How To Find No Of Neutrons
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
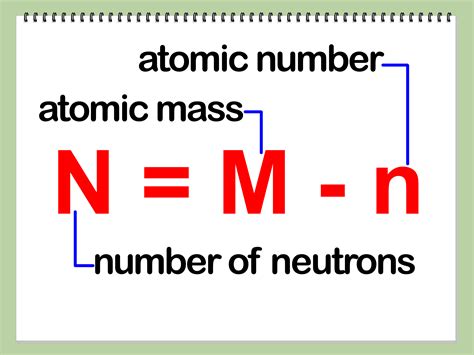
Table of Contents
- How To Find No Of Neutrons
- Table of Contents
- How to Find the Number of Neutrons: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- The Importance of Atomic Number and Mass Number
- Calculating the Number of Neutrons: The Formula
- How to Find the Atomic Number and Mass Number
- Locating the Atomic Number on the Periodic Table
- Identifying the Mass Number: Isotopes and Isotopic Notation
- Average Atomic Mass and Natural Abundance
- Practical Examples: Calculating Neutron Numbers
- Beyond the Basics: Applications and Advanced Concepts
- Advanced Considerations: Nuclear Stability and Isotope Abundance
- Conclusion: Mastering Neutron Calculation
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How to Find the Number of Neutrons: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the number of neutrons in an atom is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics. Understanding this allows us to grasp the properties of elements and isotopes, predict nuclear reactions, and even delve into the intricacies of nuclear energy. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to confidently calculate the number of neutrons in any atom, regardless of its complexity.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we dive into the calculations, let's refresh our understanding of atomic structure. An atom consists of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also residing in the atom's nucleus. Neutrons contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The key to finding the number of neutrons lies in understanding the relationship between these particles and the atom's mass number.
The Importance of Atomic Number and Mass Number
To determine the number of neutrons, we need two crucial pieces of information:
-
Atomic Number (Z): This is the number of protons in the atom's nucleus. It uniquely identifies the element and can be found on the periodic table. For example, the atomic number of carbon (C) is 6, meaning every carbon atom has 6 protons.
-
Mass Number (A): This represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus. It's an approximation of the atom's total mass and is usually a whole number. Mass numbers are often included in isotopic notation, like ¹²C, where the superscript 12 is the mass number.
Calculating the Number of Neutrons: The Formula
The relationship between the number of protons (Z), neutrons (N), and the mass number (A) is elegantly simple:
A = Z + N
Therefore, to find the number of neutrons (N), we rearrange the formula:
N = A - Z
This formula is the cornerstone of neutron calculation. By knowing the mass number and atomic number, we can directly calculate the number of neutrons.
How to Find the Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number is readily available on the periodic table. Every element has its unique atomic number listed. However, finding the mass number requires a bit more attention.
Locating the Atomic Number on the Periodic Table
The periodic table is your go-to resource for the atomic number. Each element's symbol (e.g., H for hydrogen, O for oxygen) is accompanied by its atomic number, typically located above or below the symbol.
Identifying the Mass Number: Isotopes and Isotopic Notation
Unlike the atomic number, the mass number isn't a fixed value for an element. This is due to the existence of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with differing numbers of neutrons. This leads to variations in the atom's mass.
Isotopic notation is used to represent isotopes. It follows this format:
^A_Z X
Where:
- A is the mass number (protons + neutrons)
- Z is the atomic number (number of protons)
- X is the element's symbol
For example, ¹²C represents a carbon-12 isotope with a mass number of 12 and an atomic number of 6 (you can find this on the periodic table). Another carbon isotope, ¹⁴C (carbon-14), has a mass number of 14.
Average Atomic Mass and Natural Abundance
Often, you might encounter the average atomic mass of an element on the periodic table. This value is a weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element, considering their relative abundances. While it provides the average mass, it doesn't directly provide the mass number of a specific isotope. To determine the number of neutrons, you need the mass number of a specific isotope.
Practical Examples: Calculating Neutron Numbers
Let's illustrate the calculation process with several examples:
Example 1: Carbon-12 (¹²C)
- Identify the mass number (A): A = 12
- Find the atomic number (Z) from the periodic table: Z = 6 (for Carbon)
- Calculate the number of neutrons (N): N = A - Z = 12 - 6 = 6
Therefore, carbon-12 has 6 neutrons.
Example 2: Uranium-235 (²³⁵U)
- Identify the mass number (A): A = 235
- Find the atomic number (Z) from the periodic table: Z = 92 (for Uranium)
- Calculate the number of neutrons (N): N = A - Z = 235 - 92 = 143
Therefore, uranium-235 has 143 neutrons.
Example 3: Oxygen-16 (¹⁶O)
- Identify the mass number (A): A = 16
- Find the atomic number (Z) from the periodic table: Z = 8 (for Oxygen)
- Calculate the number of neutrons (N): N = A - Z = 16 - 8 = 8
Therefore, oxygen-16 has 8 neutrons.
Beyond the Basics: Applications and Advanced Concepts
The ability to calculate the number of neutrons has far-reaching implications across various scientific fields:
-
Nuclear Chemistry: Understanding isotopic composition is crucial for nuclear reactions, radioactive decay, and nuclear energy applications. The number of neutrons significantly influences nuclear stability and reactivity.
-
Nuclear Medicine: Many medical isotopes used in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures have specific neutron counts that determine their decay properties and suitability for specific applications.
-
Geochronology: Radioactive isotopes with specific neutron numbers are used for dating geological samples and determining the age of rocks and fossils.
-
Material Science: The number of neutrons influences the properties of materials, particularly in nuclear materials and advanced materials research.
Advanced Considerations: Nuclear Stability and Isotope Abundance
While the formula N = A - Z provides a straightforward calculation, understanding the factors influencing nuclear stability adds another layer of complexity. Nuclear stability is significantly influenced by the neutron-to-proton ratio. For lighter elements, a ratio close to 1:1 is generally stable. However, heavier elements require a higher neutron-to-proton ratio for stability. This explains why many heavier isotopes are radioactive.
The abundance of each isotope also plays a role in interpreting average atomic mass values. Some isotopes are far more common in nature than others. Understanding isotope abundance is essential for accurate calculations involving natural samples.
Conclusion: Mastering Neutron Calculation
Calculating the number of neutrons in an atom is a fundamental skill for anyone studying chemistry, physics, or related fields. By understanding atomic structure, using the simple formula N = A - Z, and accessing the necessary information from the periodic table, you can confidently determine the number of neutrons in any given atom. Remember to always clearly identify the specific isotope you are working with, as the mass number varies among isotopes of the same element. This knowledge is a stepping stone to understanding the complexities of nuclear physics and its widespread applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Two Types Of Currents
Mar 16, 2025
-
Alternative Forms Of The Same Gene Are Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Is Heavier A Pound Or A Kilogram
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Energy An Object Has Because Of Its Motion
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Hottest Part Of Earth
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find No Of Neutrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
