Minimum Wage Is An Example Of
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
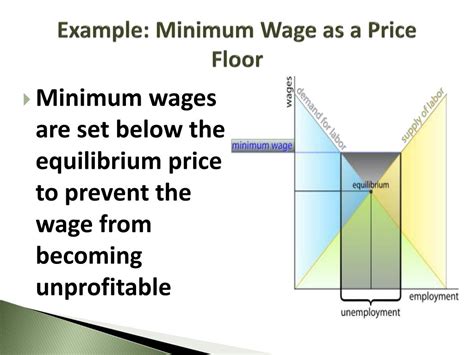
Table of Contents
Minimum Wage: An Example of Market Intervention, Social Policy, and Economic Debate
Minimum wage laws, mandating a minimum hourly wage for employees, are a complex and multifaceted topic, serving as a potent example of the intersection of market economics, social policy, and political ideology. They're not simply a matter of setting a number; they are a battleground for competing economic theories and deeply held beliefs about the role of government in society. This article delves into the various aspects of minimum wage, examining its effects on employment, income inequality, and the broader economy, while exploring the arguments for and against its implementation.
Minimum Wage as Market Intervention
At its core, minimum wage legislation is a direct intervention in the free market. In a perfectly competitive market, wages are determined by the interaction of supply and demand. The supply of labor is determined by the number of workers willing and able to work at a given wage, while the demand for labor is determined by employers' willingness to hire at that wage. The equilibrium wage, where supply equals demand, is the market-clearing wage.
Minimum wage laws, however, artificially raise the minimum wage above this market-clearing level. This creates a price floor, meaning that wages cannot fall below the mandated minimum. This intervention has several potential consequences:
Surplus of Labor (Unemployment)
When the minimum wage is set above the equilibrium wage, the quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity of labor demanded. This creates a surplus of labor, often manifesting as increased unemployment, particularly among low-skilled workers whose productivity might not justify the higher wage. Empirical evidence on the impact of minimum wage on unemployment is mixed, with some studies finding a significant negative effect, especially amongst young and less-skilled workers, and others showing little or no effect. The magnitude of the effect often depends on factors like the size of the minimum wage increase, the local economic conditions, and the elasticity of labor demand.
Reduced Hiring
Employers, facing higher labor costs, may respond to the minimum wage by hiring fewer workers or delaying hiring decisions. This is particularly true for small businesses with tighter margins, which may find it more difficult to absorb the increased labor costs. This reduction in hiring can disproportionately affect young people and those entering the workforce.
Increased Labor Costs and Prices
The increased labor costs associated with minimum wage hikes can lead to higher prices for goods and services. Businesses may pass on these increased costs to consumers to maintain profitability, contributing to inflation. The extent to which this occurs depends on factors like the elasticity of demand for the goods and services produced by the affected businesses.
Minimum Wage as Social Policy
Beyond its purely economic aspects, minimum wage is also a significant piece of social policy. It's often viewed as a means to:
Reduce Poverty and Income Inequality
Proponents of minimum wage argue that it helps to alleviate poverty and reduce income inequality by ensuring that low-wage workers earn a living wage. A living wage is defined as the minimum income necessary to meet basic needs, such as food, shelter, and clothing. While minimum wage doesn't always guarantee a living wage, it can provide a crucial safety net for low-income families. However, critics argue that minimum wage increases may not significantly impact poverty if it leads to job losses or reduced working hours.
Improve Worker Morale and Productivity
A higher minimum wage can improve worker morale and productivity. Workers who feel fairly compensated are more likely to be motivated and engaged in their work. This increased productivity can, in turn, benefit businesses by improving efficiency and reducing employee turnover.
Promote Social Justice and Economic Fairness
Minimum wage is often framed as a matter of social justice and economic fairness. It reflects a societal commitment to ensuring a basic standard of living for all workers, preventing exploitation, and reducing the disparity between the rich and the poor.
Minimum Wage: The Ongoing Economic Debate
The economic effects of minimum wage remain a subject of ongoing debate among economists. There's no single, universally accepted conclusion on its overall impact. The debate often revolves around:
Elasticity of Labor Demand
A key factor influencing the impact of minimum wage is the elasticity of labor demand. If labor demand is inelastic (meaning it doesn't change much in response to wage changes), the impact of a minimum wage increase on employment will be relatively small. Conversely, if labor demand is elastic (meaning it changes significantly in response to wage changes), the impact on employment will be more substantial.
Substitution Effects
Minimum wage increases can lead to substitution effects. Employers might substitute capital (machinery, technology) for labor to reduce their labor costs. This can lead to job losses in the long run.
Spillover Effects
Minimum wage increases in one sector can have spillover effects on other sectors. For instance, if wages rise in the fast-food industry, employers in other low-wage sectors may also face pressure to increase wages to remain competitive.
Productivity Impacts
Some argue that a higher minimum wage can incentivize businesses to invest in productivity-enhancing technologies and improve worker training, offsetting the increased labor costs.
Alternative Perspectives on Minimum Wage
Beyond the traditional supply-and-demand analysis, several alternative perspectives offer additional insights into the impact of minimum wage laws:
Efficiency Wages
The efficiency wage theory suggests that paying workers above the market-clearing wage can increase productivity by reducing employee turnover, improving morale, and attracting higher-quality workers. This could offset some of the negative employment effects associated with minimum wage increases.
Bargaining Power
Minimum wage can be viewed as a way to enhance the bargaining power of low-wage workers, especially in industries where unions are weak or non-existent. A minimum wage floor provides a baseline for negotiation and can prevent exploitation.
Conclusion: A nuanced view of Minimum Wage
Minimum wage laws represent a complex interplay of economic theory and social policy. While they can offer a crucial safety net for low-wage workers and promote social justice, their impact on employment and the broader economy remains a subject of debate. The effectiveness of minimum wage policies often depends on various factors, including the size of the increase, the local economic context, and the elasticity of labor demand. A nuanced understanding requires considering both the potential benefits and drawbacks, recognizing the lack of a single, universally applicable answer to the question of optimal minimum wage levels. The ongoing discussion necessitates further research and careful consideration of the specific economic and social context in which minimum wage laws are implemented. Moreover, alternative approaches, such as strengthening unions, promoting skills development, and investing in social safety nets, can be considered alongside or in conjunction with minimum wage policies to address income inequality and improve worker well-being. Ultimately, determining the appropriate minimum wage necessitates a balanced approach that weighs economic efficiency with social equity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Force Increase On An Inclined Plane
May 09, 2025
-
Interesting Words That Start With V
May 09, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast A Light Microscope And An Electron Microscope
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 6 25 Meters In Feet And Inches
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Are In 50 Millimeters
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Minimum Wage Is An Example Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.