How Many Valence Electrons Are In Be
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
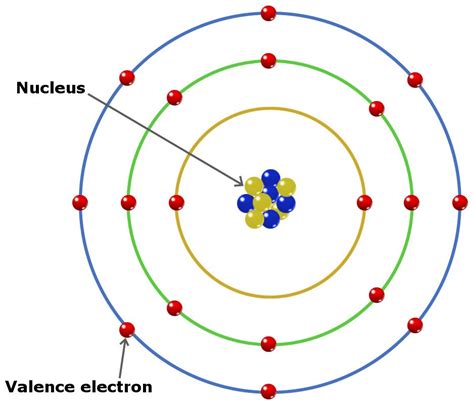
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons are in Be? Understanding Beryllium's Reactivity
Beryllium (Be), an intriguing alkaline earth metal, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is crucial to comprehending its chemical behavior and properties. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of beryllium, explaining not only its valence electron count but also the implications of this count for its reactivity, bonding characteristics, and applications.
Unveiling Beryllium's Electron Configuration
To determine the number of valence electrons in beryllium, we need to explore its electron configuration. The electron configuration describes how electrons are distributed among the different energy levels and orbitals within an atom. Beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, possesses four electrons in total. These electrons are arranged according to the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, filling the lowest energy levels first.
The Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule in Action
The Aufbau principle dictates that electrons fill atomic orbitals in order of increasing energy levels. The lowest energy level is the 1s orbital, which can accommodate a maximum of two electrons. Following this, the next lowest energy level is the 2s orbital, which also holds a maximum of two electrons.
Hund's rule states that electrons will individually occupy each orbital within a subshell before doubling up in any one orbital. This means that electrons will first fill each orbital singly, with parallel spins, before pairing up in the same orbital with opposite spins.
Therefore, the electron configuration of beryllium is 1s²2s².
Determining the Valence Electrons: The Outermost Shell
Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost electron shell of an atom. These electrons are most involved in chemical bonding and determine an element's chemical reactivity. In the case of beryllium, the outermost shell is the second shell (n=2), which contains two electrons in the 2s orbital.
Consequently, beryllium has 2 valence electrons.
Implications of Two Valence Electrons: Reactivity and Bonding
The presence of two valence electrons significantly influences beryllium's chemical behavior. Elements strive for stability, often achieved by acquiring a full outer electron shell (octet rule). For beryllium, this means either losing its two valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration like helium (1s²) or, less commonly, sharing electrons to form covalent bonds.
Beryllium's Preference: Ionic Bonding
Beryllium readily loses its two valence electrons to form a +2 cation (Be²⁺). This ionic bonding is prevalent in its compounds. The loss of these electrons leads to a stable electron configuration, making the process energetically favorable.
Covalent Bonding: A Less Common Occurrence
While ionic bonding is more characteristic of beryllium, it can also participate in covalent bonding, particularly with highly electronegative elements like fluorine and oxygen. In these cases, beryllium shares its two valence electrons to form stable covalent bonds.
Exploring Beryllium's Properties and Applications
The unique properties of beryllium are directly related to its electronic structure and the number of its valence electrons. These properties lead to a variety of applications:
Lightweight and High Strength: Aerospace Applications
Beryllium's low density coupled with its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it invaluable in aerospace applications. It's used in high-speed aircraft, spacecraft, and missiles, where weight reduction is critical.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity: Heat Management
Beryllium possesses an exceptional thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. This property finds use in high-precision instruments, electronics, and heat sinks.
Transparency to X-rays: Medical Imaging
Beryllium's transparency to X-rays makes it a crucial material for X-ray windows in medical imaging equipment. This allows for clear transmission of X-rays without significant attenuation.
Nuclear Applications: Neutron Moderation
Beryllium's ability to moderate neutrons finds application in nuclear reactors. It is used to slow down neutrons, enhancing their interaction with nuclear fuel.
The Chemical Reactivity of Beryllium: A Closer Look
While beryllium possesses only two valence electrons, its reactivity is not as straightforward as it might initially seem. The relatively small size of the beryllium atom and the high effective nuclear charge (the positive charge experienced by valence electrons) result in a higher ionization energy compared to other alkaline earth metals. This means it requires more energy to remove the valence electrons, impacting its overall reactivity.
Reactivity with Water and Acids
Beryllium reacts slowly with water and dilute acids, unlike the more reactive alkaline earth metals. This slow reactivity is linked to the formation of a protective oxide layer on the surface of the beryllium, which hinders further reaction.
Reactivity with Halogens and Oxygen
Beryllium reacts readily with halogens (e.g., fluorine, chlorine) and oxygen to form stable beryllium halides (BeX₂) and beryllium oxide (BeO), respectively. These reactions are exothermic, releasing energy as the stable compounds are formed.
Safety Considerations: Working with Beryllium
Beryllium's unique properties also necessitate careful consideration of its safety implications. Beryllium and its compounds can pose significant health risks, especially if inhaled as a fine dust. This exposure can lead to chronic beryllium disease (CBD), a serious lung condition. Therefore, appropriate safety measures and handling procedures are essential when working with beryllium and its compounds.
Conclusion: Beryllium's Significance in Science and Technology
Beryllium, with its two valence electrons, plays a vital role in various scientific and technological fields. Its unique properties, stemming directly from its electronic configuration, make it a valuable material for aerospace, medical, nuclear, and other advanced applications. However, careful consideration must be given to its toxicity, emphasizing the importance of safe handling and usage. Understanding the fundamental aspects of beryllium's electronic structure, especially the number of valence electrons and its consequences, is essential for appreciating its significance and potential, while also mitigating its associated risks. This knowledge forms a crucial foundation for continued research and development in various fields reliant on this remarkable element.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 24 And 14
Mar 18, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 2 And 8
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Sentence That Shows Strong Or Sudden Feeling
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is Used To Split Things Apart
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Turns Of Calvin Cycle For One Glucose
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Are In Be . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
