How To Find An Area Of A Square
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
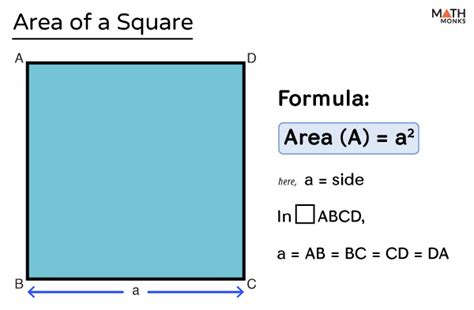
Table of Contents
How to Find the Area of a Square: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the area of a square is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from basic geometry to advanced engineering. This comprehensive guide will walk you through different methods, explain the underlying principles, and offer practical examples to solidify your understanding. Whether you're a student brushing up on your geometry skills or an adult revisiting fundamental math concepts, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to calculate the area of any square.
Understanding Squares and Their Properties
Before diving into the area calculation, let's establish a clear understanding of what a square is. A square is a two-dimensional geometric shape with four equal sides and four right angles (90-degree angles). This specific combination of properties distinguishes it from other quadrilaterals like rectangles, parallelograms, and rhombuses. The equal sides and right angles are key to the simple formula used for calculating its area.
The Fundamental Formula: Side Squared
The most straightforward and widely used method for calculating the area of a square relies on a single measurement: the length of one of its sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, knowing the length of one side is enough to determine its area. The formula is elegantly simple:
Area = side * side = side²
This means you simply multiply the length of one side by itself (or square it). The resulting value represents the area of the square. The unit of measurement for the area will be the square of the unit used for the side length (e.g., if the side is measured in centimeters, the area will be in square centimeters (cm²)).
Example 1: A Simple Calculation
Let's say we have a square with a side length of 5 centimeters. Using the formula:
Area = 5 cm * 5 cm = 25 cm²
The area of the square is 25 square centimeters.
Example 2: Working with Decimals
The formula works equally well with decimal side lengths. Consider a square with a side length of 3.5 meters.
Area = 3.5 m * 3.5 m = 12.25 m²
The area of the square is 12.25 square meters.
Example 3: Using Fractions
Even if the side length is expressed as a fraction, the process remains the same. For a square with a side of ¾ inches:
Area = (¾ in) * (¾ in) = ⁹⁄₁₆ in²
The area of the square is ⁹⁄₁₆ square inches. This can be converted to a decimal (0.5625 square inches) if needed.
Alternative Methods and Advanced Concepts
While the side-squared method is the most efficient, understanding alternative approaches can broaden your perspective and problem-solving skills.
Using the Diagonal
Although less common, it’s possible to calculate the area of a square if you only know its diagonal length. This method involves using the Pythagorean theorem. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In a square, the diagonal acts as the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle formed by two adjacent sides. Let's denote the diagonal as 'd' and the side length as 's'. The Pythagorean theorem gives us:
d² = s² + s² = 2s²
Solving for s², we get:
s² = d²/2
Since the area is s², we can directly substitute:
Area = d²/2
This formula allows us to calculate the area using only the diagonal length.
Example 4: Calculating Area from the Diagonal
Suppose the diagonal of a square is 10 meters. Using the formula:
Area = (10 m)² / 2 = 100 m² / 2 = 50 m²
The area of the square is 50 square meters.
Relating Area to Perimeter
The perimeter of a square is the total length of its four sides. Since all sides are equal, the perimeter (P) is simply four times the side length (s):
P = 4s
We can rearrange this equation to find the side length:
s = P/4
Substituting this into the area formula, we get:
Area = (P/4)² = P²/16
This allows us to calculate the area if only the perimeter is known.
Example 5: Calculating Area from Perimeter
Let's assume a square has a perimeter of 24 centimeters. Using the formula:
Area = (24 cm)² / 16 = 576 cm² / 16 = 36 cm²
The area of the square is 36 square centimeters.
Practical Applications of Calculating Square Area
The ability to calculate the area of a square has wide-ranging applications in various fields:
- Construction and Engineering: Determining the amount of material needed for flooring, roofing, or wall covering.
- Land Surveying: Calculating the area of square-shaped land parcels.
- Interior Design: Planning room layouts and furniture arrangements.
- Gardening and Landscaping: Designing garden beds and pathways.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: Creating and manipulating 2D shapes and objects.
- Manufacturing and Production: Calculating the surface area of components.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Even a seemingly simple calculation can lead to errors if not approached carefully. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Incorrect Unit Conversion: Ensure all measurements are in the same units before performing the calculation. Converting units incorrectly is a frequent source of errors.
- Misunderstanding the Formula: Double-check the formula and make sure you're using the correct one based on the information provided (side length, diagonal, or perimeter).
- Calculation Errors: Use a calculator or double-check your manual calculations to minimize the possibility of arithmetic mistakes.
- Forgetting Units: Always include the appropriate square units (cm², m², in², etc.) in your final answer.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Scenarios
While we've focused on calculating the area of simple squares, the concept extends to more complex situations. For instance, you might encounter problems involving:
- Squares within squares: Calculate the area of the inner and outer squares to find the area of the region between them.
- Squares combined with other shapes: Calculate the areas of the individual shapes and add them together to find the total area.
- Squares in three-dimensional contexts: Applying the area calculation to the faces of cubes or other three-dimensional shapes.
Mastering the basic formula and understanding its variations will equip you to tackle these more complex scenarios effectively.
Conclusion
Finding the area of a square, while a seemingly simple task, underpins many practical applications and deeper mathematical concepts. Understanding the fundamental formula, its alternative derivations, and potential pitfalls ensures accuracy and confidence in your calculations. By practicing with various examples and exploring different approaches, you'll develop a robust understanding of this essential geometrical concept. Remember to always double-check your work and pay close attention to units to avoid common mistakes. With consistent practice and a clear understanding of the principles, calculating the area of a square will become second nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Four Letter Words From A To Z
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Big Is 5cm By 5cm
Mar 10, 2025
-
5 Letter Words Ending With On
Mar 10, 2025
-
Which Of These Statements Is True
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 2 5 As A Percent
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find An Area Of A Square . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
