Lowest Common Multiple Of 8 And 10
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
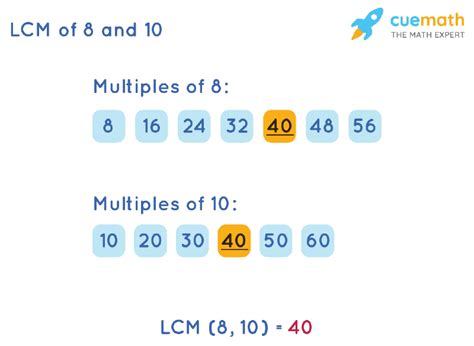
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 8 and 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and exploring different methods can significantly enhance your mathematical abilities. This comprehensive guide delves deep into calculating the LCM of 8 and 10, exploring various approaches and highlighting their practical applications. We'll move beyond simply finding the answer and explore the "why" behind the methods, making this a resource beneficial for students and anyone interested in strengthening their number theory skills.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Factors, Multiples, and the LCM
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 8 and 10, let's solidify our understanding of some key terms:
Factors:
Factors are numbers that divide evenly into another number without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, and 8. The factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, and 10. Notice that 2 is a common factor of both 8 and 10.
Multiples:
Multiples are the products of a number and any integer. For instance, some multiples of 8 are 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48... Some multiples of 10 are 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60... Observe that 40 appears in both lists.
Lowest Common Multiple (LCM):
The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest positive number that is a multiple of all the numbers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into without leaving a remainder. In our case, we are seeking the LCM of 8 and 10.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80...
Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100...
As we can see, the smallest multiple that appears in both lists is 40. Therefore, the LCM of 8 and 10 is 40. While simple for small numbers, this method becomes cumbersome and inefficient for larger numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
Prime factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
To find the LCM using prime factorization:
- Identify the prime factors: We have 2 and 5.
- Find the highest power of each prime factor: The highest power of 2 is 2³ (from the factorization of 8), and the highest power of 5 is 5¹ (from the factorization of 10).
- Multiply the highest powers together: 2³ x 5 = 8 x 5 = 40
Therefore, the LCM of 8 and 10 is 40, confirming the result from the previous method. This method is significantly more efficient for larger numbers where listing multiples would be impractical.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) are closely related. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. We can use the following formula:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
First, let's find the GCD of 8 and 10. The factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, 8. The factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, 10. The greatest common factor is 2.
Now, we can apply the formula:
LCM(8, 10) = (8 x 10) / GCD(8, 10) = (80) / 2 = 40
This method elegantly connects the LCM and GCD, providing an alternative approach to finding the LCM. Finding the GCD can be done using various methods, including the Euclidean algorithm, which is particularly useful for larger numbers.
Real-World Applications of LCM
Understanding LCM extends beyond the classroom and has practical applications in various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses depart from a station at different intervals. One bus leaves every 8 minutes, and another every 10 minutes. The LCM (40 minutes) determines when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
-
Construction and Engineering: LCM is crucial in aligning repetitive patterns in construction, ensuring seamless integration of different components.
-
Music: In music theory, LCM helps determine the least common denominator for rhythmic patterns, facilitating the creation of harmonious musical compositions.
-
Project Management: When tasks have different cycle times, LCM helps determine when all tasks will be completed simultaneously.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The concept of LCM extends beyond two numbers. You can calculate the LCM of multiple numbers using the prime factorization method or by extending the GCD approach. Understanding the LCM is fundamental to more advanced mathematical concepts such as modular arithmetic and abstract algebra.
Conclusion
Finding the LCM of 8 and 10, while seemingly a simple arithmetic problem, opens doors to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts and their wide-ranging applications. The various methods explored—listing multiples, prime factorization, and using the GCD—demonstrate different approaches to problem-solving, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Mastering these methods not only improves your computational skills but also enhances your understanding of number theory and its relevance in real-world scenarios. The LCM, therefore, is more than just a mathematical operation; it’s a key concept that underlies many aspects of our quantitative world. By thoroughly grasping these principles, you equip yourself with valuable tools for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and real-world problems. So, next time you encounter an LCM problem, remember the power and versatility of these different approaches and choose the method that best suits the context.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Is The Circulatory System Similar To A Road And Highway System
May 09, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 42 And 24
May 09, 2025
-
The Male Accessory Glands Include The
May 09, 2025
-
The Starting Molecule For Glycolysis Is
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Months In Three Years
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 8 And 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.