Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
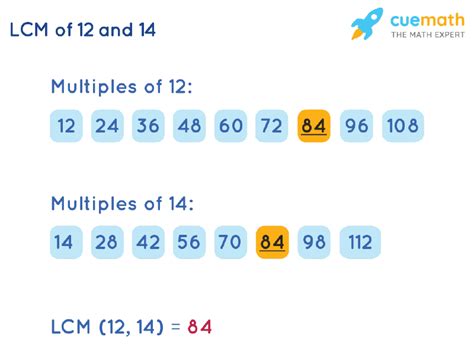
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 14 and 12: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in number theory with wide-ranging applications in various fields, from scheduling problems to music theory. This article delves into the intricacies of finding the LCM, specifically focusing on the numbers 14 and 12. We'll explore multiple methods, discuss the underlying mathematical principles, and even touch upon real-world applications to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 14 and 12, let's establish a clear understanding of the concept. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's a crucial tool for solving problems where we need to find a common point of occurrence or synchronization.
Think of it like this: Imagine two gears with 14 and 12 teeth respectively. The LCM represents the number of rotations required for both gears to return simultaneously to their starting positions.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 14 and 12
Several methods can efficiently determine the LCM of 14 and 12. We will explore three common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, particularly suitable for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70, 84, 98, 112, 126, 140, 154, 168, ...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120, 132, 144, 156, 168, ...
Notice that 84 appears in both lists. However, a smaller common multiple, 84, appears first. Therefore, the LCM of 14 and 12 is 84.
This method becomes less practical with larger numbers, as listing multiples can be time-consuming.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
- Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations and multiply them together.
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 7: 7¹ = 7
LCM(14, 12) = 2² x 3 x 7 = 4 x 3 x 7 = 84
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and conceptual clarity.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The GCD is the largest positive integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The relationship is given by the formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we find the GCD of 14 and 12 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide the larger number (14) by the smaller number (12): 14 = 1 x 12 + 2
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (12) and the smaller number with the remainder (2): 12 = 6 x 2 + 0
- The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 2. Therefore, GCD(14, 12) = 2.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(14, 12) = (14 x 12) / GCD(14, 12) = (168) / 2 = 84
This method is efficient and demonstrates the interconnectedness of LCM and GCD.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The LCM has numerous practical applications across various domains:
1. Scheduling and Synchronization
Imagine you have two buses that depart from the same station but with different schedules. One bus departs every 12 minutes, and the other departs every 14 minutes. The LCM (84 minutes) determines when both buses will depart simultaneously again. This principle extends to various scheduling scenarios, from manufacturing processes to traffic light synchronization.
2. Music Theory
In music, the LCM helps determine the least common period of repeating musical patterns or rhythms. For example, if one musical phrase repeats every 12 beats and another repeats every 14 beats, they will align again after 84 beats.
3. Fractions and Least Common Denominator
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators (least common denominator or LCD) is crucial. This allows you to express the fractions with a common denominator, simplifying the addition or subtraction process. For instance, adding 1/12 and 1/14 requires finding the LCD, which is 84.
4. Project Management
In project management, tasks might have different completion cycles. The LCM can help determine when multiple tasks will be completed simultaneously, allowing for better resource allocation and project planning.
5. Gear Ratios
As mentioned earlier, the LCM plays a role in determining the synchronization of gears with different numbers of teeth.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The concept of LCM extends beyond two numbers. You can calculate the LCM of three or more numbers using similar methods (prime factorization is generally most efficient). For instance, to find the LCM of 12, 14, and another number, say 21, you would perform prime factorization on all three numbers and then follow the steps described previously for finding the LCM.
Conclusion
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of 14 and 12, or any set of numbers, is a fundamental skill with widespread applications. The three methods explored – listing multiples, prime factorization, and the GCD method – each offer unique advantages depending on the context and the size of the numbers involved. Understanding the LCM is essential for solving problems involving synchronization, scheduling, music theory, fractions, and various other areas. By mastering these methods, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for tackling numerous mathematical challenges. Remember that the choice of method depends on the complexity of the problem and the numbers involved; however, the prime factorization method usually provides the most efficient and conceptually clear solution for larger or more complex scenarios.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Electrons Are In 1 Coulomb
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find The Average Cost Of A Function
May 09, 2025
-
How Does A Switch Work In A Circuit
May 09, 2025
-
8 Millimeters Equals How Many Centimeters
May 09, 2025
-
Words Starting With S For Kindergarten
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.