How Many Protons Are In Potassium
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
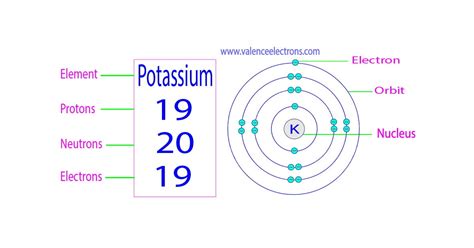
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Are in Potassium? Unpacking Atomic Structure and its Significance
Potassium, a vital element for life, plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of protons it possesses, is fundamental to grasping its chemical behavior and biological function. This comprehensive guide delves into the details of potassium's atomic makeup, exploring the concept of atomic number, isotopes, and the implications of proton count in various fields.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Foundation of Chemistry
Before diving into the specifics of potassium, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. Every atom consists of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's identity.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also residing in the nucleus. Their number can vary within an element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The atomic number of an element is the defining characteristic, representing the number of protons in its nucleus. This number is unique to each element and is used to organize the periodic table. Knowing the atomic number allows us to identify an element and predict its chemical properties.
Potassium: A Biological Superstar
Potassium (K), with its atomic number of 19, plays an indispensable role in various biological processes. Its importance stems directly from its atomic structure and, most importantly, the 19 protons within its nucleus. This determines its electron configuration and its reactivity. This reactivity is crucial for functions like:
- Maintaining electrolyte balance: Potassium ions (K⁺) are vital for maintaining the proper balance of fluids and electrolytes within cells and the body. This balance is crucial for nerve and muscle function.
- Nerve impulse transmission: The movement of potassium ions across cell membranes is essential for the transmission of nerve impulses. The precise number of protons in the potassium atom dictates its ionic charge and its interaction with other charged particles in the nervous system.
- Muscle contraction: Potassium ions also participate in muscle contraction, ensuring coordinated muscle movement. The electrochemical gradients established by potassium are key to the process.
- Regulation of blood pressure: Proper potassium levels contribute to maintaining healthy blood pressure. Imbalances can lead to serious health consequences.
- Enzyme activation: Potassium acts as a cofactor for several enzymes, influencing a wide array of metabolic reactions. The presence of 19 protons facilitates the correct interactions needed for enzymatic activity.
Isotopes of Potassium: Variations on a Theme
While the number of protons always remains 19 for potassium, the number of neutrons can vary. These variations result in different isotopes of potassium. The most common isotopes are:
- Potassium-39 (³⁹K): This is the most abundant isotope, comprising about 93.3% of naturally occurring potassium. It has 19 protons and 20 neutrons.
- Potassium-40 (⁴⁰K): A radioactive isotope present in trace amounts (0.012%). It has 19 protons and 21 neutrons. Its radioactivity is significant in geological dating and has implications for biological systems, albeit at low levels.
- Potassium-41 (⁴¹K): This stable isotope comprises about 6.7% of naturally occurring potassium. It contains 19 protons and 22 neutrons.
The presence of different isotopes doesn't alter the chemical properties significantly because the number of protons (and thus, electrons) remains constant. However, the different masses of isotopes can influence physical properties like the rate of diffusion. The radioactivity of ⁴⁰K plays a unique role in various applications.
The Significance of the 19 Protons: Implications in Various Fields
The fact that potassium has 19 protons isn't just an academic detail. This fundamental aspect of its atomic structure has significant implications across diverse fields:
1. Biology and Medicine:
The 19 protons in potassium define its chemical behavior, making it an essential electrolyte. In medicine, potassium levels are closely monitored, and imbalances can be addressed through dietary adjustments or medication. The precise number of protons dictates how potassium ions interact with other ions and molecules within the body.
2. Agriculture:
Potassium is a crucial macronutrient for plant growth. Understanding its atomic structure helps in developing fertilizers and optimizing nutrient uptake in plants. The proper potassium levels are essential for healthy plant development and yield. The number of protons directly relates to potassium's reactivity and its ability to support plant physiological processes.
3. Geology and Dating:
The radioactive isotope ⁴⁰K is used in radiometric dating techniques. By measuring the ratio of ⁴⁰K to its decay products (⁴⁰Ar and ⁴⁰Ca), geologists can determine the age of rocks and minerals. The presence of 19 protons in ⁴⁰K, despite its radioactivity, does not alter the principle used for dating.
4. Industrial Applications:
Potassium and its compounds have various industrial applications. For example, potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used in the production of soaps and detergents. The chemical reactivity inherent to its 19 protons plays a crucial role in these applications.
5. Nuclear Physics:
The study of potassium's isotopes, especially the radioactive ⁴⁰K, provides valuable insights into nuclear physics, including radioactive decay processes and nuclear reactions. The understanding of its atomic structure, including the 19 protons, is crucial for analyzing its nuclear behavior.
Conclusion: The Importance of Atomic Precision
The simple fact that potassium has 19 protons is fundamental to understanding its numerous roles in biology, chemistry, geology, and other fields. This seemingly small number dictates its chemical reactivity, its biological function, and its applications in various technologies. From maintaining electrolyte balance in the human body to assisting in radiometric dating of ancient rocks, the significance of potassium's 19 protons cannot be overstated. This number provides the key to unlocking a deeper understanding of this essential element and its multifaceted influence on the world around us. Further research continues to unravel the intricate details of potassium's interactions and its contributions to various scientific fields. The foundational knowledge of atomic structure, and particularly the precise proton count, remains paramount to ongoing advancements in these diverse disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Relationship Between Concentration And Rate Of Reaction
Apr 08, 2025
-
6 Faces 12 Edges And 8 Vertices
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Is The Motor End Plate
Apr 08, 2025
-
How Big Is 18cm In Inches
Apr 08, 2025
-
Two Compounds A And B Have The Formula
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Are In Potassium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.