How Many Lines Of Symmetry Has A Pentagon
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
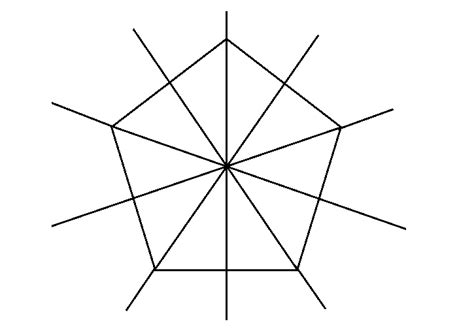
Table of Contents
- How Many Lines Of Symmetry Has A Pentagon
- Table of Contents
- How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Pentagon Have? Exploring Symmetry in Regular and Irregular Pentagons
- Defining Lines of Symmetry
- Regular Pentagon: A Perfect Balance
- Determining the Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Pentagon
- Irregular Pentagons: A Different Story
- Lines of Symmetry in Irregular Pentagons: The Variability
- Mathematical Proof for Regular Pentagon's Symmetry
- Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
- Identifying Lines of Symmetry: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Conclusion: Symmetry's Significance in Geometry
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Pentagon Have? Exploring Symmetry in Regular and Irregular Pentagons
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and geometry, describes the harmonious balance and proportion within a shape. Understanding lines of symmetry is crucial to comprehending a shape's properties and characteristics. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of pentagons and their lines of symmetry, differentiating between regular and irregular pentagons and exploring the mathematical principles behind their symmetrical properties. We'll examine various examples and provide practical ways to identify lines of symmetry in pentagons.
Defining Lines of Symmetry
Before we explore the symmetries of pentagons, let's clearly define what a line of symmetry is. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, both halves would perfectly overlap. Not all shapes possess lines of symmetry; some shapes may have none, while others can have multiple.
Regular Pentagon: A Perfect Balance
A regular pentagon is a five-sided polygon where all five sides are equal in length, and all five interior angles are equal (each measuring 108°). This perfect uniformity directly impacts its symmetry. A regular pentagon exhibits a higher degree of symmetry compared to its irregular counterparts.
Determining the Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has five lines of symmetry. These lines can be visualized in two ways:
-
Lines of symmetry through vertices and midpoints of opposite sides: Draw a line from one vertex (corner) to the midpoint of the opposite side. Repeat this process for each vertex. You'll find five such lines, each acting as a line of symmetry.
-
Lines of symmetry through midpoints of opposite sides (Illustrative): It is also possible, although less common to conceptualize, to think of the lines of symmetry as running directly through the midpoints of opposite sides. Imagine connecting the midpoints of two sides that are directly across from each other. You will again find five such lines that represent lines of symmetry.
Visualizing the Symmetry: Imagine folding a regular pentagon along any of these five lines. The two halves will perfectly overlap, confirming their symmetrical nature. The existence of these five lines of symmetry is a direct consequence of the regular pentagon's equal sides and angles. This perfect balance ensures that the shape remains identical regardless of how it’s rotated or reflected.
Irregular Pentagons: A Different Story
An irregular pentagon, unlike its regular counterpart, doesn't have the constraint of equal sides and angles. Its sides and angles can vary in length and measure. This variation significantly impacts the number of lines of symmetry.
Lines of Symmetry in Irregular Pentagons: The Variability
Irregular pentagons may have zero, one, or at most, five lines of symmetry. However, it is highly unusual for an irregular pentagon to possess more than one line of symmetry. The probability of an irregular pentagon having multiple lines of symmetry is extremely low, almost negligible. Most irregular pentagons will exhibit no symmetry at all.
Example Scenarios:
-
Zero lines of symmetry: The vast majority of randomly drawn irregular pentagons will have no lines of symmetry. The asymmetry of their sides and angles prevents any such line from existing.
-
One line of symmetry: A rare case would be an irregular pentagon with a single line of symmetry. This would require a very specific arrangement of its sides and angles, leading to a bilateral symmetry where only one line divides it into mirror images.
-
More than one line of symmetry (Highly Unlikely): It's theoretically possible for an irregular pentagon to have more than one line of symmetry, but the probability is extremely low. This would involve a highly specific and improbable combination of side and angle lengths and measures. Essentially, such a pentagon would approach the characteristics of a regular pentagon.
Mathematical Proof for Regular Pentagon's Symmetry
The existence of five lines of symmetry in a regular pentagon can be mathematically proven using rotational symmetry. A regular pentagon has rotational symmetry of order 5. This means it can be rotated about its center by 72° (360°/5) and still appear unchanged. Each of these five rotational positions corresponds to a line of symmetry.
Furthermore, the five lines of symmetry are also reflective symmetries, each dividing the pentagon into two congruent halves that are mirror images of each other. These reflective symmetries are directly related to the rotational symmetries, and together, they completely define the symmetrical properties of the regular pentagon.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding lines of symmetry has practical applications in various fields:
-
Design and Art: Artists and designers use symmetry principles extensively to create visually appealing and balanced compositions. The regular pentagon's symmetry is often used in creating logos, patterns, and architectural designs.
-
Engineering and Architecture: Symmetrical structures are often more stable and efficient. The understanding of symmetrical properties is crucial in designing bridges, buildings, and other structures.
-
Nature: Symmetrical patterns frequently appear in nature, such as in the arrangement of petals in some flowers (although five-petaled flowers are not always perfectly symmetrical). The understanding of symmetry provides insights into natural processes and patterns.
Identifying Lines of Symmetry: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s a simple guide to help you identify lines of symmetry in any polygon, including pentagons:
-
Visual Inspection: Examine the shape carefully. Look for lines that might divide the shape into two identical mirror image halves.
-
Folding Test (for physical shapes): If you have a physical representation of the pentagon (e.g., a cutout), try folding it along different lines. If the two halves overlap perfectly, you've found a line of symmetry.
-
Geometric Analysis (for diagrams): If you have a diagram of the pentagon, carefully measure the lengths of the sides and the angles. Look for relationships that might suggest symmetry.
-
Software Tools: Several software applications (CAD programs, graphic design software) can help you identify lines of symmetry using automated tools and functions.
Conclusion: Symmetry's Significance in Geometry
The number of lines of symmetry in a pentagon depends heavily on whether it's regular or irregular. While a regular pentagon boasts five lines of symmetry, reflecting its perfect balance, irregular pentagons typically exhibit far less symmetry, often possessing zero or just one line of symmetry. Understanding the relationship between a shape's properties (such as side lengths and angles) and its lines of symmetry is fundamental to grasping the principles of geometric symmetry. The concepts explored here have far-reaching implications in various fields, showcasing the practical importance and aesthetic appeal of symmetry in both mathematics and the real world. Further exploration into other polygons and their symmetry characteristics can deepen your understanding of geometric concepts and their applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Moles In One Liter Of Water
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Are The Factor Pairs For 15
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Has A Pentagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
