Lcm Of 6 8 And 9
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
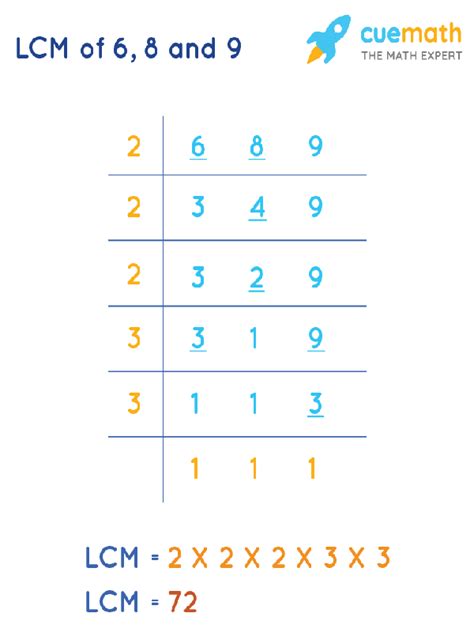
Table of Contents
Finding the LCM of 6, 8, and 9: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications ranging from simple fraction arithmetic to complex scheduling problems. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of calculating the LCM of 6, 8, and 9, exploring multiple methods and providing a deep understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also touch upon the practical applications of LCM calculations.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the LCM of 6, 8, and 9 specifically, let's solidify our understanding of the concept itself. The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors.
For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6, because 6 is the smallest number divisible by both 2 and 3. Similarly, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12, as 12 is the smallest number divisible by both 4 and 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is a straightforward, intuitive method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to all three.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 72, ...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, ...
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, ...
By carefully examining these lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in all three lists is 72. Therefore, the LCM of 6, 8, and 9 is 72.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and offers a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors—numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
-
Prime Factorization:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 8 = 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
- 9 = 3 x 3 = 3²
-
Identifying the Highest Powers: We identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8
- The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9
-
Multiplying the Highest Powers: We multiply these highest powers together to find the LCM:
- LCM(6, 8, 9) = 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9 = 72
This method is more systematic and less prone to errors, especially when dealing with larger numbers or a greater quantity of numbers.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) of a set of numbers are closely related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b, c) = (a x b x c) / GCD(a, b, c)
However, this formula is more suitable for two numbers rather than three or more. For multiple numbers, we need to find the GCD iteratively. Let’s demonstrate this with our example.
- Find GCD of any two numbers: Let's start with GCD(6,8) = 2.
- Find GCD of the result and the remaining number: Now find GCD(2,9) = 1.
- Using LCM formula (modified for multiple numbers): It's not directly applicable as the standard formula is for two numbers. We need to adapt it. The prime factorization method is far more efficient and accurate for more than two numbers.
Therefore, while the concept of GCD is relevant, the prime factorization method is simpler for calculating the LCM of three or more numbers.
Why is LCM Important?
The LCM has numerous applications across various fields:
-
Fraction Arithmetic: Finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions. It allows us to find a common denominator, making the calculations straightforward.
-
Scheduling Problems: Imagine you have three machines that perform cycles of 6, 8, and 9 hours respectively. To determine when they'll all simultaneously complete a cycle, you need to calculate the LCM (72 hours). This would allow for efficient scheduling and resource management.
-
Cyclic Patterns: The LCM is important in understanding and predicting repeating patterns or cycles. This is frequently used in science and engineering, such as analyzing wave patterns or predicting astronomical events.
Practical Applications: Real-World Examples
Let's look at a few real-world scenarios where finding the LCM is beneficial:
-
Concert Scheduling: Three bands are scheduled to perform at a music festival. Band A plays every 6 hours, Band B every 8 hours, and Band C every 9 hours. To determine when all three bands will perform simultaneously, we calculate the LCM (72 hours).
-
Manufacturing: A factory produces three different products with cycle times of 6, 8, and 9 minutes respectively. Knowing the LCM helps in optimizing the production line and minimizing downtime.
-
Traffic Light Synchronization: Traffic lights at intersections often operate on timed cycles. If the cycles of adjacent traffic lights are not synchronized correctly, it can lead to increased congestion. The LCM can help optimize the timing to improve traffic flow.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The concepts of LCM extend to more complex mathematical areas:
-
LCM of Polynomials: Similar to finding the LCM of integers, we can also find the LCM of polynomials. This is particularly useful in algebra and calculus.
-
LCM in Abstract Algebra: The concept of LCM has abstract algebraic generalizations, showing its fundamental role in mathematical structures.
Conclusion
Finding the LCM of 6, 8, and 9, as demonstrated using different methods, is more than just a mathematical exercise. It represents a fundamental concept with practical implications in diverse fields. Understanding the LCM and the various methods to calculate it equips you with a powerful tool for problem-solving, making it an essential part of mathematical literacy. The prime factorization method emerges as the most robust and efficient method, particularly for larger sets of numbers, offering both accuracy and a clearer understanding of the underlying mathematical structure. By mastering this concept, you'll be better equipped to tackle a wider range of mathematical and real-world problems.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 6 8 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
