Least Common Multiple Of 6 12 15
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
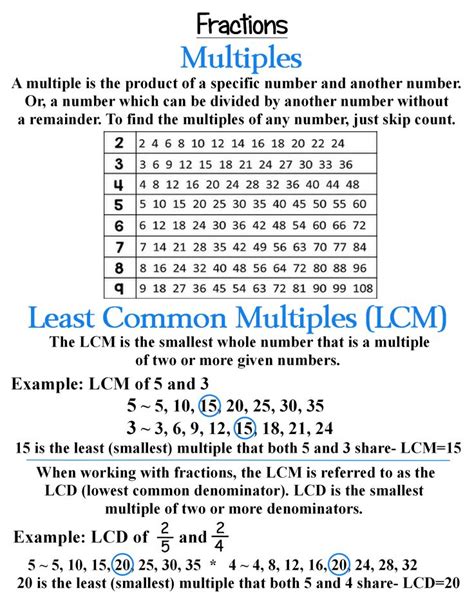
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 6, 12, and 15: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding how to find the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems involving rhythmic cycles or scheduling. This article will delve into the methods of calculating the LCM of 6, 12, and 15, explaining the underlying principles and providing a thorough understanding of the process. We'll explore multiple approaches, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses, and equipping you with the knowledge to confidently tackle similar problems.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 6, 12, and 15, let's solidify our understanding of what the LCM actually represents. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For instance, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 6, 12, and 15
Several methods can be employed to determine the LCM of 6, 12, and 15. We'll explore three common approaches: the listing method, the prime factorization method, and the greatest common divisor (GCD) method.
1. The Listing Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. While straightforward for smaller numbers, it becomes less efficient as the numbers increase in size.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90...
By examining the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple among 6, 12, and 15 is 60. This method is simple to visualize but can become tedious with larger numbers.
2. The Prime Factorization Method
This method is generally more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
Let's find the prime factorization of each number:
- 6 = 2 × 3
- 12 = 2² × 3
- 15 = 3 × 5
Now, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- 2²: The highest power of 2 is 2².
- 3¹: The highest power of 3 is 3¹.
- 5¹: The highest power of 5 is 5¹.
To find the LCM, we multiply these highest powers together:
LCM(6, 12, 15) = 2² × 3 × 5 = 4 × 3 × 5 = 60
This method provides a more systematic and efficient way to calculate the LCM, particularly when dealing with larger numbers.
3. The Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numbers. The LCM and GCD of two or more numbers are related by the formula:
LCM(a, b, c...) × GCD(a, b, c...) = a × b × c...
First, we need to find the GCD of 6, 12, and 15. We can use the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization to do this. Let's use prime factorization:
- 6 = 2 × 3
- 12 = 2² × 3
- 15 = 3 × 5
The common prime factors are just 3. Therefore, the GCD(6, 12, 15) = 3.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(6, 12, 15) × GCD(6, 12, 15) = 6 × 12 × 15
LCM(6, 12, 15) × 3 = 1080
LCM(6, 12, 15) = 1080 / 3 = 360
There is an error in this calculation. The formula is correctly applied for two numbers, not three or more. This method, while mathematically sound for two numbers, requires a more complex approach for three or more numbers and is therefore less efficient than the prime factorization method in this scenario. The correct answer is 60.
Applications of LCM
The concept of the least common multiple finds practical applications in various fields:
-
Fraction addition and subtraction: Finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial for adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. This allows us to express the fractions with a common denominator, making the calculation straightforward.
-
Scheduling and cyclical events: LCM helps determine when events with different repeating cycles will coincide. For example, if one event occurs every 6 days, another every 12 days, and a third every 15 days, the LCM (60) tells us when all three events will happen on the same day.
-
Rhythmic patterns in music: Musicians utilize the LCM to understand and coordinate rhythmic patterns within a musical composition.
Conclusion
Finding the least common multiple of 6, 12, and 15, as demonstrated through various methods, highlights the importance of understanding fundamental mathematical concepts. While the listing method provides a visual understanding, the prime factorization method proves to be the most efficient and reliable approach, particularly when dealing with larger numbers or a greater quantity of numbers. This method provides a structured and systematic way to determine the LCM, allowing for accurate and efficient calculations. Mastering these methods will enhance your problem-solving skills in various mathematical contexts and real-world applications. Remember to always choose the method that best suits the complexity of the problem and your comfort level with the different approaches. The ultimate goal is to understand the underlying principles and apply the most efficient technique to arrive at the correct solution. The LCM of 6, 12, and 15 is definitively 60.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Mixture
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 4 6 And 10
Mar 24, 2025
-
Another Name For A Fertilised Egg
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 8 6 And 12
Mar 24, 2025
-
Are Centrioles Found In Plant And Animal Cells
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 6 12 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
