Lateral Surface Area Of Rectangular Prism
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
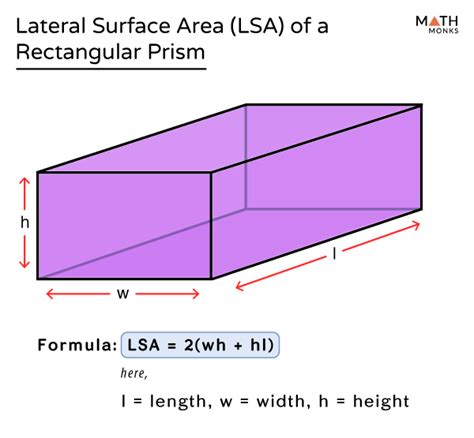
Table of Contents
Understanding and Calculating the Lateral Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
The rectangular prism, a three-dimensional shape with six rectangular faces, is a fundamental geometric solid encountered frequently in various fields, from architecture and engineering to packaging and everyday objects. Understanding its properties, particularly its surface area, is crucial for numerous applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of the lateral surface area of a rectangular prism, providing clear explanations, formulas, practical examples, and real-world applications.
What is a Rectangular Prism?
Before diving into the lateral surface area, let's establish a firm understanding of what a rectangular prism actually is. A rectangular prism, also known as a cuboid, is a three-dimensional shape characterized by:
- Six rectangular faces: These faces are all parallelograms, meaning opposite sides are parallel and equal in length.
- Twelve edges: These are the line segments where the faces meet.
- Eight vertices: These are the points where the edges intersect.
- Right angles: All the angles formed by the edges are right angles (90 degrees).
Think of a shoebox, a brick, or a die – these are all perfect examples of rectangular prisms.
Defining Lateral Surface Area
The total surface area of a rectangular prism includes the area of all six faces. However, the lateral surface area focuses specifically on the area of the four vertical faces, excluding the top and bottom bases. Imagine peeling off the top and bottom of a cereal box – what remains is the lateral surface area. This distinction is crucial for many practical applications, such as calculating the amount of material needed for the sides of a container without including the top and bottom.
Formula for Lateral Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
The formula for calculating the lateral surface area (LSA) of a rectangular prism is straightforward:
LSA = 2h(l + w)
Where:
- LSA represents the lateral surface area.
- h represents the height of the rectangular prism.
- l represents the length of the rectangular prism.
- w represents the width of the rectangular prism.
This formula essentially calculates the area of each of the four lateral faces (2lh + 2wh) and adds them together for the total lateral surface area. Understanding the derivation of this formula is key to grasping its application. Each lateral face is a rectangle. Two opposite faces have dimensions of length (l) and height (h), and the other two opposite faces have dimensions of width (w) and height (h). Adding the areas of these four rectangles yields the formula above.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Let's solidify our understanding with a step-by-step example. Consider a rectangular prism with the following dimensions:
- Length (l) = 10 cm
- Width (w) = 5 cm
- Height (h) = 8 cm
Following the formula:
- Add the length and width: 10 cm + 5 cm = 15 cm
- Multiply the sum by the height: 15 cm * 8 cm = 120 cm²
- Multiply the result by 2: 120 cm² * 2 = 240 cm²
Therefore, the lateral surface area of this rectangular prism is 240 square centimeters.
Practical Applications of Lateral Surface Area
The concept of lateral surface area extends far beyond theoretical geometry. It has numerous practical applications in various fields:
1. Construction and Architecture:
-
Estimating material costs: Architects and builders use lateral surface area calculations to determine the amount of materials needed for building walls, fences, or the sides of structures. This is crucial for accurate cost estimations and efficient project planning. Accurate calculations minimize material waste and save money.
-
Designing ventilation systems: Understanding the lateral surface area of ducts and other ventilation components is essential for optimizing airflow and designing efficient HVAC systems.
2. Packaging and Manufacturing:
-
Designing packaging: Manufacturers utilize lateral surface area calculations to determine the amount of material required for packaging boxes, cans, and other containers. Optimizing the surface area can minimize material use and reduce costs.
-
Labeling products: The lateral surface area determines the size of labels needed for products, ensuring complete coverage.
3. Engineering and Design:
-
Heat transfer calculations: In engineering, lateral surface area plays a critical role in calculating heat transfer rates in various systems. This is crucial in designing heat exchangers, cooling systems, and other thermal management applications.
-
Fluid dynamics: The lateral surface area impacts fluid flow and drag in applications involving pipes, conduits, and other fluid-carrying systems. Optimizing the surface area can enhance efficiency and reduce energy losses.
4. Everyday Applications:
-
Painting a wall: Calculating the lateral surface area of a wall helps determine the amount of paint needed for a project.
-
Wrapping a gift: Calculating the lateral surface area can help determine the amount of wrapping paper required.
Relating Lateral Surface Area to Total Surface Area
It's important to distinguish the lateral surface area from the total surface area. While the lateral surface area considers only the four vertical sides, the total surface area includes all six faces.
The formula for the total surface area (TSA) of a rectangular prism is:
TSA = 2(lw + lh + wh)
The relationship between LSA and TSA is:
TSA = LSA + 2(lw)
Where 2(lw) represents the area of the top and bottom faces. Understanding this relationship allows for flexible calculations depending on the specific needs of a given problem.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The fundamental concept of lateral surface area can be extended to more complex three-dimensional shapes. For instance, understanding the lateral surface area of a rectangular prism provides a foundation for calculating the surface area of other prisms, such as triangular prisms or hexagonal prisms. The core principles remain the same; it involves identifying the lateral faces and calculating their individual areas before summing them up for the total lateral surface area.
Furthermore, the concept can be applied to curved surfaces through approximation techniques involving infinitesimally small rectangular elements. This lays the groundwork for understanding more complex surface area calculations in calculus.
Conclusion: Mastering Lateral Surface Area Calculations
The lateral surface area of a rectangular prism is a fundamental concept with far-reaching practical applications. By understanding the formula, applying the step-by-step calculation process, and recognizing its relevance in various fields, you can effectively utilize this knowledge in problem-solving and real-world scenarios. From construction projects to product packaging, mastering lateral surface area calculations offers valuable skills with significant practical implications. The ability to calculate and understand this geometric property proves invaluable in numerous professions and everyday situations. Remember to always clearly define the dimensions of the prism before beginning your calculations to ensure accuracy and avoid errors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Factors Of 68
Mar 10, 2025
-
Ice Melting Is A Chemical Change
Mar 10, 2025
-
Is Neon Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 10, 2025
-
Why Do We Call Fossil Fuels Non Renewable
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Inches In Meter Stick
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lateral Surface Area Of Rectangular Prism . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
