Molar Mass Of Pb No3 2
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
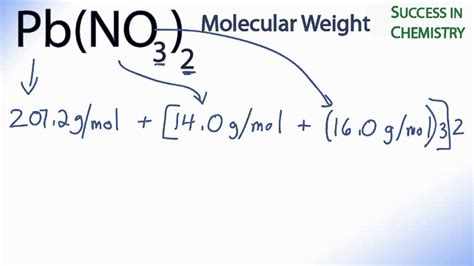
Table of Contents
Determining the Molar Mass of Lead(II) Nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂)
Lead(II) nitrate, a crystalline white powder with the chemical formula Pb(NO₃)₂, is a significant compound in various applications, from laboratory reagents to industrial processes. Understanding its molar mass is crucial for accurate stoichiometric calculations and quantitative analysis in chemistry. This article comprehensively explores the calculation and significance of the molar mass of Pb(NO₃)₂, incorporating essential concepts of atomic mass, molar mass, and the implications in various chemical contexts.
Understanding Molar Mass
Before delving into the specifics of lead(II) nitrate, let's establish a foundational understanding of molar mass. Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole, a fundamental unit in chemistry, represents Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). Therefore, the molar mass expresses the mass of 6.022 x 10²³ formula units of a substance in grams.
The molar mass of an element is numerically equivalent to its atomic weight (atomic mass) found on the periodic table. For example, the atomic weight of carbon (C) is approximately 12.01, so the molar mass of carbon is 12.01 g/mol. For compounds, the molar mass is the sum of the molar masses of all the atoms present in the chemical formula.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Pb(NO₃)₂
To calculate the molar mass of lead(II) nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂), we need to consider the atomic masses of its constituent elements: lead (Pb), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O). These values are readily available on a periodic table.
- Lead (Pb): The atomic weight of lead is approximately 207.2 g/mol.
- Nitrogen (N): The atomic weight of nitrogen is approximately 14.01 g/mol.
- Oxygen (O): The atomic weight of oxygen is approximately 16.00 g/mol.
Step-by-step calculation:
-
Identify the number of atoms of each element: In one formula unit of Pb(NO₃)₂, we have:
- 1 lead (Pb) atom
- 2 nitrogen (N) atoms (from two nitrate ions, NO₃⁻)
- 6 oxygen (O) atoms (3 oxygen atoms per nitrate ion x 2 nitrate ions)
-
Calculate the mass contribution of each element:
- Lead: 1 Pb atom x 207.2 g/mol = 207.2 g/mol
- Nitrogen: 2 N atoms x 14.01 g/mol = 28.02 g/mol
- Oxygen: 6 O atoms x 16.00 g/mol = 96.00 g/mol
-
Sum the individual contributions: Add the mass contributions from each element to obtain the molar mass of Pb(NO₃)₂:
207.2 g/mol (Pb) + 28.02 g/mol (N) + 96.00 g/mol (O) = 331.22 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of lead(II) nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂) is approximately 331.22 g/mol.
Significance of Molar Mass in Chemical Calculations
The molar mass of Pb(NO₃)₂ is a critical value in a variety of chemical calculations, including:
1. Stoichiometry:
Stoichiometry deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. Knowing the molar mass allows you to convert between mass and moles of Pb(NO₃)₂, essential for determining reactant amounts, limiting reactants, theoretical yields, and percent yields.
Example: Consider a reaction where you need to react 10 grams of Pb(NO₃)₂ with another substance. Using the molar mass (331.22 g/mol), you can convert the mass of Pb(NO₃)₂ to moles:
10 g Pb(NO₃)₂ × (1 mol Pb(NO₃)₂ / 331.22 g Pb(NO₃)₂) = 0.0302 moles Pb(NO₃)₂
This conversion is crucial for determining the stoichiometric relationships in the reaction.
2. Solution Concentration:
Molar mass is fundamental when preparing solutions of known concentrations, particularly molarity (moles of solute per liter of solution). If you need to prepare a 0.1 M solution of Pb(NO₃)₂, you'll use the molar mass to calculate the required mass of Pb(NO₃)₂ to dissolve in a specific volume of solvent.
3. Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas:
In analytical chemistry, molar mass plays a significant role in determining the empirical and molecular formulas of unknown compounds. By combining molar mass data with elemental composition analysis (e.g., combustion analysis), the molecular formula can be established.
4. Titrations:
In titrations, where a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution, molar mass is critical for calculating the concentration of the unknown based on the volume of titrant used.
Applications of Lead(II) Nitrate
Understanding the molar mass of Pb(NO₃)₂ is critical because of its diverse applications:
- Laboratory Reagent: Pb(NO₃)₂ is commonly used in chemistry laboratories as a source of lead ions for various experiments, including synthesis and qualitative analysis.
- Industrial Applications: It finds applications in the production of lead-based pigments, explosives, and matches.
- Photography: Historically, it has been used in photography.
- Electroplating: It serves as an electrolyte in lead electroplating processes.
Safety Precautions
Lead(II) nitrate is toxic and should be handled with care. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves and eye protection, when working with this compound. Avoid inhalation and skin contact. Proper disposal according to local regulations is crucial to prevent environmental contamination.
Conclusion
The accurate determination of the molar mass of Pb(NO₃)₂ (331.22 g/mol) is crucial for numerous chemical calculations and understanding its role in various applications. From stoichiometry and solution preparation to analytical chemistry and industrial processes, the molar mass serves as a fundamental parameter for quantitative analyses. Remember that handling this compound requires careful attention to safety guidelines due to its toxicity. This in-depth understanding empowers chemists and other professionals to work safely and effectively with lead(II) nitrate in various contexts. Always consult reliable resources like chemistry textbooks and reputable online sources for further information and safety procedures.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
420 Degrees To Radians In Simplest Form
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Advantage Of Sexual Reproduction Over Asexual Reproduction
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Molecular Mass Of Kno3
May 09, 2025
-
The Two Sides Of Dna Are Held Together By
May 09, 2025
-
Three Main Parts Of A Seed
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Molar Mass Of Pb No3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.