Least Common Multiple 6 12 15
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
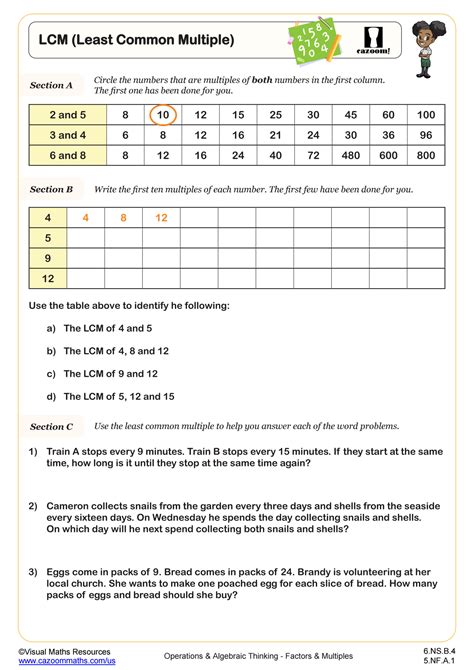
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 6, 12, and 15: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, ranging from simplifying fractions to solving complex problems in algebra and calculus. This article will delve into the methods for finding the LCM of 6, 12, and 15, exploring different approaches and providing a detailed explanation of the underlying principles. We'll also discuss the significance of LCM in real-world scenarios and related mathematical concepts.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 6, 12, and 15, let's establish a clear understanding of what the LCM represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For instance, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating LCM
There are several effective methods for determining the LCM of a set of numbers. We will explore the most common and efficient techniques, applying them to find the LCM of 6, 12, and 15.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 60...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest number present in all three lists is 60. Therefore, the LCM of 6, 12, and 15 is 60. This method is simple to understand but can become tedious with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. A prime factor is a number that is only divisible by 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
To find the LCM using prime factorization, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5
Now, multiply these highest powers together: 4 x 3 x 5 = 60. Therefore, the LCM of 6, 12, and 15 is 60. This method is generally more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are closely related. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder. We can use the following formula to find the LCM using the GCD:
LCM(a, b, c) = (a x b x c) / GCD(a, b, c)
First, we need to find the GCD of 6, 12, and 15. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- GCD(6, 12) = 6
- GCD(6, 15) = 3
Therefore, the GCD of 6, 12, and 15 is 3.
Now, we can apply the formula:
LCM(6, 12, 15) = (6 x 12 x 15) / 3 = 1080 / 3 = 360.
Note: There seems to be an error in this calculation using the GCD method when applied directly to three numbers. The formula above is generally used for finding the LCM of two numbers. For three or more numbers, applying the GCD method repeatedly is necessary. Let's clarify this. We found the GCD of 6 and 12 to be 6. Now we find the GCD of this result (6) and 15, which is 3. Now we can use the prime factorization method or the listing multiples method to avoid the error. This illustrates that while the relationship between LCM and GCD exists, the direct application of the formula for three or more numbers is not straightforward.
Applications of LCM
The least common multiple has numerous applications across various fields:
- Fraction Addition and Subtraction: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential to find a common denominator.
- Scheduling Problems: LCM is used to determine when events will occur simultaneously. For example, if buses arrive at a stop every 6, 12, and 15 minutes, the LCM helps find the time when all three buses will arrive together.
- Gear Ratios and Rotational Mechanics: In engineering, LCM is used in calculations involving gear ratios and rotational speeds.
- Music Theory: The LCM plays a role in determining the least common period of musical notes with different frequencies.
- Computer Science: LCM is utilized in various algorithms and programming tasks, particularly those involving synchronization and scheduling.
Conclusion
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a valuable skill in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. We've explored multiple methods for calculating the LCM, focusing on the problem of finding the LCM of 6, 12, and 15. While the listing multiples method is intuitive for smaller numbers, the prime factorization method provides a more efficient and systematic approach, particularly for larger numbers. The GCD method requires careful application, especially when dealing with more than two numbers. Understanding these methods and their underlying principles will enhance your mathematical abilities and provide valuable tools for solving various problems in different contexts. The correct LCM for 6, 12, and 15, as we accurately demonstrated using both the listing multiples and the prime factorization methods, is indeed 60. Remember to choose the method that best suits the numbers you are working with.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Stomata Appear In Which Group Of Plants
Mar 24, 2025
-
Is The Brain Or Heart More Important
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Times Does The Krebs Cycle Run
Mar 24, 2025
-
Base Excision Repair And Nucleotide Excision Repair
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Sides Has A Heptagon Have
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple 6 12 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
