Is Salt A Element Compound Or Mixture
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
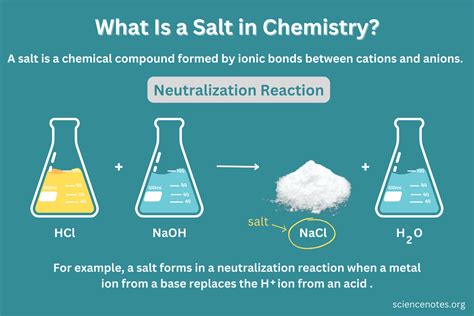
Table of Contents
Is Salt an Element, Compound, or Mixture? A Deep Dive into Sodium Chloride
The seemingly simple question, "Is salt an element, compound, or mixture?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of chemistry's fundamental building blocks. While the answer might seem obvious to some, a deeper understanding requires delving into the definitions of elements, compounds, and mixtures, and then applying those definitions to the specific case of salt, chemically known as sodium chloride (NaCl).
Understanding the Basics: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Before we classify salt, let's clarify the distinctions between elements, compounds, and mixtures. These classifications are based on the types of atoms present and the way they are bonded together.
Elements: The Fundamental Building Blocks
Elements are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom. These atoms cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples include oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and gold (Au). The periodic table organizes all known elements, each represented by its unique symbol and atomic number. Each element possesses distinct physical and chemical properties that define its behavior.
Compounds: Atoms United
Compounds are substances formed when two or more different elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. This combination involves the formation of chemical bonds, which are strong forces that hold the atoms together. These bonds are crucial; they dictate the properties of the compound, which are often vastly different from the properties of the constituent elements. Water (H₂O), for example, is a compound formed by the chemical bonding of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The properties of water are vastly different from the properties of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is always 2:1 in a water molecule. This fixed ratio is a defining characteristic of compounds. Compounds can only be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical processes.
Mixtures: A Blend of Substances
Mixtures, on the other hand, are physical combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated using physical methods like filtration, distillation, or evaporation. The composition of a mixture is not fixed, meaning the ratio of the components can vary. Examples of mixtures include air (a mixture of gases), saltwater (a mixture of salt and water), and sand (a mixture of different minerals).
Salt: A Case Study in Chemical Bonding
Now, let's apply this knowledge to sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt. Table salt is composed of two elements: sodium (Na), a highly reactive alkali metal, and chlorine (Cl), a highly reactive halogen gas. Neither sodium nor chlorine exists freely in nature in their elemental forms. Sodium is a soft, silvery-white metal that reacts violently with water. Chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas that is toxic and corrosive.
However, when sodium and chlorine react, they form a completely different substance: sodium chloride. This transformation occurs through an ionic bond, a type of chemical bond formed by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. Sodium readily loses one electron to become a positively charged ion (Na⁺), while chlorine readily gains one electron to become a negatively charged ion (Cl⁻). The strong electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions creates the ionic bond holding the sodium chloride crystal lattice together. The resulting compound, NaCl, is a white crystalline solid with a salty taste. This clearly demonstrates that salt is a compound, not an element or a mixture.
Distinguishing Salt from Mixtures
It's important to contrast the characteristics of salt (NaCl) with a simple mixture of sodium and chlorine. A mixture of sodium and chlorine would consist of separate sodium atoms and chlorine molecules, retaining their individual hazardous properties. A mixture of sodium and chlorine would be dangerous, whereas sodium chloride, even in large quantities, is safe for consumption (in moderation, of course). This drastic difference in properties highlights the fundamental difference between a mixture and a compound.
The Crystal Structure of Salt
Understanding the crystal structure of sodium chloride further solidifies its classification as a compound. Sodium chloride forms a cubic crystal lattice, where sodium and chlorine ions are arranged in a repeating pattern. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions, and each chloride ion is surrounded by six sodium ions. This highly ordered arrangement is a characteristic feature of compounds, not mixtures. The precise and fixed arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice is maintained through the strong ionic bonds between the sodium and chloride ions.
The Importance of Chemical Bonding in Defining Compounds
The key takeaway here is that the chemical bonding between sodium and chlorine atoms is what differentiates salt from a mere mixture of its constituent elements. The formation of ionic bonds results in a new substance with unique properties distinct from its components. This is the defining characteristic of a chemical compound. The atoms are chemically bonded, not merely physically mixed.
Beyond Table Salt: Other Types of Salt
While table salt is the most common form of sodium chloride, it's crucial to note that the term "salt" encompasses a broader range of ionic compounds. Any compound formed by the reaction of an acid and a base is considered a salt. These salts can have various properties and applications depending on the specific acid and base involved. For example, ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) and potassium chloride (KCl) are salts with properties and applications distinct from sodium chloride.
However, all salts share the fundamental characteristic of being ionic compounds—the result of a chemical reaction between an acid and a base, resulting in a new substance with distinct properties from its constituent elements. Therefore, these other salts, like sodium chloride, also fall into the category of compounds, not elements or mixtures.
Debunking Misconceptions about Salt
The notion that salt is a mixture might stem from the fact that it can be dissolved in water to form a saltwater solution. However, this dissolution process is a physical change, not a chemical change. The sodium and chloride ions are separated by water molecules, but the ionic bonds between them remain intact. Upon evaporation of the water, the sodium chloride crystals reform, demonstrating that no chemical transformation occurred.
Salt and Impurities
It's important to note that commercially produced table salt may contain small amounts of additives, such as iodine or anticaking agents. These additives are present in minor quantities and are physically mixed with the sodium chloride. However, these trace impurities do not change the fundamental nature of table salt as a compound. Pure sodium chloride remains a compound regardless of the presence of these minor impurities.
Conclusion: Salt is a Compound
In conclusion, based on our exploration of elements, compounds, and mixtures, and a detailed examination of sodium chloride's properties and structure, the answer is unequivocal: salt (sodium chloride) is a compound. It is formed by the chemical combination of two different elements, sodium and chlorine, through ionic bonding. Its properties differ significantly from those of its constituent elements. The fixed ratio of sodium and chlorine ions in its crystalline structure further reinforces this classification. The ability to dissolve in water is a physical, not chemical, process, and any impurities are merely physical mixtures. Therefore, the classification of salt as a compound is firmly established by its chemical nature and composition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 120 Minutes In Hours
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Quarts In 2 Cubic Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
40 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 20 Percent Of 1000
Mar 10, 2025
-
Adjectives That Start With The Letter B
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Salt A Element Compound Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
