Molar Mass Of Mg Oh 2
Juapaving
May 14, 2025 · 5 min read
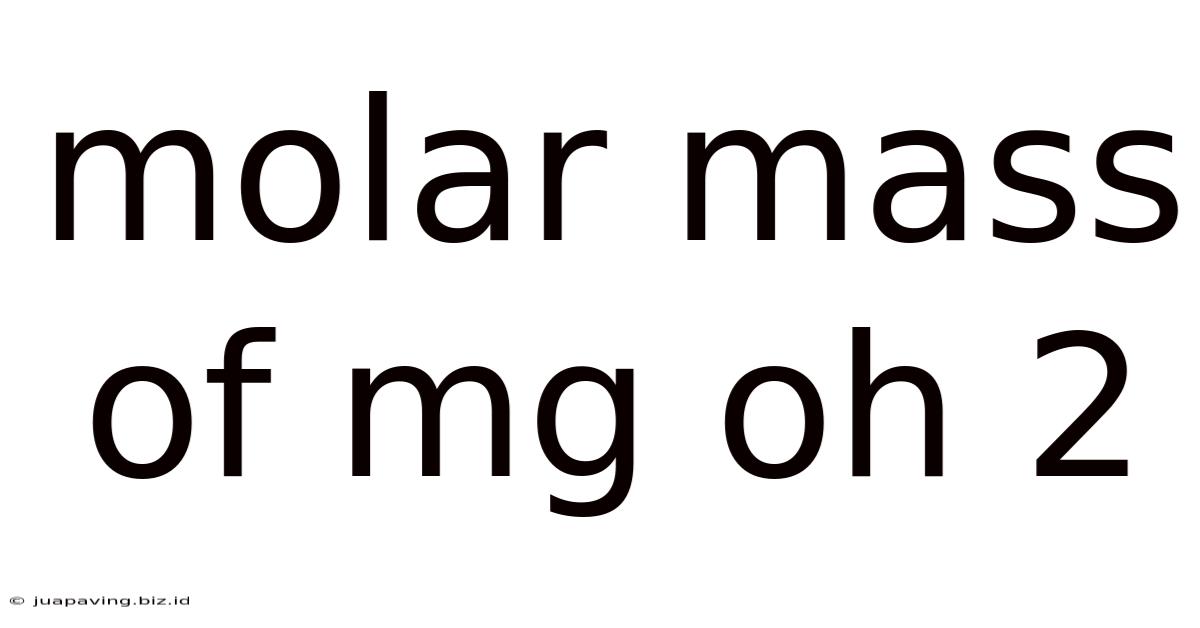
Table of Contents
Understanding the Molar Mass of Mg(OH)₂: A Comprehensive Guide
Magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)₂, is a common inorganic compound with numerous applications, from antacids to wastewater treatment. Understanding its molar mass is crucial for various chemical calculations and applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of calculating and utilizing the molar mass of Mg(OH)₂, exploring its significance in stoichiometry, solution preparation, and various chemical processes.
What is Molar Mass?
Before diving into the specifics of Mg(OH)₂, let's establish a clear understanding of molar mass. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry, representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). The molar mass is numerically equivalent to the atomic weight or molecular weight of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Calculating the Molar Mass of Mg(OH)₂
Calculating the molar mass of Mg(OH)₂ involves adding the atomic masses of its constituent elements, considering the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
-
Identify the elements: Mg(OH)₂ contains Magnesium (Mg), Oxygen (O), and Hydrogen (H).
-
Determine the number of atoms of each element: There is one Magnesium atom (Mg), two Oxygen atoms (O), and two Hydrogen atoms (H).
