How To Find The Perimeter For A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
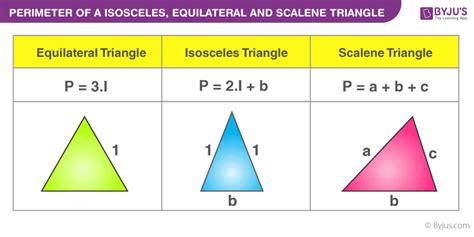
Table of Contents
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the perimeter of a triangle might seem like a simple task, especially when compared to calculating the area or solving complex geometric problems. However, understanding the different methods and applying them correctly, especially when dealing with various types of triangles, requires a solid grasp of fundamental concepts. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about calculating the perimeter of a triangle, regardless of its shape or the information provided.
Understanding the Basics: What is Perimeter?
Before diving into the specifics of triangles, let's define the term "perimeter." The perimeter of any polygon, including a triangle, is simply the total distance around its outer edges. It's the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Think of it as walking around the triangle; the perimeter is the total distance you'd cover.
Calculating the Perimeter of a Triangle: The Fundamental Approach
The most straightforward method for calculating the perimeter of a triangle involves adding the lengths of its three sides. This is true regardless of whether the triangle is equilateral, isosceles, scalene, acute, obtuse, or right-angled. The formula is concise and easy to remember:
Perimeter (P) = side a + side b + side c
Where 'a', 'b', and 'c' represent the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Example 1: Simple Perimeter Calculation
Let's say we have a triangle with sides of length 5 cm, 7 cm, and 10 cm. To find the perimeter:
P = 5 cm + 7 cm + 10 cm = 22 cm
Therefore, the perimeter of this triangle is 22 centimeters.
Different Types of Triangles and Their Perimeters
While the fundamental formula remains the same, understanding the properties of different triangle types can sometimes simplify the calculation process or provide additional insights.
1. Equilateral Triangles
An equilateral triangle is characterized by all three sides being equal in length. This simplifies the perimeter calculation significantly. If we know the length of one side ('a'), the perimeter is simply:
Perimeter (P) = 3 * a
Example 2: Equilateral Triangle Perimeter
If an equilateral triangle has a side length of 6 inches, its perimeter is:
P = 3 * 6 inches = 18 inches
2. Isosceles Triangles
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. Let's say the two equal sides have length 'a' and the third side has length 'b'. The perimeter is:
Perimeter (P) = 2 * a + b
Example 3: Isosceles Triangle Perimeter
If an isosceles triangle has two sides of 4 cm each and a third side of 6 cm, its perimeter is:
P = (2 * 4 cm) + 6 cm = 14 cm
3. Scalene Triangles
A scalene triangle has all three sides of different lengths. In this case, there's no shortcut; you must add the lengths of all three sides individually using the basic formula:
Perimeter (P) = a + b + c
Example 4: Scalene Triangle Perimeter
For a scalene triangle with sides of 3, 4, and 5 units, the perimeter is:
P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 units
Calculating Perimeter with Other Given Information
Sometimes, you might not be given the lengths of all three sides directly. You might have information about angles, area, or other related properties. In these cases, you'll need to use additional geometric principles to find the side lengths before calculating the perimeter.
1. Using Trigonometry (Right-Angled Triangles)
If you're dealing with a right-angled triangle and have information about one side and one angle (other than the right angle), you can use trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) to find the lengths of the other sides. Once you have all three side lengths, you can calculate the perimeter using the standard formula.
Example 5: Perimeter using Trigonometry
Consider a right-angled triangle with one leg of length 8 cm and an angle of 30° opposite to it. Using trigonometry:
- Opposite side / Hypotenuse = sin(30°)
- 8 cm / Hypotenuse = 0.5
- Hypotenuse = 16 cm
Using the Pythagorean theorem (a² + b² = c²), we can find the length of the other leg:
- 8² + b² = 16²
- b² = 192
- b ≈ 13.86 cm
Therefore, the perimeter is approximately 8 cm + 13.86 cm + 16 cm = 37.86 cm
2. Using Heron's Formula (Indirectly)
Heron's formula is primarily used to calculate the area of a triangle given the lengths of its three sides. However, if you know the area and the lengths of two sides, you can use Heron's formula to find the length of the third side and then calculate the perimeter. This approach is more complex and generally not the most efficient method for finding the perimeter directly.
3. Using Coordinates in a Cartesian Plane
If the vertices of the triangle are given as coordinates in a Cartesian plane (x, y), you can use the distance formula to calculate the lengths of the sides. The distance formula is derived from the Pythagorean theorem:
Distance = √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
Where (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) are the coordinates of two vertices. After calculating the lengths of all three sides, use the standard perimeter formula.
Practical Applications of Calculating Triangle Perimeters
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle extends far beyond simple geometry problems. It has numerous practical applications across various fields:
- Engineering and Construction: Determining the amount of material needed for fencing, building frameworks, or designing structural components.
- Surveying and Land Measurement: Calculating distances and boundaries of land parcels.
- Cartography and Mapmaking: Determining distances between points on a map.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: Used in algorithms for rendering and collision detection.
- Architecture and Design: In planning layouts and calculating the necessary materials for projects.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those interested in delving deeper into the world of triangle geometry, exploring concepts like:
- Triangle Inequality Theorem: This theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
- Circumradius and Inradius: These are the radii of the circumcircle and incircle of a triangle, respectively. Their relationship with the triangle's sides and area offers further avenues for calculation and analysis.
- Area Calculation Methods: Exploring different area formulas (Heron's formula, base times height) can provide additional tools for solving problems involving triangles.
Mastering the calculation of the perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry and mathematics. By understanding the basic formula and adapting your approach based on the available information, you can confidently solve a wide range of problems and apply this knowledge to practical real-world scenarios. Remember to always double-check your calculations and consider using diagrams to visualize the problem before starting your calculations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Centimeters Are In 50 Millimeters
May 09, 2025
-
Describe The Epithelium Found In The Uterine Tube
May 09, 2025
-
What Animal Lay Eggs And Is Not A Bird
May 09, 2025
-
Label The Anatomy Of The Male
May 09, 2025
-
Electrical Resistivity Of A Given Metallic Wire Depends Upon
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find The Perimeter For A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.