Is Mitochondria Found In Plant Cells
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
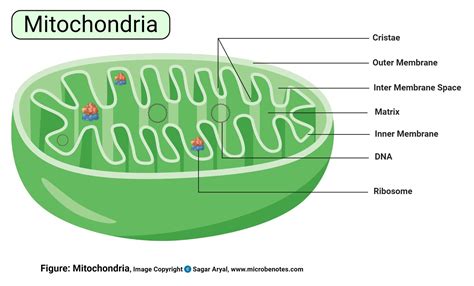
Table of Contents
- Is Mitochondria Found In Plant Cells
- Table of Contents
- Is Mitochondria Found in Plant Cells? A Deep Dive into Plant Cell Organelles
- The Ubiquitous Mitochondria: Powerhouses of the Cell
- Mitochondria in Plant Cells: A Specialized Role
- The Interplay Between Mitochondria and Chloroplasts: A Symbiotic Relationship
- Mitochondrial Dynamics in Plant Cells: Fusion and Fission
- Mitochondrial Genetics in Plants: Unique Features
- The Importance of Mitochondrial Health in Plant Productivity
- Research and Future Directions: Exploring the Mysteries of Plant Mitochondria
- Conclusion: Mitochondria are Essential for Plant Life
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Is Mitochondria Found in Plant Cells? A Deep Dive into Plant Cell Organelles
The question, "Is mitochondria found in plant cells?" might seem simple, but the answer unlocks a fascinating world of cellular biology and the intricacies of plant life. The short answer is a resounding yes. Plant cells, like animal cells, possess mitochondria, but the specifics of their function and interaction with other organelles add layers of complexity to their role in the plant's overall health and productivity. This article will delve deep into the presence, function, and importance of mitochondria in plant cells, exploring their unique characteristics and contributions to the plant kingdom.
The Ubiquitous Mitochondria: Powerhouses of the Cell
Before focusing specifically on plant cells, let's establish a foundational understanding of mitochondria. These organelles, often dubbed the "powerhouses of the cell," are fundamental to nearly all eukaryotic cells. Their primary role is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's primary energy currency. This process, known as cellular respiration, involves a series of biochemical reactions that break down glucose and other organic molecules to release energy. This energy, stored in the high-energy phosphate bonds of ATP, fuels countless cellular processes, from protein synthesis to cell division and transport.
Mitochondria are characterized by their unique double-membrane structure. The outer membrane is smooth, while the inner membrane is highly folded into cristae, significantly increasing the surface area available for the crucial electron transport chain reactions integral to ATP production. The space between the two membranes is called the intermembrane space, and the area enclosed by the inner membrane is known as the mitochondrial matrix, where the Krebs cycle takes place. Within the matrix, mitochondria also possess their own DNA (mtDNA), ribosomes, and the machinery for protein synthesis, a testament to their endosymbiotic origin.
Mitochondria in Plant Cells: A Specialized Role
While the fundamental role of mitochondria in generating ATP remains consistent across eukaryotic cells, their function in plant cells is subtly but significantly different due to the unique metabolic demands of plant life. Plants, unlike animals, are capable of photosynthesis, a process that uses sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose. This seemingly eliminates the need for respiration, but this is a misconception.
Photosynthesis provides the raw materials for cellular respiration, primarily glucose. The ATP generated through photosynthesis is largely used for the processes directly related to photosynthesis itself, while the mitochondria provide the ATP needed for other crucial cellular functions, including:
- Growth and Development: The energy demands of growth and development in plants are substantial, requiring significant ATP production by the mitochondria. This includes cell division, differentiation, and the biosynthesis of various cellular components.
- Nutrient Uptake and Transport: Plants need to absorb nutrients from the soil and transport them throughout their system. This active transport process requires energy provided by mitochondrial ATP.
- Stress Response: Plants are constantly exposed to various environmental stresses, such as drought, heat, cold, and salinity. Mitochondria play a crucial role in mediating stress responses by producing the necessary energy and regulating cellular processes.
- Signal Transduction: Mitochondria are not just energy factories; they also participate in complex cellular signaling pathways, influencing gene expression and plant development.
- Maintaining Ion Homeostasis: Plant cells frequently need to maintain specific ionic balances. This requires energy expenditure regulated and facilitated by mitochondria.
The Interplay Between Mitochondria and Chloroplasts: A Symbiotic Relationship
The presence of both mitochondria and chloroplasts in plant cells highlights a fascinating interplay between these two crucial organelles. Chloroplasts, the sites of photosynthesis, produce glucose and other organic molecules, which are then utilized by mitochondria in cellular respiration to generate ATP. This symbiotic relationship ensures a continuous flow of energy throughout the plant cell, supporting its diverse metabolic activities. The coordination between these two organelles is vital for efficient energy management within the plant cell. Disruptions in this communication can lead to decreased growth rates, diminished stress tolerance, and even cell death.
Mitochondrial Dynamics in Plant Cells: Fusion and Fission
Mitochondria are not static entities; they are constantly undergoing processes of fusion (merging) and fission (division). These dynamic processes are crucial for maintaining mitochondrial health, distributing mtDNA, and adapting to changing cellular conditions. In plant cells, mitochondrial dynamics are particularly important because they are influenced by environmental factors and developmental cues. For example, stress conditions can trigger changes in mitochondrial morphology and function.
Mitochondrial Genetics in Plants: Unique Features
Plant mitochondrial genomes (mtDNAs) are considerably larger and more complex than those found in animal cells. They often contain numerous repeated sequences and introns, adding to the complexity of their genetic organization and expression. The inheritance of mtDNA in plants is also unique, often showing cytoplasmic inheritance patterns distinct from nuclear inheritance.
The Importance of Mitochondrial Health in Plant Productivity
The health and function of mitochondria are directly linked to plant productivity and stress tolerance. Any disruption in mitochondrial function, caused by genetic mutations, environmental stresses, or pathogen attacks, can have far-reaching consequences, impacting growth, yield, and overall plant fitness. Understanding the intricacies of mitochondrial biology in plants is therefore crucial for developing strategies to enhance crop productivity and improve plant resilience to climate change.
Research and Future Directions: Exploring the Mysteries of Plant Mitochondria
Research on plant mitochondria is an active and rapidly evolving field. Scientists are constantly uncovering new details about their function, regulation, and interaction with other cellular components. Future research will likely focus on:
- Improving our understanding of mitochondrial dynamics and their regulation under various environmental conditions.
- Developing strategies to enhance mitochondrial function and improve plant stress tolerance.
- Exploring the role of mitochondria in plant development and reproductive processes.
- Investigating the potential of mitochondrial engineering to improve crop yields and quality.
Conclusion: Mitochondria are Essential for Plant Life
In conclusion, the presence of mitochondria in plant cells is undeniable. They are not merely energy producers but actively participate in various cellular processes crucial for plant growth, development, and response to environmental challenges. Their unique characteristics, interactions with chloroplasts, and dynamic nature make them fascinating and vital components of the plant cell machinery. Continued research in this field will undoubtedly reveal further insights into the remarkable complexity and importance of these cellular powerhouses in shaping the plant kingdom. Understanding their role is key to developing sustainable agricultural practices and ensuring food security in a changing world. The simple answer, “yes, mitochondria are found in plant cells,” opens a door to a complex and essential world of plant biology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write Equations For Lines Of Best Fit Calculator
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is Conjugate Acid Of Nh3
Apr 02, 2025
-
At The Bend In A River The Main Erosion Is
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is The Square Root Of 42 Rational Or Irrational
Apr 02, 2025
-
Round 45 To The Nearest 10
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Mitochondria Found In Plant Cells . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
