Lowest Common Multiple Of 7 And 3
Juapaving
Mar 05, 2025 · 5 min read
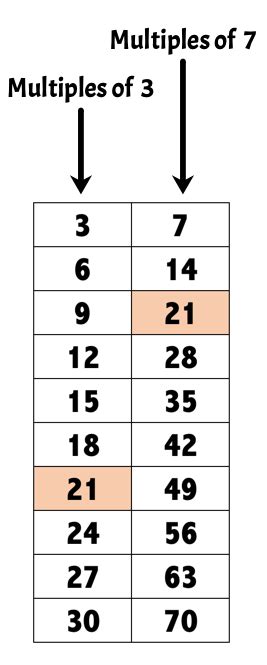
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 7 and 3: A Deep Dive
The concept of the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) is fundamental in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding LCMs is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving equations, and tackling various problems in diverse fields like scheduling and music theory. This article delves into the intricacies of finding the LCM of 7 and 3, exploring multiple methods and illustrating the broader significance of LCM calculations. We will cover various methods, from prime factorization to the least common multiple formula, demonstrating their application and explaining why they work.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
Before jumping into the specifics of finding the LCM of 7 and 3, let's solidify our understanding of what an LCM actually is. The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the numbers you're considering can divide into evenly.
For instance, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and so on. Multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, etc. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore the LCM(2,3) = 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The simplest method for finding the LCM, especially for smaller numbers like 7 and 3, involves listing the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest number appearing in both lists is 21. Therefore, the LCM of 7 and 3 is 21.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more robust method, particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors – numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
-
Prime Factorization of 7: 7 is a prime number, so its prime factorization is simply 7.
-
Prime Factorization of 3: 3 is also a prime number, so its prime factorization is 3.
To find the LCM using prime factorization, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations. In this case:
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 7 is 7¹ = 7
Multiply these highest powers together: 3 x 7 = 21. Therefore, the LCM(7,3) = 21.
Method 3: The Formula Method (Using GCD)
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD). The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. There's a handy formula connecting LCM and GCD:
LCM(a, b) = (|a * b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where:
- a and b are the two numbers
- |a * b| represents the absolute value of the product of a and b
- GCD(a, b) is the Greatest Common Divisor of a and b.
Let's apply this to 7 and 3:
-
Find the GCD of 7 and 3: Since 7 and 3 are both prime numbers and have no common factors other than 1, their GCD is 1.
-
Apply the formula: LCM(7, 3) = (|7 * 3|) / GCD(7, 3) = 21 / 1 = 21
This confirms that the LCM of 7 and 3 is 21.
Why is the LCM Important?
The LCM has far-reaching applications across various mathematical and real-world contexts:
1. Fraction Addition and Subtraction:
Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires the LCM. For example, to add 1/7 and 1/3, we need to find the LCM of 7 and 3 (which is 21) and then convert the fractions to have a denominator of 21 before adding them.
2. Scheduling Problems:
The LCM is crucial in solving scheduling problems. Imagine two buses departing from the same station. One bus leaves every 7 minutes, and the other leaves every 3 minutes. The LCM (21 minutes) determines when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
3. Cyclic Patterns:
LCMs are helpful in identifying the points where repeating or cyclical patterns coincide. For instance, in music theory, understanding LCM helps determine when different rhythmic patterns will align.
4. Algebra and Number Theory:
The concept of LCM is fundamental in various algebraic and number theoretical proofs and calculations. It's often used to simplify equations and solve Diophantine equations (equations where solutions are restricted to integers).
The Special Case of Relatively Prime Numbers
The numbers 7 and 3 are examples of relatively prime numbers, also known as coprime numbers. Relatively prime numbers are numbers that have no common factors other than 1. This means their GCD is 1. In such cases, finding the LCM is particularly straightforward: it's simply the product of the two numbers. This is a valuable shortcut when dealing with relatively prime numbers. Therefore, for relatively prime numbers a and b, LCM(a, b) = a * b.
Extending to More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, we consider all prime factors of all the numbers and take the highest power of each. For the formula method, we can extend it iteratively; first find the LCM of two numbers, then find the LCM of that result and the next number, and so on.
Conclusion
Finding the LCM of 7 and 3, while seemingly a simple task, highlights the fundamental importance of this concept in mathematics and various applications. Whether you utilize the method of listing multiples, prime factorization, or the formula involving the GCD, the result remains consistent: the LCM of 7 and 3 is 21. Understanding the LCM empowers you to approach a wide range of mathematical problems and real-world scenarios with greater clarity and efficiency. The understanding of LCM is not limited to just its mathematical applications, but also extends to practical applications in scheduling, pattern recognition, and other areas. Mastering this concept is a crucial step towards developing a strong foundation in mathematics and problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Highest Common Factor Of 8 And 16
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Are The Factors For 11
Mar 06, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 8
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is 83 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Organelle Is Known As The Powerhouse Of The Cell
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 7 And 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
