How Many Electrons Are In A Double Bond
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
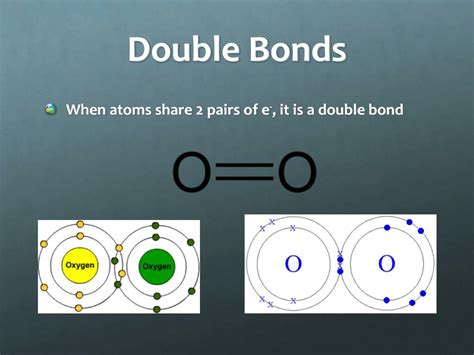
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons Are in a Double Bond? A Deep Dive into Chemical Bonding
Understanding chemical bonding is fundamental to grasping the behavior of matter. A key aspect of this understanding involves comprehending the nature of different types of bonds, including the ubiquitous double bond. This article delves deep into the question: how many electrons are in a double bond? We'll explore the concept, providing a clear and comprehensive explanation suitable for both beginners and those seeking a more nuanced understanding.
The Basics of Chemical Bonding
Before we tackle double bonds, let's establish a foundational understanding of chemical bonding. Atoms bond together to achieve a more stable electron configuration, typically resembling that of a noble gas (full outer electron shell). This stability is achieved through the sharing or transfer of electrons.
There are several types of chemical bonds, including:
-
Ionic bonds: These involve the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another, creating ions (charged atoms). This typically occurs between atoms with significantly different electronegativities (ability to attract electrons). Example: NaCl (sodium chloride).
-
Covalent bonds: These involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. This sharing creates a stable electron configuration for both atoms involved. Covalent bonds are common between atoms with similar electronegativities. Examples abound, including water (H₂O) and methane (CH₄). Covalent bonds are further categorized, including single, double, and triple bonds.
-
Metallic bonds: These are found in metals and involve a "sea" of delocalized electrons shared among a lattice of positively charged metal ions.
Understanding Double Bonds
A double bond is a type of covalent bond where two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. This is in contrast to a single bond, which involves only one shared electron pair, and a triple bond, which involves three shared electron pairs.
Therefore, the answer to the question "How many electrons are in a double bond?" is four. Two pairs of electrons contribute a total of four electrons to the bond. These electrons are not necessarily equally shared; the extent of sharing depends on the electronegativities of the atoms involved. However, the core concept remains that four electrons constitute the double bond.
Visualizing Double Bonds: A Molecular Orbital Approach
To visualize the four electrons in a double bond, we can use the concept of molecular orbitals. Molecular orbitals are regions of space where electrons are likely to be found in a molecule. In a double bond, we have a sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond.
-
Sigma (σ) bond: This is a strong, single bond formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals. It accounts for two electrons in the double bond.
-
Pi (π) bond: This is a weaker bond formed by the sideways overlap of p-orbitals. It also accounts for two electrons. The presence of a pi bond is what distinguishes a double bond from a single bond.
The combination of one sigma bond and one pi bond constitutes the double bond, with a total of four electrons involved in the bonding interaction.
Examples of Double Bonds in Organic Chemistry
Double bonds are prevalent in organic chemistry, playing a crucial role in the structure and reactivity of numerous organic molecules. Here are some prime examples:
-
Alkenes: These hydrocarbons contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Ethene (C₂H₄), the simplest alkene, provides a clear illustration of a double bond. Each carbon atom shares two electrons with the other carbon atom, forming the double bond, and each carbon atom also shares a single electron with two hydrogen atoms.
-
Carbonyl groups: These functional groups contain a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O). They are found in aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters. The double bond between carbon and oxygen significantly influences the reactivity of these molecules.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): This molecule boasts two double bonds, each between a carbon atom and an oxygen atom. Understanding the double bonds in CO₂ is crucial for understanding its chemical properties and environmental impact.
The Impact of Double Bonds on Molecular Geometry and Reactivity
The presence of a double bond significantly impacts the geometry and reactivity of a molecule.
Geometry: Double bonds exhibit a restricted rotation around the bond axis. This is because of the sideways overlap of p-orbitals in the pi bond. This restricted rotation affects the overall three-dimensional shape of the molecule. In contrast, single bonds allow for free rotation.
Reactivity: The presence of a double bond often makes the molecule more reactive compared to a similar molecule containing only single bonds. The pi electrons are relatively exposed and susceptible to attack by electrophilic reagents (electron-seeking species), leading to a variety of chemical reactions, such as addition reactions.
Delocalized Electrons and Resonance Structures
In some molecules, the four electrons in a double bond are not localized to a single pair of atoms but can be delocalized over multiple atoms. This phenomenon is known as resonance, and it leads to the formation of resonance structures. Benzene (C₆H₆) is a classic example, where the six pi electrons are delocalized across the six carbon atoms, resulting in a more stable molecule. While each individual resonance structure shows alternating single and double bonds, in reality the electron density is evenly distributed across the ring.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
For a deeper dive, consider exploring these more advanced concepts related to double bonds:
-
Bond order: This is a measure of the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. For a double bond, the bond order is two.
-
Bond length: Double bonds are generally shorter than single bonds due to the stronger attraction between the atoms resulting from the increased electron density between them.
-
Bond energy: Double bonds typically have higher bond energies than single bonds, meaning more energy is required to break them.
-
Spectroscopy: Techniques like infrared (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy can be used to identify and characterize double bonds in molecules.
Conclusion
A double bond comprises four electrons, shared between two atoms as two pairs. These electrons occupy distinct molecular orbitals – a sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond. Understanding the nature and characteristics of double bonds is paramount in organic and inorganic chemistry, influencing molecular geometry, reactivity, and overall chemical properties. This knowledge serves as a foundational building block in comprehending complex chemical processes and molecular interactions. The concepts discussed here lay a solid groundwork for more advanced studies in chemical bonding and molecular structure. Continued exploration of these principles will undoubtedly deepen your understanding of the fascinating world of chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Cellular Organelle Responsible For Protein Synthesis Is
May 09, 2025
-
Calculate Area Of A Scalene Triangle
May 09, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 484
May 09, 2025
-
Identify The Meso Isomer Of The Following Compound
May 09, 2025
-
All Events That Occur During One Heartbeat
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Are In A Double Bond . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.