Lines Of Symmetry On A Octagon
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 5 min read
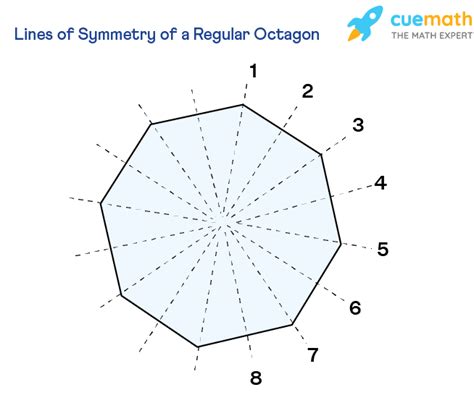
Table of Contents
Lines of Symmetry on an Octagon: A Comprehensive Exploration
The octagon, an eight-sided polygon, presents a fascinating case study in geometry, particularly when examining its lines of symmetry. Understanding these lines is crucial not only for appreciating the octagon's inherent geometric properties but also for applications in various fields, from art and design to engineering and architecture. This article delves deep into the lines of symmetry of a regular octagon, exploring their identification, properties, and practical implications.
Defining Lines of Symmetry
Before we dive into the specifics of an octagon, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two congruent halves that are mirror images of each other. This means that if you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap. Different shapes possess varying numbers of lines of symmetry, depending on their regularity and structure.
The Regular Octagon: A Special Case
A regular octagon is defined as an octagon with all eight sides of equal length and all eight interior angles of equal measure (135°). This regularity significantly impacts the number and nature of its lines of symmetry. Unlike irregular octagons, which may possess fewer or no lines of symmetry, the regular octagon exhibits a higher degree of symmetry.
Identifying Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Octagon
A regular octagon possesses a total of eight lines of symmetry. These lines can be categorized into two types:
1. Lines of Symmetry through Opposite Vertices
Four lines of symmetry pass through opposite vertices (corners) of the octagon. Imagine drawing a line connecting two vertices that are directly across from each other. This line divides the octagon perfectly in half, creating two mirror-image halves. These lines are also known as axes of symmetry. Because there are four pairs of opposite vertices, there are four lines of symmetry of this type.
2. Lines of Symmetry through Midpoints of Opposite Sides
The other four lines of symmetry pass through the midpoints of opposite sides. These lines are perpendicular to the sides they bisect. Again, imagine drawing a line connecting the midpoints of two opposite sides. This line will perfectly bisect the octagon, creating two identical halves. Because there are four pairs of opposite sides, there are four lines of symmetry of this type.
Visualizing the Lines of Symmetry
To fully grasp the concept, it's helpful to visualize the lines of symmetry on a regular octagon. Imagine a perfectly symmetrical octagon drawn on paper. Now, draw lines connecting:
- Opposite vertices: Draw lines from vertex 1 to vertex 5, vertex 2 to vertex 6, vertex 3 to vertex 7, and vertex 4 to vertex 8. (Numbering the vertices consecutively starting from any point).
- Midpoints of opposite sides: Draw lines connecting the midpoint of side 1 to the midpoint of side 5, the midpoint of side 2 to the midpoint of side 6, the midpoint of side 3 to the midpoint of side 7, and the midpoint of side 4 to the midpoint of side 8.
You will observe that all eight lines you've drawn are lines of symmetry, confirming the total of eight lines of symmetry in a regular octagon.
Mathematical Proof of Lines of Symmetry
The existence of eight lines of symmetry in a regular octagon isn't just an observation; it can be proven mathematically. The high degree of rotational symmetry in a regular octagon (rotational symmetry of order 8) directly relates to its lines of symmetry. Each rotational symmetry corresponds to a line of symmetry. Since a regular octagon can be rotated 8 times by 45 degrees before returning to its original position, there are 8 rotational symmetries. This leads to 8 lines of symmetry.
Applications of Lines of Symmetry in Octagons
The understanding of lines of symmetry in octagons has several practical applications:
- Architecture and Design: Octagonal structures are used in various architectural designs, from ancient buildings to modern constructions. Understanding lines of symmetry helps architects create balanced and visually appealing structures. The symmetry contributes to the structural integrity and stability of the buildings.
- Art and Crafts: In artistic creations, the lines of symmetry in an octagon serve as guiding principles for creating symmetrical patterns and designs. Many tessellations and geometric art forms utilize octagons and their lines of symmetry.
- Engineering and Manufacturing: The principles of symmetry are essential in engineering and manufacturing to ensure balance, stability, and efficient distribution of forces. Many mechanical parts and designs incorporate octagonal shapes where symmetry is critical.
- Computer Graphics and Game Design: In digital art and game development, octagons and their lines of symmetry play a crucial role in creating symmetrical characters, objects, and environments. Understanding these principles is vital for creating visually appealing and balanced designs.
Irregular Octagons and Lines of Symmetry
It's important to note that the eight lines of symmetry are specific to regular octagons. Irregular octagons, where sides and angles are not equal, may have fewer lines of symmetry, or even none at all. The number of lines of symmetry in an irregular octagon depends on its specific shape and proportions. There's no fixed rule for irregular octagons.
Exploring Further: Higher-Order Polygons
The exploration of lines of symmetry isn't limited to octagons. Similar principles apply to other regular polygons. A regular polygon with 'n' sides possesses 'n' lines of symmetry if 'n' is odd and 'n' lines of symmetry + 'n/2' lines of symmetry if 'n' is even. This pattern highlights the relationship between the number of sides and the number of lines of symmetry.
Conclusion: The Significance of Symmetry
The lines of symmetry in a regular octagon are more than just a geometric curiosity. They represent an underlying principle of balance, harmony, and visual appeal, influencing fields from architecture and design to art and technology. Understanding these lines provides a deeper appreciation for the mathematical elegance and practical implications of this fundamental geometric shape. Furthermore, the exploration of lines of symmetry extends beyond octagons, demonstrating a broader mathematical principle applicable to a wide range of shapes and designs. This article has only scratched the surface, leaving plenty of room for further investigation and exploration of the fascinating world of symmetry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Physical Appearance Of An Organism
May 12, 2025
-
An Ion With A Positive Charge
May 12, 2025
-
What Is The Modulus Of Elasticity Of Steel
May 12, 2025
-
6 Quarts Is Equal To How Many Cups
May 12, 2025
-
Sodium Bicarbonate And Hydrochloric Acid Balanced Equation
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lines Of Symmetry On A Octagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.