How Many Electrons Can The Fourth Energy Level Hold
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
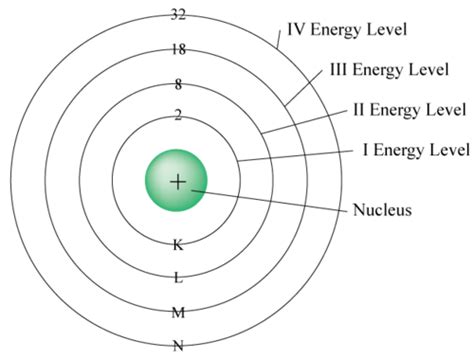
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons Can the Fourth Energy Level Hold? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Understanding the electron configuration of atoms is fundamental to grasping the principles of chemistry and physics. A key aspect of this understanding lies in knowing how many electrons each energy level can accommodate. This article delves into the specifics of the fourth energy level, explaining not only the maximum number of electrons it can hold but also the underlying quantum mechanical principles that govern this capacity.
The Quantum Mechanical Model and Electron Shells
Before we explore the fourth energy level, let's briefly review the quantum mechanical model of the atom. This model depicts electrons not as orbiting the nucleus in fixed paths like planets around a sun (as in the Bohr model), but rather as existing in regions of space called orbitals. These orbitals are defined by a set of quantum numbers:
-
Principal Quantum Number (n): This number determines the energy level of the electron and its average distance from the nucleus. The value of n can be any positive integer (1, 2, 3, 4, ...). Higher values of n represent higher energy levels and greater distances from the nucleus. The fourth energy level, therefore, has n = 4.
-
Azimuthal Quantum Number (l): This number determines the shape of the orbital and its angular momentum. For a given value of n, l can range from 0 to n - 1. These values correspond to different subshells: l = 0 (s subshell), l = 1 (p subshell), l = 2 (d subshell), l = 3 (f subshell).
-
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml): This number determines the orientation of the orbital in space. For a given value of l, ml can range from -l to +l, including 0. This means that each subshell contains a specific number of orbitals: s subshell (1 orbital), p subshell (3 orbitals), d subshell (5 orbitals), f subshell (7 orbitals).
-
Spin Quantum Number (ms): This number describes the intrinsic angular momentum (spin) of the electron. It can have only two values: +1/2 (spin up) or -1/2 (spin down). This means that each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, one with spin up and one with spin down (Pauli Exclusion Principle).
Decomposing the Fourth Energy Level
Now, let's apply these quantum numbers to the fourth energy level (n = 4). Remember that the number of subshells within a given energy level is equal to the value of n. Therefore, the fourth energy level contains four subshells:
-
4s subshell (l = 0): This subshell has one orbital, which can hold a maximum of two electrons.
-
4p subshell (l = 1): This subshell has three orbitals, each capable of holding two electrons. Therefore, the 4p subshell can hold a total of six electrons.
-
4d subshell (l = 2): This subshell has five orbitals, each capable of holding two electrons. This means the 4d subshell can hold a maximum of ten electrons.
-
4f subshell (l = 3): This subshell has seven orbitals, each holding two electrons. Consequently, the 4f subshell can accommodate a total of fourteen electrons.
Calculating the Total Electron Capacity
To find the total number of electrons the fourth energy level can hold, we simply add up the electron capacities of each subshell:
2 (4s) + 6 (4p) + 10 (4d) + 14 (4f) = 32 electrons
Therefore, the fourth energy level can hold a maximum of 32 electrons.
Exceptions and Filling Order
While the above calculation provides the theoretical maximum, it's important to note that the filling of electron orbitals doesn't always strictly follow the n+l rule (Aufbau principle). Electron-electron repulsions and other quantum mechanical effects can cause slight deviations. However, the maximum capacity of 32 electrons for the fourth energy level remains consistent. The order of filling is generally: 4s, 3d, 4p, 4d, 4f.
For example, consider the element Radon (Rn), which has an atomic number of 86. Its electron configuration includes a completely filled fourth energy level: [Xe] 6s<sup>2</sup> 4f<sup>14</sup> 5d<sup>10</sup> 6p<sup>6</sup>. Note that although the 5d and 6s orbitals are higher in energy than the 4f orbital, the 4f subshell fills before the 5d and 6s orbitals according to the rules of quantum mechanics.
Implications and Applications
Understanding the electron capacity of different energy levels has far-reaching implications across various scientific fields. It forms the basis for:
-
Predicting chemical properties: The number and arrangement of electrons in the outermost energy level (valence electrons) determine an element's reactivity and bonding behavior.
-
Spectroscopy: Electronic transitions between energy levels are responsible for the absorption and emission of light by atoms, a phenomenon exploited in spectroscopic techniques for analyzing the composition of matter.
-
Materials science: The electronic structure of materials dictates their physical and chemical properties, influencing their applications in various technologies. For instance, the electronic configurations of semiconductors are crucial to their function in electronic devices.
-
Nuclear physics: Understanding the electron configuration provides context for the interactions between electrons and the nucleus and its stability.
-
Astrophysics: The electronic structure of atoms in stars and other celestial bodies helps explain the light emitted and provides clues about their compositions and evolution.
Conclusion
The fourth energy level, with its capacity to hold 32 electrons, plays a vital role in the structure and behavior of atoms. This capacity arises from the underlying principles of quantum mechanics, which govern the arrangement of electrons in orbitals and subshells. Understanding this electron capacity is crucial for comprehending the chemical and physical properties of elements and for numerous applications across various scientific disciplines. The detailed explanation of quantum numbers and the stepwise calculation of electron capacity provides a comprehensive understanding of atomic structure and its implications, making it a valuable tool for students and researchers alike. By exploring the maximum number of electrons each energy level can hold and the factors influencing electron configuration, we gain a deeper appreciation of the intricate world of atomic structure and the properties of matter.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Find The Number Of Edges On This Solid
May 09, 2025
-
Are Hydrogen Bonds Weaker Than Covalent Bonds
May 09, 2025
-
Which Is A Point Mutation And Not A Frameshift Mutation
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Compounds
May 09, 2025
-
Which Statement About Dna Replication Is Correct
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Can The Fourth Energy Level Hold . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.