Is Nh4cl An Acid Or Base
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
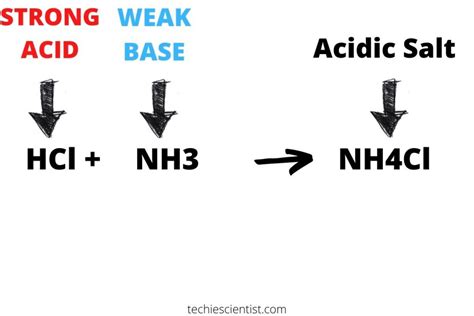
Table of Contents
Is NH₄Cl an Acid or a Base? Understanding Ammonium Chloride's Nature
Ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl), a common salt, often sparks confusion regarding its acidic or basic nature. While it's formed from a weak base (ammonia, NH₃) and a strong acid (hydrochloric acid, HCl), its behavior in solution isn't as straightforward as simply classifying it as neutral. This article delves deep into the chemical properties of NH₄Cl, exploring its interaction with water, its pH, and its applications, ultimately answering the question: Is NH₄Cl an acid or a base?
Understanding Acid-Base Theories
Before diving into the specifics of ammonium chloride, it's crucial to grasp the fundamental concepts of acid-base theories. Several theories explain acid-base behavior, each offering a slightly different perspective:
1. Arrhenius Theory:
This theory defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) in aqueous solutions, and bases as substances that produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻). While seemingly simple, this theory has limitations, as it doesn't account for acid-base reactions in non-aqueous solvents.
2. Brønsted-Lowry Theory:
A more comprehensive theory, Brønsted-Lowry defines acids as proton donors (H⁺) and bases as proton acceptors. This theory expands the scope of acid-base reactions to include those without hydroxide ions.
3. Lewis Theory:
The most general theory, Lewis theory defines acids as electron-pair acceptors and bases as electron-pair donors. This broader definition encompasses a wider range of reactions than the previous two theories.
The Hydrolysis of Ammonium Chloride
The key to understanding NH₄Cl's behavior lies in its hydrolysis in water. Hydrolysis is a reaction where a salt reacts with water to produce an acidic or basic solution. When NH₄Cl dissolves in water, it dissociates completely into its constituent ions:
NH₄Cl(s) → NH₄⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq)
The ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) is the crucial player here. It's the conjugate acid of the weak base ammonia (NH₃). This means it can donate a proton (H⁺) to water molecules:
NH₄⁺(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ NH₃(aq) + H₃O⁺(aq)
This equilibrium reaction produces hydronium ions (H₃O⁺), which are responsible for the acidic nature of the solution. The chloride ion (Cl⁻), being the conjugate base of a strong acid (HCl), is a very weak base and doesn't significantly affect the pH.
Why NH₄Cl is Acidic
The acidity of an ammonium chloride solution stems from the relatively strong tendency of the ammonium ion to donate a proton. While ammonia is a weak base, its conjugate acid, the ammonium ion, is a relatively weak acid. However, the equilibrium reaction favors the formation of hydronium ions, resulting in a solution with a pH lower than 7. This pH is typically in the range of 4-6, depending on the concentration of NH₄Cl.
In essence, the presence of the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺), which acts as a weak acid, dominates the behavior of the solution, making it acidic. The chloride ion (Cl⁻) plays a negligible role in determining the solution's pH.
Factors Affecting the Acidity of NH₄Cl Solutions
Several factors can influence the acidity of an ammonium chloride solution:
-
Concentration: A more concentrated solution of NH₄Cl will have a lower pH (more acidic) than a dilute solution. This is because a higher concentration of NH₄⁺ ions leads to a greater production of hydronium ions.
-
Temperature: The extent of hydrolysis, and thus the acidity, can be influenced by temperature. Generally, increasing temperature can slightly increase the acidity.
-
Presence of other ions: The presence of other ions in the solution can affect the equilibrium and subsequently the pH. This is especially true if the other ions are involved in acid-base reactions themselves.
Applications of Ammonium Chloride
The acidic nature of ammonium chloride, along with its other properties, makes it useful in various applications:
-
Medicine: It's used as an expectorant in cough medicines, helping to loosen phlegm and make it easier to cough up. Its acidity can also help to control the pH in certain medicinal preparations.
-
Agriculture: Ammonium chloride serves as a nitrogen source for plants, although it can acidify the soil over time. Therefore, its use requires careful soil pH management.
-
Industry: It finds applications in various industrial processes, including galvanizing, metal cleaning, and as a component in some fertilizers. Its ability to act as a buffer solution also makes it useful in certain industrial processes.
-
Food Industry: It is used in limited quantities as a food additive, mainly in bakery goods, serving as a yeast food and regulating pH levels in baked goods.
-
Analytical Chemistry: It is a component of some buffer solutions for maintaining the pH during chemical reactions and analyses.
Comparing NH₄Cl to Other Salts
Let's compare NH₄Cl's behavior to that of other salts formed from various acid-base combinations:
-
NaCl (Sodium Chloride): Formed from a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH), NaCl solutions are neutral (pH ≈ 7). Neither the Na⁺ nor the Cl⁻ ions significantly affect the pH of water.
-
NaCH₃COO (Sodium Acetate): Formed from a strong base (NaOH) and a weak acid (CH₃COOH), sodium acetate solutions are basic (pH > 7). The acetate ion (CH₃COO⁻) acts as a weak base, accepting protons from water.
-
NH₄F (Ammonium Fluoride): This is a more complex case. Both NH₄⁺ (weak acid) and F⁻ (weak base) will undergo hydrolysis. The relative strengths of their conjugate acids and bases will determine whether the solution is slightly acidic or basic. Often, ammonium fluoride results in a nearly neutral solution.
Conclusion: Is NH₄Cl an Acid or a Base?
To definitively answer the question: Ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) acts as a weak acid in aqueous solutions. While it's formed from a weak base and a strong acid, the hydrolysis of the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) leads to the production of hydronium ions (H₃O⁺), resulting in a pH lower than 7. This acidic behavior is crucial in understanding its various applications and its interactions with other substances. The chloride ion plays a minimal role in determining the overall acidity of the solution. Therefore, classifying NH₄Cl simply as a neutral salt would be inaccurate given its behaviour in aqueous solution. It is important to note that the degree of acidity is dependent on concentration and temperature. This detailed explanation provides a comprehensive understanding of ammonium chloride's chemical properties and behavior in aqueous solutions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is A Singal Bond Stronger Than Pi
Apr 06, 2025
-
Is The Melting Point A Physical Property
Apr 06, 2025
-
All Of The Following Are Greenhouse Gasses Except
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Additive Inverse Of 9 2
Apr 06, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 4 And 8
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Nh4cl An Acid Or Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
