Identify The Area Of The Cell Where Glycolysis Occurs
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
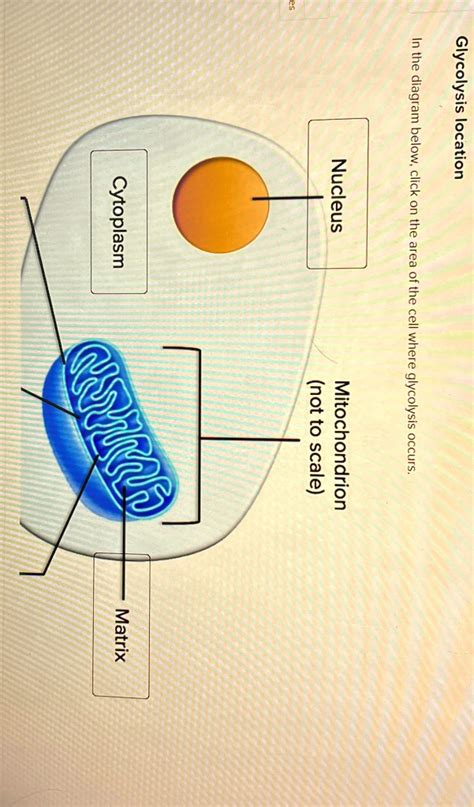
Table of Contents
Identifying the Area of the Cell Where Glycolysis Occurs: A Deep Dive into Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis, the foundational process of cellular respiration, is a captivating metabolic pathway crucial for energy production in virtually all living organisms. Understanding where this process unfolds within the complex architecture of a cell is fundamental to grasping its significance and intricacies. This comprehensive article delves into the precise location of glycolysis, exploring the cellular compartments involved, the reasons behind its specific location, and the implications for cellular function and overall metabolism.
The Cytoplasm: The Stage for Glycolysis
The unequivocal answer to the question "Where does glycolysis occur?" is the cytoplasm. Unlike many other stages of cellular respiration, which are confined to specific organelles, glycolysis unfolds freely within the cell's cytoplasm. This is a significant feature distinguishing it from processes like the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, which are tightly regulated within the mitochondria.
Understanding the Cytoplasm's Role
The cytoplasm, the jelly-like substance filling the cell between the nucleus and the cell membrane, is a dynamic environment teeming with enzymes, metabolites, and other cellular components. Its fluid nature allows for the free diffusion and interaction of the molecules involved in glycolysis, facilitating the smooth progression of this vital metabolic pathway.
The enzymes catalyzing each step of glycolysis are dissolved within the cytoplasm, readily available to bind to their substrates and drive the reaction forward. This proximity of enzymes and substrates optimizes the efficiency of the glycolytic pathway, allowing for rapid energy production when needed.
The Significance of Cytoplasmic Location
The cytoplasmic location of glycolysis isn't arbitrary; it carries several crucial implications:
-
Accessibility of substrates: Glucose, the primary substrate for glycolysis, readily enters the cell through specialized membrane transporters. Its presence in the cytoplasm ensures immediate availability to the glycolytic enzymes.
-
Rapid energy production: The cytoplasmic location allows for quick responses to energy demands. When a cell requires a rapid burst of ATP, glycolysis can swiftly provide it without the delay of transporting substrates to and from organelles.
-
Evolutionary perspective: The fact that glycolysis is a very ancient metabolic pathway, present even in prokaryotic cells which lack membrane-bound organelles, strongly suggests that the cytoplasmic location was the original and most efficient site for its operation.
A Detailed Look at the Glycolytic Pathway
Before delving further into the intricacies of glycolytic location, let's briefly revisit the key steps involved in this metabolic pathway:
Phase 1: Energy Investment Phase
This phase involves the phosphorylation of glucose and its conversion into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P). Two ATP molecules are consumed in this process, preparing the glucose molecule for subsequent energy-yielding steps.
- Step 1: Hexokinase: Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate.
- Step 2: Phosphoglucose Isomerase: Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerized to fructose-6-phosphate.
- Step 3: Phosphofructokinase: Fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. This is the committed step of glycolysis, a highly regulated process.
- Step 4: Aldolase: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is cleaved into two three-carbon molecules: dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
- Step 5: Triose Phosphate Isomerase: DHAP is isomerized to G3P.
Phase 2: Energy Payoff Phase
This phase witnesses the oxidation and phosphorylation of G3P, resulting in the net production of ATP and NADH.
- Step 6: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: G3P is oxidized and phosphorylated, generating 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
- Step 7: Phosphoglycerate kinase: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate transfers a phosphate group to ADP, forming ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate.
- Step 8: Phosphoglycerate mutase: 3-phosphoglycerate is isomerized to 2-phosphoglycerate.
- Step 9: Enolase: 2-phosphoglycerate is dehydrated, forming phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP).
- Step 10: Pyruvate kinase: PEP transfers a phosphate group to ADP, forming ATP and pyruvate.
The entire process yields a net gain of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules per glucose molecule.
Exceptions and Variations: Glycolysis Beyond the Cytoplasm
While the cytoplasm is the primary location for glycolysis in most cells, there are exceptions and nuances to consider:
Specialized Cells and Tissues
Some specialized cells or tissues might exhibit minor variations in the precise location or regulation of glycolysis. For example, certain aspects of glycolytic regulation might differ in muscle cells versus liver cells due to their distinct metabolic roles. However, the core process remains confined to the cytoplasm.
Compartmentalization in Certain Organisms
In some organisms, specific steps of glycolysis might be associated with particular structures or compartments within the cytoplasm. This isn't a change in location per se, but rather a spatial organization within the cytoplasmic environment to optimize efficiency.
Conclusion: The Cytoplasm's Central Role in Energy Metabolism
Glycolysis, a cornerstone of cellular energy production, unfolds within the dynamic environment of the cell's cytoplasm. This location allows for efficient substrate access, rapid ATP generation in response to energy demands, and easy integration with other metabolic pathways. Understanding the precise cellular location of glycolysis is vital for comprehending its significance and its crucial role in the overall energy balance of the cell. The seemingly simple process is a testament to the elegant organization and efficiency of cellular machinery, highlighting the crucial role of the cytoplasm in the life of the cell. Further research continues to unravel the intricate details of glycolysis regulation and its interactions with other metabolic processes, emphasizing the importance of this fundamental pathway in cellular biology.
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Cellular Organelle Responsible For Protein Synthesis Is
May 09, 2025
-
Calculate Area Of A Scalene Triangle
May 09, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 484
May 09, 2025
-
Identify The Meso Isomer Of The Following Compound
May 09, 2025
-
All Events That Occur During One Heartbeat
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Identify The Area Of The Cell Where Glycolysis Occurs . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.