Is Nh4no3 An Acid Or Base
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
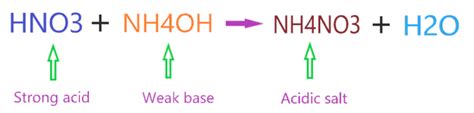
Table of Contents
Is NH₄NO₃ an Acid or a Base? Understanding Ammonium Nitrate's Properties
Ammonium nitrate (NH₄NO₃) is a chemical compound that often sparks curiosity due to its seemingly contradictory nature. Many wonder: is it an acid or a base? The answer isn't a simple "yes" or "no," as its behavior depends on the context and the chemical reaction it's involved in. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ammonium nitrate, exploring its properties, reactions, and its classification as a salt rather than a straightforward acid or base.
Understanding Acids and Bases
Before diving into ammonium nitrate's classification, let's refresh our understanding of acids and bases. Several definitions exist, but we'll focus on two prominent ones:
1. Arrhenius Definition:
According to Arrhenius, an acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in an aqueous solution, while a base increases the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻). This definition is simple but limited in scope.
2. Brønsted-Lowry Definition:
The Brønsted-Lowry definition provides a broader perspective. A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton (H⁺) donor, and a Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. This definition expands the concept beyond just aqueous solutions.
The Nature of Ammonium Nitrate (NH₄NO₃)
Ammonium nitrate is a salt. It's formed from the reaction of a strong acid (nitric acid, HNO₃) and a weak base (ammonium hydroxide, NH₄OH). This is crucial to understanding its behavior. The reaction is:
HNO₃(aq) + NH₄OH(aq) → NH₄NO₃(aq) + H₂O(l)
The resulting salt, NH₄NO₃, doesn't directly contribute a significant amount of H⁺ or OH⁻ ions to the solution. Instead, its behavior is dictated by the hydrolysis of its ions.
Hydrolysis of Ammonium Nitrate Ions
When ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, it dissociates into its constituent ions:
NH₄NO₃(aq) → NH₄⁺(aq) + NO₃⁻(aq)
Now, let's examine each ion separately:
1. Ammonium Ion (NH₄⁺):
The ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of the weak base ammonia (NH₃). It can donate a proton, acting as a weak acid. This reaction is represented as:
NH₄⁺(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ NH₃(aq) + H₃O⁺(aq)
The equilibrium lies significantly to the left, meaning only a small fraction of ammonium ions donate protons. This results in a slightly acidic solution.
2. Nitrate Ion (NO₃⁻):
The nitrate ion is the conjugate base of the strong acid nitric acid (HNO₃). Since nitric acid is a strong acid, its conjugate base is extremely weak and doesn't significantly react with water to produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻). Therefore, the nitrate ion has negligible influence on the pH of the solution.
pH of Ammonium Nitrate Solution
Due to the weak acidity of the ammonium ion and the negligible effect of the nitrate ion, an ammonium nitrate solution exhibits a slightly acidic pH. The pH is typically below 7, but not significantly so. The exact pH depends on the concentration of the ammonium nitrate solution. A more concentrated solution will be slightly more acidic than a dilute solution.
Ammonium Nitrate: Not a Simple Acid or Base, But a Salt
It's crucial to reiterate that ammonium nitrate is not inherently an acid or base in the traditional sense. It's a salt formed from the neutralization of a strong acid and a weak base. Its slightly acidic nature stems from the hydrolysis of the ammonium ion. This subtle difference is essential for correctly understanding its chemical properties and behavior.
Practical Applications and Safety Considerations
Ammonium nitrate's unique properties make it useful in various applications, including:
-
Fertilizers: Its high nitrogen content makes it a valuable component in fertilizers, providing essential nutrients for plant growth.
-
Explosives: When combined with certain fuels, ammonium nitrate can form explosive mixtures. This application highlights the importance of handling it carefully and responsibly.
-
Cold Packs: The dissolution of ammonium nitrate in water is an endothermic process, meaning it absorbs heat. This property is utilized in instant cold packs for injuries.
Safety Precautions: Ammonium nitrate can be dangerous if not handled properly. It's essential to follow safety guidelines, especially when working with large quantities or in applications where it could be used in explosive mixtures. Always refer to the safety data sheet (SDS) for detailed instructions.
Distinguishing Ammonium Nitrate from Other Salts
Understanding ammonium nitrate's behavior requires comparing it to other salts formed from different acid-base combinations:
-
Salt of Strong Acid and Strong Base: These salts, such as sodium chloride (NaCl), have a neutral pH because neither ion significantly hydrolyzes.
-
Salt of Weak Acid and Strong Base: These salts, such as sodium acetate (CH₃COONa), have a slightly basic pH due to the hydrolysis of the weak acid's conjugate base.
-
Salt of Strong Acid and Weak Base: This is where ammonium nitrate falls. It has a slightly acidic pH due to the hydrolysis of the weak base's conjugate acid.
-
Salt of Weak Acid and Weak Base: The pH of these salts is dependent on the relative strengths of the weak acid and weak base.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium nitrate's classification as an acid or base is nuanced. It's not simply an acid or a base but a salt exhibiting weak acidic properties due to the hydrolysis of the ammonium ion. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately predicting its behavior in chemical reactions and safely handling this versatile but potentially hazardous compound. Its various applications, from agriculture to medicine, underscore its importance, emphasizing the need to learn and appreciate the complex chemistry behind it. By comprehending the intricacies of its chemical properties, we can effectively utilize its benefits while mitigating potential risks. This understanding extends to appreciating the broader concepts of acid-base chemistry and the importance of considering the specific context when classifying chemical compounds. The depth of chemistry behind a seemingly simple salt like ammonium nitrate illustrates the complexity and fascination of the chemical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Are Not Considered Greenhouse Gases
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Is In 4 Hours
Mar 20, 2025
-
Things That Start With A X
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Smallest Unit That Makes Up Matter
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Time Rate Of Doing Work Is Called
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Nh4no3 An Acid Or Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
