Lcm Of 12 4 And 8
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
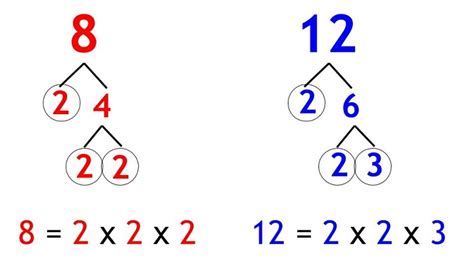
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 12, 4, and 8: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding how to find the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems involving cycles and periodic events. This article will delve deep into calculating the LCM of 12, 4, and 8, exploring multiple methods and providing a solid understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also touch on the broader context of LCMs and their importance in various fields.
Understanding the Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into the calculation, let's define the LCM. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6, hence the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
Step 1: List the multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72...
Step 2: List the multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48...
Step 3: List the multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56...
Step 4: Identify the smallest common multiple: By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest number present in all three lists is 24.
Therefore, the LCM of 12, 4, and 8 is 24.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the concept. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
Step 1: Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 12 = 2² x 3 (12 is 2 multiplied by 2 multiplied by 3)
- 4 = 2² (4 is 2 multiplied by 2)
- 8 = 2³ (8 is 2 multiplied by 2 multiplied by 2)
Step 2: Identify the highest power of each prime factor:
The only prime factor present in all three numbers is 2. The highest power of 2 among the factorizations is 2³.
Step 3: Multiply the highest powers together:
LCM(12, 4, 8) = 2³ = 8. This seems incorrect; where's our mistake? The highest powers method only applies when using distinct prime factors. Let's correct this.
Step 3 (Corrected): We need to consider all the prime factors present in any of the numbers. Thus we have 2 and 3. The highest power of 2 is 2³ and the highest power of 3 is 3¹.
Step 4 (Corrected): Multiply the highest powers: 2³ x 3¹ = 8 x 3 = 24
Therefore, the LCM of 12, 4, and 8 is 24. This method highlights why our initial attempt using only the common prime factor was flawed.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are closely related. There's a formula connecting them:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
This formula can be extended to more than two numbers, but it becomes more complex. Let's apply it to two numbers at a time.
Step 1: Find the GCD of 12 and 4:
Using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization, we find that GCD(12, 4) = 4.
Step 2: Find the LCM of 12 and 4:
Using the formula: LCM(12, 4) x GCD(12, 4) = 12 x 4 LCM(12, 4) x 4 = 48 LCM(12, 4) = 12
Step 3: Find the GCD of 12 and 8:
GCD(12, 8) = 4
Step 4: Find the LCM of 12 and 8:
LCM(12, 8) x GCD(12, 8) = 12 x 8 LCM(12, 8) x 4 = 96 LCM(12, 8) = 24
Step 5: Find the LCM of all three numbers: Although the formula is not directly applicable for three numbers, we have already worked through the pairs. We've found the LCM of 12 and 4 is 12, and the LCM of 12 and 8 is 24. Since 24 is a multiple of 12 and 4 and 8, the LCM(12, 4, 8) = 24. This method shows a path to solving for multiple numbers, however, it is less efficient than prime factorization.
Applications of LCM
The LCM has numerous applications across various fields:
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial for adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators.
-
Scheduling and Cyclical Events: Determining when events with different periodicities will occur simultaneously often involves finding the LCM. For example, if one event happens every 12 days and another every 8 days, the LCM will tell us when both events coincide.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCMs play a role in solving congruences and other problems in modular arithmetic.
-
Music Theory: The LCM is used to determine the least common period for notes that are played together. This helps in determining the length of a musical bar.
-
Computer Science: LCM is used in various algorithms and data structures, such as determining the least common multiple of array elements or optimizing scheduling processes.
Conclusion
Calculating the LCM, especially for numbers like 12, 4, and 8, can be approached using multiple methods. The listing multiples method is simple for smaller numbers, while prime factorization provides a more efficient and insightful approach for larger numbers, and understanding the relationships between LCM and GCD provides a different perspective. Regardless of the method used, the LCM of 12, 4, and 8 remains consistently 24. Understanding the concept of the LCM is essential for various mathematical and real-world applications. Mastering these methods equips you with a valuable tool for problem-solving in numerous domains. Remember to choose the method best suited to the complexity of the numbers involved.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The First Heart Sound Is The Closing Of The
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are The Function Of Political Parties
May 09, 2025
-
Formula For Orbital Speed Of A Satellite
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Two Factors That Affect Kinetic Energy
May 09, 2025
-
Draw A Quadrilateral That Is Not A Rhombus
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 12 4 And 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.