Is Hcn A Strong Or Weak Acid
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
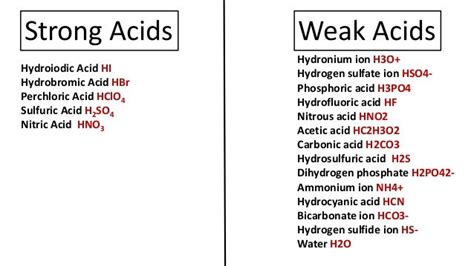
Table of Contents
Is HCN a Strong or Weak Acid? A Comprehensive Exploration
Hydrogen cyanide (HCN), also known as prussic acid, is a chemical compound that sparks considerable interest, particularly concerning its acidic nature. The question, "Is HCN a strong or weak acid?" is crucial for understanding its behavior in various chemical reactions and its implications for safety and environmental considerations. This comprehensive exploration will delve into the details, examining its dissociation, pKa value, conjugate base, and practical applications, ultimately providing a clear answer to this important query.
Understanding Acid Strength: A Foundation
Before classifying HCN, let's establish a clear understanding of acid strength. Acids are substances that donate protons (H⁺ ions) in a solution. Strong acids completely dissociate into their ions in water, meaning almost all the acid molecules donate their protons. Weak acids, on the other hand, only partially dissociate, resulting in an equilibrium between the undissociated acid and its ions. This equilibrium is described by the acid dissociation constant, Ka, and its negative logarithm, pKa.
The Role of Ka and pKa
The Ka value reflects the extent of dissociation. A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid because more protons are released into the solution. Conversely, a lower Ka value signifies a weaker acid. Since Ka values often span several orders of magnitude, the pKa value (pKa = -log₁₀Ka) is often used for easier comparison. A lower pKa indicates a stronger acid.
HCN: A Detailed Examination
HCN is a weak acid. Its relatively low Ka value and correspondingly higher pKa value confirm this classification. Let's break down the reasons behind its weakness.
The Dissociation Equilibrium of HCN
When HCN is dissolved in water, it undergoes partial dissociation according to the following equilibrium:
HCN(aq) ⇌ H⁺(aq) + CN⁻(aq)
This equilibrium strongly favors the undissociated HCN molecule, implying that only a small fraction of HCN molecules donate their protons. This limited dissociation is the hallmark of a weak acid.
The pKa Value of HCN
The pKa value of HCN is approximately 9.2. This value is significantly higher than the pKa values of strong acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl, pKa ≈ -7) or sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄, pKa₁ ≈ -3). The high pKa value for HCN reinforces its classification as a weak acid. Remember, a higher pKa means a lower Ka, indicating limited dissociation.
The Conjugate Base: CN⁻
The dissociation of HCN produces the cyanide ion (CN⁻), its conjugate base. The cyanide ion is a relatively weak base, meaning it has a limited tendency to accept protons. This is directly related to the weak acidic nature of HCN; a weak acid has a weak conjugate base, and vice versa. The stability of the CN⁻ ion also plays a role in HCN's weak acidity.
Practical Implications of HCN's Weak Acidity
The weak acidity of HCN has several crucial implications in various fields:
Toxicity and Safety
While HCN is a weak acid, its toxicity is significant. Its ability to inhibit cellular respiration makes it extremely dangerous, even in relatively small concentrations. This toxicity is independent of its acidity; the cyanide ion (CN⁻) is the primary culprit in its poisonous effects. Proper handling and safety precautions are paramount when working with HCN.
Environmental Concerns
The presence of HCN in the environment, even in low concentrations, can pose a threat to aquatic life and other organisms. Understanding its weak acidity is vital in predicting its behavior in different environmental conditions, particularly its solubility and potential for reactions with other substances.
Industrial Applications
Despite its toxicity, HCN finds applications in certain industrial processes. It's used in the production of some plastics, pesticides, and other chemicals. The controlled use and handling of HCN in these applications are crucial to minimize risks.
Analytical Chemistry
The weak acidity of HCN can be exploited in various analytical techniques, such as titrations, where the careful control of pH is crucial. Understanding its dissociation constant is essential for accurate measurements and interpretations.
Comparison with Other Acids
To better appreciate HCN's weak acidity, it's useful to compare it with other acids:
| Acid | Formula | pKa | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid | HCl | ~ -7 | Strong |
| Sulfuric Acid | H₂SO₄ | ~ -3 | Strong |
| Acetic Acid | CH₃COOH | 4.76 | Weak |
| Carbonic Acid | H₂CO₃ | 6.35 | Weak |
| Phosphoric Acid | H₃PO₄ | 2.12 | Weak |
| Hydrogen Cyanide | HCN | 9.2 | Weak |
This table illustrates that HCN has a much higher pKa than strong acids like HCl and H₂SO₄, and even higher than many weak acids.
Conclusion: HCN is Undeniably a Weak Acid
In summary, HCN is a weak acid. Its partial dissociation in water, its relatively high pKa value of approximately 9.2, and the behavior of its conjugate base, CN⁻, all firmly establish its classification as a weak acid. Understanding this fundamental property is critical for assessing its toxicity, environmental impact, and industrial applications. While its weak acidity doesn't diminish its inherent toxicity, it provides crucial information for safe handling, environmental monitoring, and chemical process optimization. Further research and precise measurements continually refine our understanding of HCN's behavior and its interactions with various chemical and biological systems. Always prioritize safety when working with or studying HCN due to its potentially hazardous nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Molecular Mass Of Kno3
May 09, 2025
-
The Two Sides Of Dna Are Held Together By
May 09, 2025
-
Three Main Parts Of A Seed
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Strong Electrolyte
May 09, 2025
-
Why Do Skeletal Muscles Work In Pairs
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Hcn A Strong Or Weak Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.