How Many Electrons Does Mn Have
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
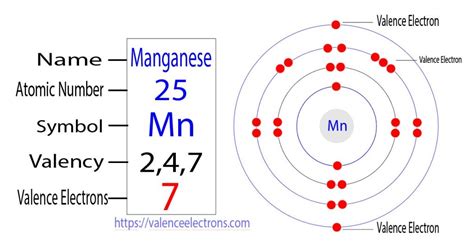
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons Does Mn Have? Exploring the Electron Configuration of Manganese
Manganese (Mn), a fascinating transition metal, plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of electrons it possesses, is fundamental to comprehending its properties and behavior. This comprehensive article delves into the electron configuration of manganese, explaining how to determine the number of electrons, its implications for chemical reactivity, and its significance in different fields.
Determining the Number of Electrons in Manganese
The number of electrons an atom possesses is directly related to its atomic number. The atomic number, denoted by 'Z', represents the number of protons in the atom's nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. For manganese, the atomic number is 25.
Therefore, a neutral manganese atom has 25 electrons.
This seemingly simple statement opens the door to a deeper understanding of manganese's chemical behavior and its place in the periodic table.
Electron Configuration and Orbital Filling
The electrons in an atom aren't randomly distributed. They occupy specific energy levels and sublevels, governed by the principles of quantum mechanics. This arrangement is known as the electron configuration. Understanding the electron configuration helps us predict the chemical properties of an element.
The electron configuration of manganese is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d⁵.
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: Two electrons occupy the first energy level (n=1), in the s subshell. The superscript '2' indicates two electrons.
- 2s²: Two electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2), in the s subshell.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2), in the p subshell. The p subshell can hold a maximum of six electrons.
- 3s²: Two electrons occupy the third energy level (n=3), in the s subshell.
- 3p⁶: Six electrons occupy the third energy level (n=3), in the p subshell.
- 4s²: Two electrons occupy the fourth energy level (n=4), in the s subshell. Note that the 4s subshell fills before the 3d subshell.
- 3d⁵: Five electrons occupy the third energy level (n=3), in the d subshell. The d subshell can hold a maximum of ten electrons.
The filling of orbitals follows the Aufbau principle (filling lower energy levels first), Hund's rule (maximizing unpaired electrons in degenerate orbitals), and the Pauli exclusion principle (no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers).
Manganese's Variable Oxidation States
The incompletely filled 3d subshell is the key to understanding manganese's diverse chemistry. Manganese exhibits a wide range of oxidation states, from +2 to +7. This means it can lose different numbers of electrons to form various ions. This versatility is a hallmark of transition metals.
Some common oxidation states and their corresponding ions are:
- Mn²⁺ (Manganese(II) ion): Loses two electrons, leaving a configuration similar to that of Chromium.
- Mn³⁺ (Manganese(III) ion): Loses three electrons.
- Mn⁴⁺ (Manganese(IV) ion): Loses four electrons.
- Mn⁷⁺ (Manganese(VII) ion): Loses seven electrons, found in permanganate (MnO₄⁻) which is a powerful oxidizing agent.
The ability to exist in multiple oxidation states contributes to manganese's catalytic activity in various chemical reactions.
The Significance of Manganese in Biology and Industry
Manganese's diverse properties make it crucial in various biological and industrial processes:
Biological Roles of Manganese
- Enzyme cofactor: Manganese acts as a cofactor in numerous enzymes, playing a crucial role in various metabolic pathways. These enzymes participate in processes such as photosynthesis, bone formation, and lipid metabolism.
- Antioxidant defense: Manganese-containing enzymes contribute to the body's antioxidant defense system, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Essential nutrient: Manganese is an essential trace mineral for humans and other organisms. Dietary deficiency can lead to various health problems.
Industrial Applications of Manganese
- Steel production: Manganese is a vital component in steel production, enhancing its strength, hardness, and toughness. It's added to steel to improve its workability and resistance to wear and tear.
- Aluminum alloys: Manganese is used in aluminum alloys to enhance their strength and corrosion resistance.
- Batteries: Manganese compounds find applications in batteries, particularly alkaline batteries and lithium-ion batteries.
- Pigments and dyes: Manganese compounds are used as pigments and dyes in various applications, including paints, ceramics, and textiles.
- Fertilizers: Manganese is an essential micronutrient for plants and is included in certain fertilizers.
Isotopes of Manganese and their Electron Configurations
Manganese has only one stable isotope, ⁵⁵Mn. All other isotopes are radioactive and decay over time. Regardless of the isotope, a neutral manganese atom will always have 25 electrons. The difference lies in the number of neutrons in the nucleus, which affects the atom's mass but not its electron configuration in the neutral state.
Manganese's Role in Different Fields: A Deeper Dive
Let's explore some specific examples of manganese's importance in various fields:
Manganese in Photosynthesis
Manganese is an integral part of Photosystem II, a crucial protein complex involved in photosynthesis. It plays a critical role in the water-splitting reaction, which is essential for producing oxygen. The manganese cluster within Photosystem II acts as a catalyst, facilitating the oxidation of water molecules and releasing electrons that are used in the subsequent steps of photosynthesis. This process is fundamental to life on Earth, as it provides the oxygen we breathe.
Manganese in Bone Formation
Manganese is involved in the process of bone formation and remodeling. It is a cofactor for several enzymes involved in collagen synthesis, a crucial component of bone structure. Adequate manganese intake is vital for maintaining bone health and preventing bone-related diseases. Deficiency can contribute to impaired bone growth and increased fracture risk.
Manganese in Metabolism
Manganese plays a role in various metabolic pathways, including carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, and protein metabolism. It is a cofactor for enzymes involved in these processes, ensuring efficient energy production and utilization. For example, manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) is an important antioxidant enzyme that protects against oxidative damage to cellular components.
Manganese in the Steel Industry: Enhancing Properties
Manganese's addition to steel significantly improves its mechanical properties. It strengthens the steel matrix, increases its hardness, and enhances its toughness. This makes manganese-containing steels ideal for various applications requiring high strength and durability, such as construction, automotive parts, and railway components.
Manganese in Batteries: Powering Devices
Manganese dioxide (MnO2) is a common cathode material in alkaline batteries and some lithium-ion batteries. Its ability to accept and release electrons makes it suitable for energy storage. These batteries power numerous devices, from everyday household items to electronic gadgets and electric vehicles. Research continues to explore new manganese-based battery materials with improved performance and sustainability.
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous Element
Manganese, with its 25 electrons, is a multifaceted element crucial to various biological and industrial processes. Its unique electron configuration leads to variable oxidation states, enabling it to act as a catalyst, cofactor, and structural component in a wide range of applications. From supporting life through photosynthesis to powering our modern technologies through batteries, manganese's importance is undeniable. Further research continues to unravel its potential in areas such as sustainable energy and advanced materials, solidifying its position as a vital element in our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Vertical Column In The Periodic Table Called
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Communicable Disease And Non Communicable Disease
May 09, 2025
-
The Energy Required To Start A Chemical Reaction Is Called
May 09, 2025
-
Which Part Of The Clavicle Articulates With The Manubrium
May 09, 2025
-
How To Calculate Rf Value Of Chromatography
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Does Mn Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.