How Many Lines Of Symmetry In A Circle
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
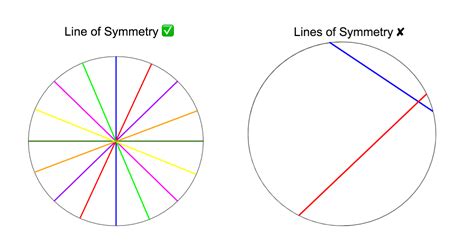
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Circle Have? An In-Depth Exploration
The seemingly simple question, "How many lines of symmetry does a circle have?" leads to a fascinating exploration of geometry, symmetry, and the very definition of these concepts. While the intuitive answer might be "infinite," a rigorous mathematical understanding requires delving deeper. This article will explore this question comprehensively, examining different perspectives and clarifying any potential misunderstandings.
Understanding Symmetry and Lines of Symmetry
Before we tackle the circle, let's solidify our understanding of symmetry and lines of symmetry. Symmetry, in its simplest form, refers to a balanced proportion of an object. A figure is symmetrical if it can be divided into two or more identical parts that are mirror images of each other. This division is often achieved using lines of symmetry.
A line of symmetry, also known as an axis of symmetry, is a line that divides a shape into two congruent halves that are mirror reflections of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap.
Consider a square. It has four lines of symmetry: two that run horizontally and vertically through the center, and two that run diagonally from corner to corner. An equilateral triangle possesses three lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side. These examples illustrate the concept clearly; however, the circle presents a unique and more complex case.
Exploring the Symmetry of a Circle: The Intuitive Approach
Intuitively, it's easy to visualize numerous lines passing through the center of a circle, dividing it into two perfectly symmetrical halves. No matter which direction you draw a line through the center, the resulting halves are mirror images. This seemingly endless possibility leads to the often-stated answer: an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
This intuitive approach captures the essence of the circle's symmetry. The rotational symmetry of a circle, where it can be rotated about its center by any angle and remain unchanged, further reinforces this sense of infinite symmetry. However, the mathematical definition of a line requires a more precise analysis.
The Mathematical Perspective: Lines and Infinity
Mathematically, a line extends infinitely in both directions. While we can draw countless lines through the center of a circle, each representing a line of symmetry, the concept of "infinity" needs careful consideration. The set of all real numbers is infinite, yet it is still a well-defined mathematical concept. Similarly, we can conceptualize the infinite lines of symmetry in a circle.
It is crucial to understand that "infinity" doesn't mean a countably large number like a billion or a trillion. It signifies a quantity beyond any finite number, exceeding any possible numerical value. The number of lines of symmetry in a circle is therefore considered infinite.
Differentiating between Lines of Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry
It is important to distinguish between lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry. While a circle has infinite lines of symmetry, it also possesses infinite rotational symmetry. This means the circle can be rotated around its center by any angle and still look exactly the same.
This rotational symmetry is a separate, yet related, property of the circle, not directly part of the count of lines of symmetry. While both demonstrate the circle's symmetrical nature, the lines of symmetry specifically refer to the lines dividing the shape into identical mirror halves.
Practical Applications and Implications
The concept of infinite lines of symmetry in a circle extends beyond theoretical geometry. It has various practical applications and implications across diverse fields:
-
Design and Art: The circle's inherent symmetry is widely utilized in art, design, and architecture. Its balanced and harmonious nature makes it a foundational element in creating visually appealing and aesthetically pleasing compositions. From mandalas to architectural designs, the circle's infinite symmetry is a cornerstone of visual balance.
-
Engineering and Physics: In engineering and physics, the symmetry of a circle simplifies complex calculations and simulations. The rotational symmetry allows for simplified models and analyses in various contexts, such as fluid dynamics or structural mechanics.
-
Nature and Biology: The circle's symmetrical properties are frequently observed in nature. From the circular arrangement of sunflower seeds to the near-perfect spherical shape of planets and stars, nature demonstrates the elegance and efficiency of this type of symmetry.
-
Mathematics and Geometry: The study of circles and their symmetries forms a fundamental part of higher-level mathematics and geometry. The concepts of infinite sets and continuous transformations are intrinsically linked to the properties of circles, advancing our understanding of advanced mathematical principles.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
It's important to address common misconceptions related to the circle's symmetry:
-
Finite Lines: Some might argue that only a finite number of lines can be drawn through the center. This is true practically, given limitations in drawing tools. However, the mathematical definition of a line is not constrained by physical limitations.
-
Discrete vs. Continuous: The lines of symmetry in a circle are not discrete individual lines, but rather form a continuous set. This distinction is vital for understanding the concept of infinity in this context.
-
Overlapping Lines: While drawing multiple lines through the center might lead to some overlapping, this does not diminish the fact that infinitely many such lines exist.
Conclusion: The Infinite Symmetry of the Circle
In conclusion, while the intuitive answer "infinite" seems appropriate, a deeper understanding requires considering the mathematical definitions of lines, symmetry, and infinity. The circle possesses an infinite number of lines of symmetry, each dividing it into two congruent halves. This unique property has profound implications across multiple disciplines, showcasing the circle's significance in geometry, design, engineering, nature, and beyond. The concept of infinite lines of symmetry in a circle is not just a mathematical curiosity; it’s a fundamental principle with far-reaching applications and implications. The exploration of this concept highlights the beauty and depth of mathematical concepts and their influence on our world. The circle's infinite symmetry serves as a testament to the elegance and power of mathematical principles in shaping our understanding of the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lcm Of 6 9 And 12
Mar 15, 2025
-
1 Out Of 7 Is What Percentage
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Amount Of Matter In An Object Is Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Characteristics Of Skeletal Muscle
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is 4 A Multiple Of 8
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry In A Circle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
