Is Carbon Dioxide A Pure Substance
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
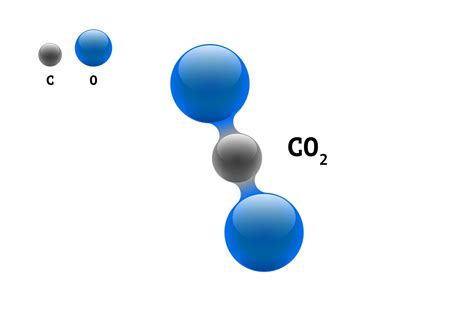
Table of Contents
Is Carbon Dioxide a Pure Substance? A Deep Dive into Chemical Composition and Properties
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a ubiquitous compound found throughout the Earth's systems, playing a vital role in various natural processes and human activities. But is it a pure substance? Understanding this requires delving into the fundamental definitions of chemistry and exploring the unique characteristics of CO2. This article will comprehensively analyze the chemical nature of carbon dioxide to definitively answer this question and explore related concepts.
Defining Pure Substances
Before we classify carbon dioxide, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a pure substance in chemistry. A pure substance is a form of matter that has a constant composition and properties throughout the sample. This means that the substance is made up of only one type of atom, molecule, or ion. It cannot be separated into simpler components by physical methods like filtration or distillation. Examples of pure substances include elements (like oxygen, O2) and compounds (like water, H2O).
The Chemical Structure of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide exists as a discrete molecule composed of one carbon atom covalently bonded to two oxygen atoms. The chemical formula, CO2, perfectly represents this structure. This covalent bonding, where electrons are shared between atoms, creates a stable and distinct molecular entity. The linear structure (O=C=O) contributes to its unique physical and chemical properties. Crucially, this consistent molecular structure is a key indicator of its purity. Every molecule of CO2 is identical – a carbon atom double-bonded to two oxygen atoms.
Distinguishing Pure Substances from Mixtures
It's essential to differentiate pure substances from mixtures. A mixture contains two or more substances physically combined but not chemically bonded. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform, like sand and water). The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can often be separated using physical methods. This contrasts sharply with a pure substance, where the components are chemically united and inseparable by physical means.
Carbon Dioxide: A Pure Compound
Given the definition of a pure substance and the consistent molecular structure of carbon dioxide, we can definitively conclude that carbon dioxide (CO2) is a pure substance. It is a pure compound, specifically, because it is formed by the chemical combination of two different elements (carbon and oxygen) in a fixed ratio (one carbon atom to two oxygen atoms). This chemical bonding makes it a distinct entity, unlike a mixture where components are simply intermingled.
Impurities in Real-World Carbon Dioxide Samples
While CO2 is inherently a pure substance, real-world samples often contain trace amounts of other substances. These impurities can arise from various sources, including:
- Air Contamination: CO2 produced industrially or naturally may contain small quantities of nitrogen, oxygen, and other atmospheric gases.
- Production Processes: Depending on the source (e.g., combustion, fermentation), impurities from the starting materials or byproducts can be present.
- Storage and Transportation: Contamination can occur during storage and transport due to interactions with container materials or leakage of other substances.
However, the presence of these trace impurities does not alter the fundamental nature of CO2 as a pure substance. A small percentage of contaminants doesn't change the intrinsic molecular composition of the majority component. The critical factor is that CO2 remains chemically uniform at a macroscopic level, even with these minor imperfections. The CO2 molecule itself is unchanged. These trace elements are viewed as contaminants, not integral parts of the substance.
Analysing Purity: Techniques for Characterization
The purity of CO2 samples can be assessed through various analytical techniques:
- Gas Chromatography (GC): This technique separates the components of a gaseous mixture based on their different interactions with a stationary phase. It allows for the identification and quantification of any impurities present in a CO2 sample.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): MS measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, enabling precise identification and quantification of individual molecules, including impurities in the CO2 sample.
- Infrared Spectroscopy (IR): IR spectroscopy analyzes the absorption of infrared radiation by molecules. The unique absorption pattern of CO2 can be used to identify its presence and detect any deviations from the pure CO2 spectrum indicative of impurities.
These techniques provide quantitative data on the composition of a CO2 sample, allowing for the precise determination of its purity level. While trace impurities might be present, these analyses help assess how close the sample is to pure CO2.
The Importance of Purity in Applications
The purity of carbon dioxide is crucial in various applications, including:
- Food and Beverage Industry: High-purity CO2 is essential for carbonation of beverages and preservation of food products. Impurities can affect taste, quality, and safety.
- Medical Applications: CO2 is used in laser surgery, as a propellant in aerosol sprays, and in other medical procedures. Purity is critical for patient safety.
- Industrial Processes: CO2 is used in various industrial processes, such as welding, fire extinguishing, and enhanced oil recovery. Impurities can affect efficiency and safety.
- Scientific Research: In research laboratories, high-purity CO2 is essential for accurate experimental results and avoiding interference from impurities.
Maintaining high purity is often achieved through various purification methods, such as distillation, absorption, and membrane separation.
Conclusion: CO2 – A Pure Substance with Real-World Implications
In conclusion, despite the possibility of trace impurities in real-world samples, carbon dioxide is fundamentally a pure substance. Its consistent molecular composition (one carbon atom covalently bonded to two oxygen atoms) fulfills the criteria of a pure compound. While various analytical techniques can quantify the presence of minor contaminants, these do not alter the intrinsic purity of CO2 itself. Understanding this distinction is critical for various applications, as the purity level significantly impacts the effectiveness, safety, and quality of processes and products utilizing carbon dioxide. The presence of impurities, however minor, can still significantly impact the quality and application. Hence maintaining and understanding the purity level of CO2 is critical across numerous sectors. This detailed examination underscores the significance of precise chemical classification and the practical implications of purity in everyday applications and scientific research.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Sides In A Parallelogram
Mar 16, 2025
-
Whats The Lcm Of 9 And 15
Mar 16, 2025
-
Lowest Common Factor Of 7 And 9
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Must Be True For Natural Selection To Occur
Mar 16, 2025
-
5 Letter Words That Start With Vi
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Carbon Dioxide A Pure Substance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
