fundamental.
- Square: Area = side²; Perimeter = 4 * side
- Rectangle: Area = length * width; Perimeter = 2 * (length + width)
These formulas are essential for practical applications, such as determining the amount of material needed for construction or calculating the dimensions of a room.
Pythagorean Theorem:
The Pythagorean Theorem (a² + b² = c²) is directly applicable to squares and rectangles, particularly when dealing with diagonals. In a rectangle, the diagonal forms the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle, allowing us to calculate the length of the diagonal if we know the lengths of the sides. This principle is crucial in various engineering and construction applications.
Coordinate Geometry:
Squares and rectangles can be easily represented using coordinate geometry. Understanding how to plot points and find equations for lines and shapes in a coordinate system allows us to perform geometric calculations more efficiently.
Transformations:
Exploring the geometric transformations (translation, rotation, reflection, dilation) that can be applied to squares and rectangles provides valuable insights into their symmetry and properties. This concept is vital in computer graphics and animation.
Advanced Applications and Theoretical Considerations
The applications of squares and rectangles extend far beyond the everyday examples mentioned earlier. They play a significant role in:
- Tessellations: Squares and rectangles are excellent examples of shapes that can tessellate (tile a plane without gaps or overlaps). This property is used in various contexts, from floor coverings to artistic designs.
- Fractals: Iterative processes using squares and rectangles can generate complex fractal patterns, highlighting the inherent mathematical complexity even within seemingly simple shapes.
- Vector Spaces: In linear algebra, understanding vectors and their operations often involves the use of rectangular coordinate systems.
The seemingly simple shapes of squares and rectangles unlock doors to advanced mathematical concepts. Their properties and relationships contribute to the richness and breadth of geometric understanding, paving the way for exploration in various mathematical disciplines.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Squares and Rectangles
Squares and rectangles, despite their apparent simplicity, are shapes of profound significance. Their four right angles and specific side length relationships lead to a wealth of properties, applications, and mathematical explorations. Their widespread use in architecture, design, engineering, and countless other fields is a testament to their utility and fundamental role in shaping our world. Understanding their characteristics and relationships contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of geometry and its relevance in various disciplines. The journey from basic definitions to advanced applications reveals the surprising depth and enduring significance of these foundational geometric shapes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 6 8 And 12
Mar 24, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 28 And 24
Mar 24, 2025
-
Why Doesnt The Moon Fall To The Earth
Mar 24, 2025
-
Examples Of Kinetic Energy In Everyday Life
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Two Organelles Are Found In Plant Cells Only
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Name Two Quadrilaterals That Have Four Right Angles . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
