Lowest Common Multiple Of 10 And 4
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
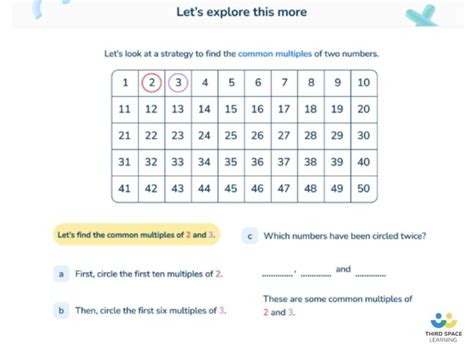
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 10 and 4: A Deep Dive
The concept of the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) is fundamental in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding LCMs is crucial for solving various problems, from simplifying fractions to scheduling events. This article will comprehensively explore the LCM of 10 and 4, using multiple approaches to illustrate the concept and provide a solid foundation for understanding LCMs in general. We'll delve into the definition, different calculation methods, real-world applications, and finally, explore some advanced concepts related to LCMs.
What is the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)?
The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors. For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30...
The common multiples are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30... The smallest of these common multiples is 6; therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Understanding the Significance of LCM
The LCM plays a crucial role in various mathematical operations and problem-solving scenarios:
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding the LCM of the denominators is essential when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. It allows you to find a common denominator, simplifying the calculation process.
-
Scheduling Problems: The LCM helps in solving scheduling problems. For example, if two events occur at intervals of 10 days and 4 days respectively, the LCM will tell you when both events will occur on the same day again.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCMs are fundamental in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory that deals with remainders after division.
-
Least Common Denominator (LCD): In the context of fractions, the LCM is also referred to as the Least Common Denominator (LCD).
Calculating the LCM of 10 and 4: Multiple Methods
Now, let's focus on finding the LCM of 10 and 4. We'll explore several methods to achieve this:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40...
As you can see, the smallest common multiple is 20. Therefore, the LCM(10, 4) = 20. This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but can become tedious with larger numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
- Prime factorization of 4: 2 x 2 = 2²
The prime factors involved are 2 and 5. We take the highest power of each prime factor: 2² and 5¹. Multiplying these together gives us: 2² x 5 = 4 x 5 = 20. Therefore, LCM(10, 4) = 20.
Method 3: Using the Formula (For Two Numbers)
For two numbers, 'a' and 'b', the LCM can be calculated using the following formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
where GCD stands for the Greatest Common Divisor.
First, we need to find the GCD of 10 and 4. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 10 and 4 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(10, 4) = 2.
Now, we can apply the formula:
LCM(10, 4) = (|10 x 4|) / GCD(10, 4) = 40 / 2 = 20
Therefore, LCM(10, 4) = 20. This method is efficient for two numbers and is commonly used in various mathematical applications.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Cooking: Imagine you're baking and need to use two ingredients that require different baking times. One ingredient requires baking every 10 minutes, and the other every 4 minutes. The LCM (20 minutes) helps determine when both ingredients will be ready at the same time.
-
Calendars: Suppose two events occur at intervals of 10 days and 4 days. The LCM will tell you when these events will coincide again.
-
Manufacturing: In production lines, machines might operate at different cycles. Determining when the machines will need maintenance at the same time relies on the LCM concept.
-
Construction: Two construction workers are laying bricks, one every 10 minutes and the other every 4 minutes. The LCM helps determine when they'll lay a brick at the same time.
-
Music: Musical rhythms and melodies often involve repetition of patterns over different time intervals. The LCM helps coordinate these patterns.
Advanced Concepts Related to LCM
-
LCM of More Than Two Numbers: The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method is particularly useful in such cases.
-
LCM and GCD Relationship: The LCM and GCD of two numbers are intimately related. For two numbers 'a' and 'b', the product of their LCM and GCD is always equal to the product of the numbers themselves:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
-
Applications in Abstract Algebra: The concept of LCM extends to more abstract algebraic structures, such as rings and ideals.
-
Computational Complexity: Efficient algorithms for calculating LCMs are crucial in computer science, particularly in cryptography and number theory.
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM of 10 and 4 and Beyond
This comprehensive exploration of finding the LCM of 10 and 4 has demonstrated the fundamental importance of this concept in various mathematical fields and practical applications. By understanding the different calculation methods, from listing multiples to prime factorization and the formula approach, you've gained a robust foundation for tackling LCM problems of any complexity. Remember, the ability to calculate LCMs effectively is a valuable skill with far-reaching applications in mathematics, computer science, and everyday problem-solving. As you progress in your mathematical studies, you'll find that the LCM is a cornerstone concept used to build upon more advanced mathematical tools and techniques. Continue practicing and exploring the fascinating world of number theory, and you'll undoubtedly find the LCM to be an indispensable tool in your mathematical arsenal.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Starting Molecule For Glycolysis Is
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Months In Three Years
May 09, 2025
-
Is 19 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
May 09, 2025
-
Is Force Increase On An Inclined Plane
May 09, 2025
-
Interesting Words That Start With V
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 10 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.