How To Find Vertex Of Parabola From Equation
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
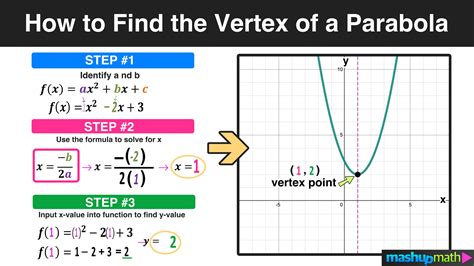
Table of Contents
How to Find the Vertex of a Parabola from its Equation
Finding the vertex of a parabola is a fundamental concept in algebra and has numerous applications in various fields, from physics to computer graphics. The vertex represents the parabola's highest or lowest point, depending on whether it opens upwards or downwards. Knowing how to locate this point is crucial for understanding the parabola's behavior and solving related problems. This comprehensive guide will explore several methods for efficiently determining the vertex of a parabola, regardless of the form of its equation.
Understanding the Parabola
Before delving into the methods, let's briefly review what a parabola is and its key features. A parabola is a U-shaped curve that is symmetric around a vertical or horizontal line called the axis of symmetry. The point where the parabola intersects its axis of symmetry is the vertex. The equation of a parabola can be expressed in various forms, each offering a slightly different approach to finding the vertex.
Methods for Finding the Vertex
The most common forms of a parabola's equation are:
- Standard Form: y = ax² + bx + c
- Vertex Form: y = a(x - h)² + k
- Intercept Form: y = a(x - p)(x - q)
Let's examine how to find the vertex for each form:
1. Finding the Vertex from Standard Form (y = ax² + bx + c)
The standard form provides the most straightforward approach. The x-coordinate of the vertex can be calculated using the formula:
x = -b / 2a
Once you have the x-coordinate, substitute it back into the original equation to find the corresponding y-coordinate:
y = a(x)² + b(x) + c
Example:
Let's consider the parabola with the equation y = 2x² - 8x + 6.
- Here, a = 2, b = -8, and c = 6.
- Using the formula, the x-coordinate of the vertex is: x = -(-8) / (2 * 2) = 2
- Substituting x = 2 into the equation: y = 2(2)² - 8(2) + 6 = 8 - 16 + 6 = -2
Therefore, the vertex of the parabola is (2, -2).
Important Note: The parabola opens upwards if 'a' is positive and downwards if 'a' is negative. This determines whether the vertex represents a minimum or maximum point.
2. Finding the Vertex from Vertex Form (y = a(x - h)² + k)
The vertex form directly reveals the vertex's coordinates. The equation is written as:
y = a(x - h)² + k
where (h, k) represents the vertex.
Example:
Consider the parabola with the equation y = 3(x + 1)² - 4.
- This equation is already in vertex form.
- Comparing it to the general form, we find that h = -1 and k = -4.
Therefore, the vertex of this parabola is (-1, -4). Note that the sign of 'h' is reversed because it's (x - h) in the formula.
3. Finding the Vertex from Intercept Form (y = a(x - p)(x - q))
The intercept form shows the x-intercepts (where the parabola crosses the x-axis) as 'p' and 'q'. The x-coordinate of the vertex is the average of the x-intercepts:
x = (p + q) / 2
Substitute this x-coordinate back into the original equation to find the y-coordinate.
Example:
Let's consider the parabola with equation y = -1(x - 3)(x + 1).
- The x-intercepts are p = 3 and q = -1.
- The x-coordinate of the vertex is: x = (3 + (-1)) / 2 = 1
- Substituting x = 1 into the equation: y = -1(1 - 3)(1 + 1) = -1(-2)(2) = 4
Therefore, the vertex is (1, 4).
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While the methods above cover the most common scenarios, let's explore some additional techniques and considerations:
Completing the Square
If the parabola's equation is in standard form and you prefer not to use the formula, you can complete the square to transform it into vertex form. This process involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square trinomial.
Example:
Let's convert y = x² - 6x + 5 into vertex form.
- Group the x terms: y = (x² - 6x) + 5
- Find the value needed to complete the square: Take half of the coefficient of x (-6), square it ((-3)² = 9), and add and subtract this value inside the parentheses: y = (x² - 6x + 9 - 9) + 5
- Factor the perfect square trinomial: y = (x - 3)² - 9 + 5
- Simplify: y = (x - 3)² - 4
Now the equation is in vertex form, and the vertex is clearly (3, -4).
Using Calculus (for advanced users)
For those familiar with calculus, the vertex can be found by taking the derivative of the parabola's equation and setting it to zero. This finds the critical point, which corresponds to the vertex. The second derivative can determine whether the vertex is a minimum or maximum.
Dealing with Non-Standard Equations
Occasionally, you might encounter parabola equations that aren't in standard, vertex, or intercept form. In such cases, you might need to manipulate the equation algebraically to convert it into one of the recognizable forms before applying the vertex-finding methods described above. This often involves expanding or factoring expressions.
Applications of Finding the Vertex
Understanding how to locate a parabola's vertex has numerous practical applications across various disciplines:
- Physics: The trajectory of a projectile, such as a ball thrown in the air, often follows a parabolic path. The vertex represents the highest point of the trajectory.
- Engineering: Parabolic shapes are used in the design of bridges, antennas, and reflectors due to their unique reflective properties. Understanding the vertex is crucial for optimizing these designs.
- Computer Graphics: Parabolas are used to create curved shapes and paths in computer-generated imagery.
- Economics: Quadratic functions, which represent parabolas, can model certain economic relationships, with the vertex often representing an optimal point such as maximum profit or minimum cost.
- Statistics: The vertex of a parabola representing a quadratic regression model can indicate the mean or median of a dataset.
Conclusion
Finding the vertex of a parabola is a versatile skill with far-reaching applications. By understanding the different forms of a parabola's equation and the methods outlined in this guide, you can efficiently determine the vertex and gain valuable insights into the parabola's behavior and its role in various problem-solving contexts. Remember to always check your work and consider the context of the problem to ensure your results are accurate and meaningful. Mastering this skill is essential for anyone working with quadratic functions and their graphical representations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Kinetic Energy Is Energy An Object Has Because Of Its
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 40
May 09, 2025
-
48 Inches Is What In Feet
May 09, 2025
-
Rna Differs From Dna In That
May 09, 2025
-
Does Crossing Over Occur In Mitosis Or Meiosis
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find Vertex Of Parabola From Equation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.