How Many Chambers Does A Fish Heart Have
Juapaving
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
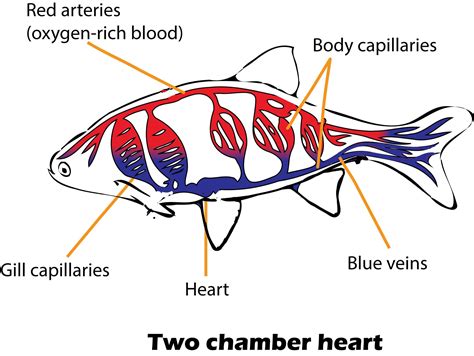
Table of Contents
How Many Chambers Does a Fish Heart Have? A Deep Dive into Fish Cardiovascular Systems
Fish, those fascinating creatures inhabiting the world's aquatic ecosystems, possess a cardiovascular system uniquely adapted to their underwater existence. A key component of this system is the heart, a vital organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. But unlike the four-chambered hearts of mammals and birds, fish hearts are simpler in structure. This article will explore the intricacies of the fish heart, focusing on its chamber count, function, and the evolutionary reasons behind its design.
The Two-Chambered Heart: A Simple Yet Efficient System
The short answer to the question, "How many chambers does a fish heart have?" is two. Unlike the complex, multi-chambered hearts of higher vertebrates, a fish heart is comprised of only two chambers: one atrium and one ventricle. This seemingly simple design is, however, perfectly suited to the demands of a fish's lifestyle.
Understanding the Atrium and Ventricle
- The Atrium: This chamber acts as a receiving area for deoxygenated blood returning from the fish's body. Think of it as a collection point before the blood moves on to the next stage.
- The Ventricle: The ventricle is the pumping chamber of the fish heart. It receives deoxygenated blood from the atrium and forcefully pumps it to the gills for oxygenation. This is where the crucial process of gas exchange takes place.
The Single Circulation Pathway
The two-chambered heart of a fish results in a single circulatory system, meaning the blood passes through the heart only once during each complete circuit of the body. This contrasts with the double circulatory system found in mammals and birds, where blood passes through the heart twice per circuit. This single circulation pathway is highly efficient for fish, given their relatively low metabolic rate compared to warm-blooded animals.
The Pathway of Blood Through a Fish's Heart
Let's trace the journey of blood through a fish's circulatory system to better understand the function of its two-chambered heart:
- Deoxygenated Blood Returns: Deoxygenated blood, carrying carbon dioxide and other waste products, returns to the heart via veins.
- Entering the Atrium: The deoxygenated blood collects in the atrium, a relatively thin-walled chamber.
- Pumping to the Ventricle: The atrium contracts, pushing the deoxygenated blood into the ventricle, a thicker-walled, more muscular chamber.
- Ventricle Contraction: The ventricle, the main pumping chamber, contracts forcefully, propelling the deoxygenated blood out of the heart.
- To the Gills for Oxygenation: The blood flows from the ventricle to the gills via the ventral aorta. This is a crucial step where gas exchange occurs. Oxygen from the water diffuses into the blood, while carbon dioxide diffuses out.
- Oxygenated Blood to the Body: Now oxygenated, the blood flows from the gills to the rest of the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs.
- Return to the Heart: After circulating throughout the body, the deoxygenated blood returns to the heart via the veins, completing the cycle.
Evolutionary Considerations: Why a Two-Chambered Heart?
The two-chambered heart is a testament to the efficiency of evolution. The simplicity of this design, while seemingly less advanced than the multi-chambered hearts of other vertebrates, offers several key advantages for fish:
- Lower Metabolic Demand: Maintaining a complex, multi-chambered heart requires significant energy. The two-chambered heart is energetically less demanding, making it suitable for the generally lower metabolic rates of fish.
- Efficient Oxygen Uptake: The single circulation system, while seemingly less efficient at first glance, is perfectly adapted to the efficient extraction of oxygen from water in the gills.
- Adaptation to Aquatic Environments: The lower blood pressure associated with a single circulation system is well-suited to the demands of life underwater. High blood pressure could be detrimental to delicate gill structures.
Variations Within the Two-Chambered Design: Not All Fish Hearts Are Identical
While the vast majority of fish possess a two-chambered heart, there are subtle variations within this basic design. Some differences include:
- Size and Shape: The size and shape of the atrium and ventricle vary depending on the species of fish and its lifestyle. Active, fast-swimming fish tend to have larger, more muscular ventricles to support their higher metabolic demands.
- Conus Arteriosus: Some fish species possess a conus arteriosus, a muscular extension of the ventricle that helps regulate blood flow to the gills. This structure is absent in others.
- Bulbus Arteriosus: In certain species, a bulbus arteriosus is present. This is a non-muscular, elastic chamber that helps to smooth out the pulsatile flow of blood from the ventricle, ensuring a more even flow to the gills.
Comparing Fish Hearts to Other Vertebrates
To fully appreciate the unique nature of the fish heart, it's helpful to compare it to the hearts of other vertebrates:
- Amphibians: Amphibians possess a three-chambered heart—two atria and one ventricle. This represents an evolutionary step towards a more efficient circulatory system, allowing for some separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- Reptiles (most): Most reptiles possess a three-chambered heart, although crocodilians have a four-chambered heart, similar to birds and mammals.
- Birds and Mammals: Birds and mammals have a four-chambered heart—two atria and two ventricles. This highly efficient design ensures complete separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, supporting their high metabolic rates and warm-blooded lifestyles.
The Fish Heart: A Remarkable Adaptation for Aquatic Life
The fish heart, with its simple yet elegant two-chambered design, is a testament to the power of natural selection. Its efficiency in oxygen uptake, its low metabolic demands, and its suitability to the pressures of aquatic life make it a remarkable adaptation. Understanding the structure and function of the fish heart provides crucial insights into the evolutionary history of vertebrates and the diversity of life on Earth. The seemingly simple two-chambered heart is far from simple; it's a marvel of engineering perfectly adapted to the needs of its aquatic inhabitants.
Further Research and Exploration
This article provides a foundational understanding of fish heart anatomy and physiology. However, further exploration into specific fish species, their unique cardiovascular adaptations, and the impact of environmental factors on heart function can lead to a richer understanding of these fascinating creatures. Consider researching the following for a deeper dive:
- Specific Fish Species: Investigate the cardiovascular systems of different fish species, comparing and contrasting their heart structures and functions.
- Impact of Environmental Factors: How do changes in water temperature, oxygen levels, or salinity affect the function of the fish heart?
- Cardiovascular Diseases in Fish: Are there cardiovascular diseases that affect fish populations? What are their causes and consequences?
- Comparative Physiology: Compare and contrast the cardiovascular systems of different vertebrate groups to understand the evolutionary pressures that shaped these systems.
By continuing to explore these areas, we can further appreciate the complexity and beauty of the fish heart and the remarkable adaptations of fish to their aquatic environment. This will not only enhance our scientific understanding but also promote conservation efforts to protect these vital aquatic ecosystems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Affects The Ocean Salinity
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many 1000s In A Million
Apr 04, 2025
-
Evaporation Of Water Endothermic Or Exothermic
Apr 04, 2025
-
Difference Between Real And Natural Numbers
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Energy Conversion Occurs During Photosynthesis
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Chambers Does A Fish Heart Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
