Is Light Energy Potential Or Kinetic
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
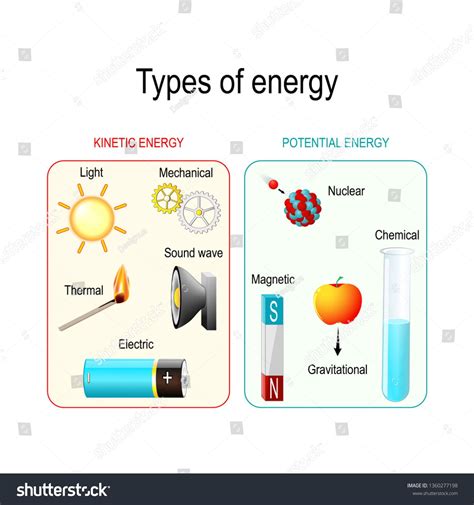
Table of Contents
Is Light Energy Potential or Kinetic? Unpacking the Wave-Particle Duality
The question of whether light energy is potential or kinetic is a fascinating one that delves into the heart of quantum mechanics and the wave-particle duality of light. The simple answer isn't a straightforward "potential" or "kinetic," but rather a nuanced understanding of how light behaves as both a wave and a particle, exhibiting characteristics of both types of energy. This exploration will delve into the properties of light, the definitions of potential and kinetic energy, and ultimately reveal why classifying light energy solely as potential or kinetic is an oversimplification.
Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy
Before diving into the intricacies of light, let's solidify our understanding of potential and kinetic energy.
Potential Energy: Stored Energy
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration. Think of a stretched rubber band, a book held high above the ground, or water held behind a dam. These objects have the potential to release energy; the rubber band to snap, the book to fall, the water to rush downstream. The energy is stored, ready to be converted into another form, typically kinetic energy.
Kinetic Energy: Energy of Motion
Kinetic energy, on the other hand, is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. A moving car, a flying bird, or a rolling ball all possess kinetic energy. The faster the object moves and the greater its mass, the higher its kinetic energy.
The Dual Nature of Light: Wave and Particle
The challenge in classifying light energy stems from its remarkable dual nature. Light exhibits properties of both waves and particles, a concept known as wave-particle duality. This duality is a cornerstone of quantum mechanics and is essential to understanding its energy characteristics.
Light as a Wave: Electromagnetic Radiation
Light is an electromagnetic wave, a self-propagating oscillation of electric and magnetic fields. These waves travel at the speed of light (approximately 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum) and carry energy across space. The wave nature of light explains phenomena like diffraction (bending of light around obstacles) and interference (the superposition of waves). The energy of a light wave is related to its frequency and wavelength. Higher frequency waves (like ultraviolet light) carry more energy than lower frequency waves (like infrared light).
Light as a Particle: Photons
Light also behaves as a stream of particles called photons. Each photon carries a discrete amount of energy, which is directly proportional to its frequency. This particle nature of light is evidenced by the photoelectric effect, where light shining on a metal surface can eject electrons, a phenomenon impossible to explain solely with the wave model. Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect, using the concept of photons, earned him the Nobel Prize.
Reconciling Wave and Particle: Energy Considerations
The apparent contradiction between the wave and particle descriptions of light is resolved through a more sophisticated understanding of energy. While light propagates as a wave, its energy is quantized, meaning it exists in discrete packets (photons). Each photon carries a specific amount of energy, and the total energy of a light beam is the sum of the energies of its individual photons.
Light's Energy: A Dynamic Balance
It's incorrect to say light energy is purely potential or purely kinetic. Instead, the energy of light is best described as a dynamic interplay between its wave and particle properties. The wave aspect describes how the energy propagates, while the particle aspect quantifies the energy in discrete units.
-
Wave-like Aspects: Light's propagation through space resembles kinetic energy; the energy is associated with the movement of the electromagnetic field. However, this isn't straightforward kinetic energy of a mass in motion.
-
Particle-like Aspects: The energy carried by each photon could be considered a form of potential energy. Before interacting with matter, the photon "holds" this energy. This potential energy transforms into kinetic energy upon interaction, such as in the photoelectric effect, where the photon’s energy is transferred to an electron, causing it to move.
Implications and Further Exploration
The dual nature of light's energy has profound implications for many scientific fields:
-
Solar Energy: Understanding the energy of photons is crucial for harnessing solar energy. Solar cells convert the energy of photons into electricity.
-
Medical Imaging: Techniques like X-ray and PET scans rely on the interaction of photons with matter to create images of the body.
-
Communication Technologies: Fiber optic communication utilizes light to transmit data; the energy of photons carries information.
-
Laser Technology: Lasers produce highly coherent light beams, making them essential for applications like surgery, manufacturing, and scientific research.
The Role of Quantum Mechanics
The wave-particle duality of light can only be fully understood within the framework of quantum mechanics. Classical physics fails to adequately describe light's behavior; quantum mechanics provides a more accurate and complete picture.
Ongoing Research
Research into light continues to push the boundaries of our understanding. Scientists constantly explore the intricate details of light-matter interactions, seeking to further refine our models and unlock new applications.
Conclusion: Beyond Simple Categorization
Classifying light energy simply as potential or kinetic energy is an oversimplification. Light's unique wave-particle duality means its energy is a dynamic blend of characteristics associated with both types of energy. The energy manifests as a wave propagating through space and exists as discrete packets (photons), each containing a specific amount of energy. This sophisticated interplay is crucial to understanding various scientific phenomena and technological advancements. The ongoing exploration of light's behavior continues to reveal deeper insights into the fundamental nature of the universe. A complete understanding demands embracing its dual nature rather than attempting to force it into a simplistic categorization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Roman Numeral For 11
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples Of Ten
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is 3 10 As A Percent
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Si Unit Of Momentum
Mar 05, 2025
-
What 2 Planets Have No Moons
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Light Energy Potential Or Kinetic . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