-
Find the atomic masses: Refer to a periodic table to obtain the atomic masses of each element. These values are typically given in atomic mass units (amu) or grams per mole (g/mol). The approximate atomic masses are:
- Magnesium (Mg): 24.31 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1.01 g/mol
-
Calculate the molar mass: Multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element present in the molecule, and then sum up the results:
Molar Mass of Mg(OH)₂ = (1 × Atomic Mass of Mg) + (2 × Atomic Mass of O) + (2 × Atomic Mass of H) Molar Mass of Mg(OH)₂ = (1 × 24.31 g/mol) + (2 × 16.00 g/mol) + (2 × 1.01 g/mol) Molar Mass of Mg(OH)₂ = 24.31 g/mol + 32.00 g/mol + 2.02 g/mol Molar Mass of Mg(OH)₂ ≈ 58.33 g/mol
Applications of Molar Mass of Mg(OH)₂
The molar mass of Mg(OH)₂ is a cornerstone in various chemical calculations and applications. Here are some key examples:
1. Stoichiometric Calculations:
In chemical reactions, the molar mass allows for the conversion between mass and moles. This is crucial for determining the quantities of reactants and products involved in a reaction. For instance, if you know the mass of Mg(OH)₂ reacting, you can calculate the number of moles using the molar mass (moles = mass / molar mass). This is fundamental in solving stoichiometry problems.
2. Solution Preparation:
Preparing solutions of a specific concentration requires precise calculations. Knowing the molar mass of Mg(OH)₂ is essential for making solutions with known molarity (moles per liter). For instance, to prepare a 1 M solution of Mg(OH)₂, you would need to dissolve 58.33 grams of Mg(OH)₂ in 1 liter of solvent.
3. Titrations:
In acid-base titrations, where Mg(OH)₂ might act as a base, the molar mass is crucial for determining the concentration of an unknown acid solution. By knowing the mass or volume of Mg(OH)₂ used to neutralize the acid, you can calculate the concentration of the acid using the stoichiometry of the reaction and the molar mass of Mg(OH)₂.
4. Industrial Applications:
The molar mass is vital in various industrial applications involving Mg(OH)₂. For example, in the production of magnesium-based materials, precise control over the amounts of reactants necessitates accurate molar mass calculations. Similarly, in wastewater treatment where Mg(OH)₂ is used for neutralizing acidic effluents, knowing the molar mass is essential for calculating the required amount to achieve the desired pH.
5. Pharmaceutical Applications:
In pharmaceutical applications, the accurate determination of Mg(OH)₂ content in formulations is crucial for efficacy and safety. The molar mass plays a vital role in quality control and dosage calculations.
Beyond the Basics: Factors Affecting Molar Mass
While the calculated molar mass of Mg(OH)₂ (58.33 g/mol) is a close approximation, it's important to acknowledge factors that can subtly affect the actual value:
-
Isotopic Abundance: The atomic masses used in the calculation are weighted averages of the isotopes of each element. The natural abundance of isotopes can vary slightly, influencing the overall molar mass.
-
Experimental Error: Experimental measurements of atomic masses always have inherent uncertainties. These uncertainties will propagate through the molar mass calculation.
-
Impurities: If the Mg(OH)₂ sample is not pure, but contains impurities, the measured molar mass will deviate from the theoretical value.
Importance of Accurate Molar Mass Determination
Accurate molar mass determination is paramount for:
-
Reliable Chemical Calculations: Inaccurate molar masses lead to errors in stoichiometric calculations, solution preparation, and other chemical processes.
-
Product Quality Control: In industrial settings, accurate molar mass determination ensures consistent product quality and reproducibility.
-
Scientific Research: Accurate molar mass data is crucial for reliable scientific research and the development of new materials and processes.
-
Safety and Efficacy: In pharmaceutical applications, accurate molar mass determination ensures product safety and efficacy.
Conclusion:
The molar mass of Mg(OH)₂, approximately 58.33 g/mol, is a fundamental quantity in numerous chemical and industrial applications. Understanding how to calculate and utilize this value accurately is crucial for successful chemical operations, from basic stoichiometry to sophisticated industrial processes. While the calculated value is a close approximation, factors like isotopic abundance and sample purity can introduce slight variations. Maintaining precision in molar mass determination ensures accuracy in various scientific and industrial contexts, ultimately contributing to the development of safe and effective products and processes. By consistently applying this knowledge, chemists and engineers can achieve reliable results and contribute to advancement in diverse fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Number In Words From 1 To 100
May 14, 2025
-
What Is 96 Inches In Feet
May 14, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 35 Out Of 40
May 14, 2025
-
Electricity Is Measured In What Unit
May 14, 2025
-
Is A Pencil A Conductor Or Insulator
May 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Molar Mass Of Mg Oh 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.