Lowest Common Multiple Of 9 And 8
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
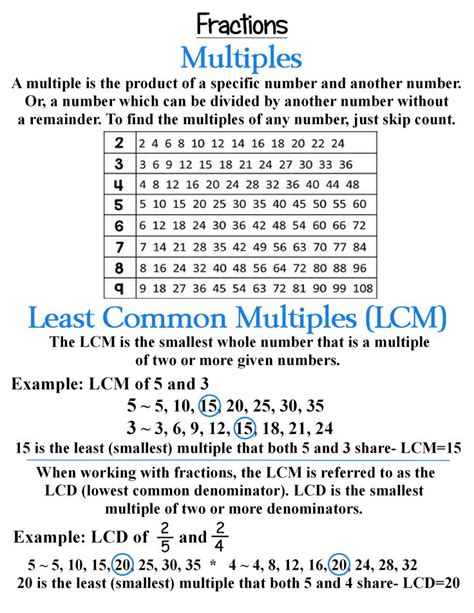
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of the Lowest Common Multiple: A Deep Dive into LCM(9, 8)
Finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding its underlying principles unlocks a world of mathematical elegance and practical applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of calculating the LCM of 9 and 8, exploring various methods and highlighting the significance of this fundamental concept in diverse fields.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What is LCM?
The lowest common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers without leaving a remainder. It's a cornerstone of number theory and finds widespread use in various mathematical operations, problem-solving, and real-world applications. Think of it as finding the smallest number that neatly accommodates multiples of all the numbers in question.
For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18…
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18…
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM(2, 3) = 6.
Calculating LCM(9, 8): Methods and Approaches
Several methods can be employed to determine the LCM of 9 and 8. Let's explore the most common and effective techniques:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90…
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80…
Observing the lists, we see that the smallest number appearing in both sequences is 72. Therefore, LCM(9, 8) = 72.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the concept. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
- Prime factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3² = 9
Multiplying these highest powers together gives us the LCM: 8 x 9 = 72. Therefore, LCM(9, 8) = 72.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are intimately related. Using the formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the GCD of 9 and 8. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 9 and 8 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(9, 8) = 1, as 9 and 8 share no common factors other than 1.
Applying the formula:
LCM(9, 8) = (9 x 8) / 1 = 72
Therefore, LCM(9, 8) = 72. This method elegantly demonstrates the interconnectedness of LCM and GCD.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The seemingly abstract concept of LCM has tangible applications across various disciplines:
1. Scheduling and Timing
Imagine two buses departing from the same station at different intervals. One bus departs every 9 minutes, and the other every 8 minutes. To find out when both buses will depart simultaneously again, we need to find the LCM(9, 8) = 72. Both buses will depart together again after 72 minutes.
2. Fraction Operations
LCM plays a vital role in adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add 1/9 and 1/8, we need to find a common denominator, which is the LCM(9, 8) = 72. This allows us to rewrite the fractions as 8/72 and 9/72, making the addition straightforward.
3. Project Management
In project management, LCM can help synchronize tasks with varying completion times. If one task takes 9 days and another takes 8 days, the LCM helps determine when both tasks can be completed simultaneously, aiding in efficient resource allocation and project planning.
4. Gear Ratios and Rotational Mechanics
In engineering, LCM is crucial for calculating gear ratios and understanding the synchronized rotation of gears with different numbers of teeth. Determining when gears will align perfectly relies heavily on the LCM of the number of teeth on each gear.
5. Music Theory
Interestingly, LCM finds its application in music theory when determining the least common multiple of the note values in a musical piece, which is crucial for rhythm and timing calculations.
Beyond the Basics: Extending the Concept
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. We can calculate the LCM of three or more integers using the prime factorization method or other advanced techniques. The principle remains the same: find the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations and multiply them together.
For instance, to find LCM(9, 8, 6):
- Prime factorization of 9: 3²
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
The highest powers are 2³ and 3². Therefore, LCM(9, 8, 6) = 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9 = 72.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of LCM
The lowest common multiple, while seemingly a simple arithmetic concept, is a powerful tool with far-reaching implications. Its applications extend across various disciplines, showcasing its importance in problem-solving and practical applications. Understanding the different methods for calculating the LCM, from listing multiples to prime factorization and utilizing the GCD, empowers us to approach mathematical challenges with greater efficiency and insight. The LCM of 9 and 8, a seemingly trivial calculation, thus serves as a gateway to appreciating the elegance and utility of this fundamental mathematical concept. Whether it's scheduling buses, adding fractions, or designing gear ratios, the LCM provides the framework for seamlessly coordinating elements with different cycles or frequencies, highlighting its enduring significance in mathematics and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Amount Of Matter In An Object Is Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Characteristics Of Skeletal Muscle
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is 4 A Multiple Of 8
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Smallest Structural And Functional Unit Of An Organism
Mar 15, 2025
-
At What Temp Does Blood Boil
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 9 And 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
